SET [GLOBAL|SESSION] <variable>
The statement SET [GLOBAL|SESSION] modifies one of TiDB's built in variables, of either SESSION or GLOBAL scope.
Synopsis
SetStmt:
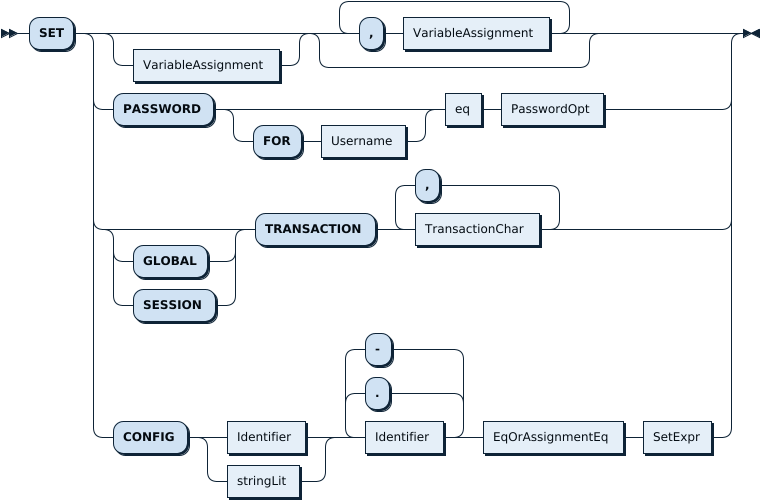
VariableAssignment:
Examples
Get the value of sql_mode.
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Update the value of sql_mode globally. If you check the value of SQL_mode after the update, you can see that the value of SESSION level has not been updated:
mysql> SET GLOBAL sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Using SET SESSION takes effect immediately:
mysql> SET SESSION sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL compatibility
The following behavior differences apply:
- Changes made with
SET GLOBALwill be propagated to all TiDB instances in the cluster. This differs from MySQL, where changes do not propagate to replicas. - TiDB presents several variables as both readable and settable. This is required for MySQL compatibility, because it is common for both applications and connectors to read MySQL variables. For example: JDBC connectors both read and set query cache settings, despite not relying on the behavior.
- Changes made with
SET GLOBALwill persist through TiDB server restarts. This means thatSET GLOBALin TiDB behaves more similar toSET PERSISTas available in MySQL 8.0 and above.