Set Up Self-Hosted Kafka Private Service Connect in Google Cloud
This document explains how to set up Private Service Connect for self-hosted Kafka in Google Cloud, and how to make it work with TiDB Cloud.
The mechanism works as follows:
- The TiDB Cloud VPC connects to the Kafka VPC through private endpoints.
- Kafka clients need to communicate directly to all Kafka brokers.
- Each Kafka broker is mapped to a unique port within the TiDB Cloud VPC.
- Leverage the Kafka bootstrap mechanism and Google Cloud resources to achieve the mapping.
There are two ways to set up Private Service Connect for self-hosted Kafka in Google Cloud:
Use the Private Service Connect (PSC) port mapping mechanism. This method requires static port-broker mapping configuration. You need to reconfigure the existing Kafka cluster to add a group of EXTERNAL listeners and advertised listeners. See Set up self-hosted Kafka Private Service Connect service by PSC port mapping.
Use Kafka-proxy. This method introduces an extra running process as the proxy between Kafka clients and Kafka brokers. The proxy dynamically configures the port-broker mapping and forwards requests. You do not need to reconfigure the existing Kafka cluster. See Set up self-hosted Kafka Private Service Connect by Kafka-proxy.
The document provides an example of connecting to a Kafka Private Service Connect service deployed across three availability zones (AZ) in Google Cloud. While other configurations are possible based on similar port-mapping principles, this document covers the fundamental setup process of the Kafka Private Service Connect service. For production environments, a more resilient Kafka Private Service Connect service with enhanced operational maintainability and observability is recommended.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have the following authorization to set up Kafka Private Service Connect in your own Google Cloud account.
- Manage VM nodes
- Manage VPC
- Manage subnets
- Manage load balancer
- Manage Private Service Connect
- Connect to VM nodes to configure Kafka nodes
Create a TiDB Cloud Dedicated cluster if you do not have one.
Get the Kafka deployment information from your TiDB Cloud Dedicated cluster.
- In the TiDB Cloud console, navigate to the Clusters page, and then click the name of your target cluster to go to its overview page.
- On the overview page, find the region of the TiDB cluster. Ensure that your Kafka cluster will be deployed to the same region.
- Click Data > Changefeed in the left navigation pane, click Create Changefeed in the upper-right corner, and then provide the following information:
- In Destination, select Kafka.
- In Connectivity Method, select Private Service Connect.
- Note down the Google Cloud project in Reminders before proceeding. You will use it to authorize the auto-accept endpoint creation request from TiDB Cloud.
- Note down the Zones of TiDB Cluster. You will deploy your TiDB cluster in these zones. It is recommended that you deploy Kafka in these zones to reduce cross-zone traffic.
- Pick a unique Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern for your Kafka Private Service Connect service.
- Input a unique random string. It can only include numbers or lowercase letters. You will use it to generate Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern later.
- Click Check usage and generate to check if the random string is unique and generate Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern that will be used to assemble the EXTERNAL advertised listener for Kafka brokers, or configure Kafka-proxy.
Note down all the deployment information. You need to use it to configure your Kafka Private Service Connect service later.
The following table shows an example of the deployment information.
| Information | Value |
|---|---|
| Region | Oregon (us-west1) |
| Google Cloud project of TiDB Cloud | tidbcloud-prod-000 |
| Zones |
|
| Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern | The unique random string: abc Generated pattern: <broker_id>.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:<port> |
Set up self-hosted Kafka Private Service Connect service by PSC port mapping
Expose each Kafka broker to TiDB Cloud VPC with a unique port by using the PSC port mapping mechanism. The following diagram shows how it works.
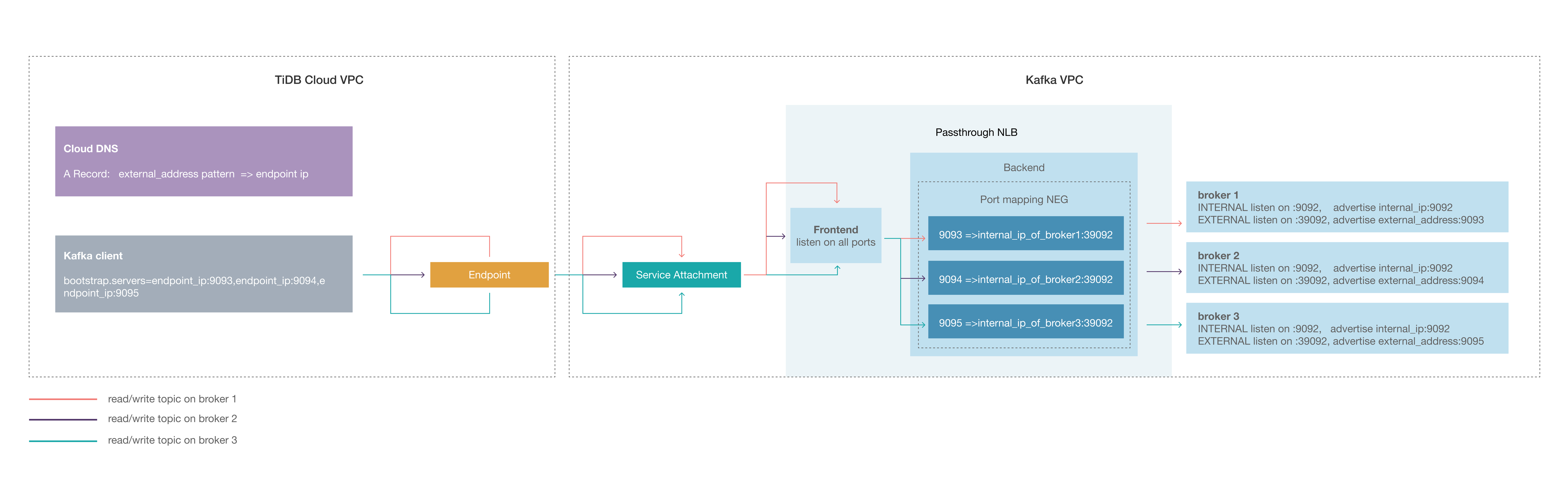
Step 1. Set up the Kafka cluster
If you need to deploy a new cluster, follow the instructions in Deploy a new Kafka cluster.
If you need to expose an existing cluster, follow the instructions in Reconfigure a running Kafka cluster.
Deploy a new Kafka cluster
1. Set up the Kafka VPC
You need to create two subnets for Kafka VPC, one for Kafka brokers, and the other for the bastion node to make it easy to configure the Kafka cluster.
Go to the Google Cloud console, and navigate to the VPC networks page to create the Kafka VPC with the following attributes:
- Name:
kafka-vpc - Subnets
- Name:
bastion-subnet; Region:us-west1; IPv4 range:10.0.0.0/18 - Name:
brokers-subnet; Region:us-west1; IPv4 range:10.64.0.0/18
- Name:
- Firewall rules
kafka-vpc-allow-customkafka-vpc-allow-ssh
2. Provisioning VMs
Go to the VM instances page to provision VMs:
Bastion node
- Name:
bastion-node - Region:
us-west1 - Zone:
Any - Machine Type:
e2-medium - Image:
Debian GNU/Linux 12 - Network:
kafka-vpc - Subnetwork:
bastion-subnet - External IPv4 address:
Ephemeral
- Name:
Broker node 1
- Name:
broker-node1 - Region:
us-west1 - Zone:
us-west1-a - Machine Type:
e2-medium - Image:
Debian GNU/Linux 12 - Network:
kafka-vpc - Subnetwork:
brokers-subnet - External IPv4 address:
None
- Name:
Broker node 2
- Name:
broker-node2 - Region:
us-west1 - Zone:
us-west1-b - Machine Type:
e2-medium - Image:
Debian GNU/Linux 12 - Network:
kafka-vpc - Subnetwork:
brokers-subnet - External IPv4 address:
None
- Name:
Broker node 3
- Name:
broker-node3 - Region:
us-west1 - Zone:
us-west1-c - Machine Type:
e2-medium - Image:
Debian GNU/Linux 12 - Network:
kafka-vpc - Subnetwork:
brokers-subnet - External IPv4 address:
None
- Name:
3. Prepare Kafka runtime binaries
Go to the detail page of the bastion node. Click SSH to log in to the bastion node. Download binaries.
# Download Kafka and OpenJDK, and then extract the files. You can choose the binary version based on your preference. wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/3.7.1/kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz tar -zxf kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz wget https://download.java.net/java/GA/jdk22.0.2/c9ecb94cd31b495da20a27d4581645e8/9/GPL/openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz tar -zxf openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzCopy binaries to each broker node.
# Run this command to authorize gcloud to access the Cloud Platform with Google user credentials # Follow the instruction in output to finish the login gcloud auth login # Copy binaries to broker nodes gcloud compute scp kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz broker-node1:~ --zone=us-west1-a gcloud compute ssh broker-node1 --zone=us-west1-a --command="tar -zxf kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz && tar -zxf openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz" gcloud compute scp kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz broker-node2:~ --zone=us-west1-b gcloud compute ssh broker-node2 --zone=us-west1-b --command="tar -zxf kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz && tar -zxf openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz" gcloud compute scp kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz broker-node3:~ --zone=us-west1-c gcloud compute ssh broker-node3 --zone=us-west1-c --command="tar -zxf kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz && tar -zxf openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz"
4. Configure Kafka brokers
Set up a KRaft Kafka cluster with three nodes. Each node acts as a broker and controller roles. For every broker:
For
listeners, all three brokers are the same and act as brokers and controller roles:- Configure the same CONTROLLER listener for all controller role nodes. If you only want to add the broker role nodes, you do not need the CONTROLLER listener in
server.properties. - Configure two broker listeners. INTERNAL for internal access; EXTERNAL for external access from TiDB Cloud.
- Configure the same CONTROLLER listener for all controller role nodes. If you only want to add the broker role nodes, you do not need the CONTROLLER listener in
For
advertised.listeners, do the following:- Configure an INTERNAL advertised listener for each broker using the internal IP address of the broker node, which allows internal Kafka clients to connect to the broker via the advertised address.
- Configure an EXTERNAL advertised listener based on Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern you get from TiDB Cloud for every broker node to help TiDB Cloud differentiate between different brokers. Different EXTERNAL advertised listeners help Kafka clients from TiDB Cloud side route requests to the right broker.
<port>differentiates brokers from Kafka Private Service Connect access points. Plan a port range for EXTERNAL advertised listeners of all brokers. These ports do not have to be actual ports listened to by brokers. They are ports listened to by the load balancer for Private Service Connect that will forward requests to different brokers.- It is recommended to configure different broker IDs for different brokers to make it easy for troubleshooting.
The planning values:
- CONTROLLER port:
29092 - INTERNAL port:
9092 - EXTERNAL:
39092 - EXTERNAL advertised listener ports range:
9093~9095
- CONTROLLER port:
Use SSH to log in to every broker node. Create a configuration file
~/config/server.propertieswith the following content for each broker node respectively.# broker-node1 ~/config/server.properties # 1. Replace {broker-node1-ip}, {broker-node2-ip}, {broker-node3-ip} with the actual IP addresses. # 2. Configure EXTERNAL in "advertised.listeners" based on the "Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern" in the "Prerequisites" section. # 2.1 The pattern is "<broker_id>.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:<port>". # 2.2 So the EXTERNAL can be "b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093". Replace <broker_id> with "b" prefix plus "node.id" properties, and replace <port> with a unique port (9093) in the port range of the EXTERNAL advertised listener. process.roles=broker,controller node.id=1 controller.quorum.voters=1@{broker-node1-ip}:29092,2@{broker-node2-ip}:29092,3@{broker-node3-ip}:29092 listeners=INTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9092,CONTROLLER://0.0.0.0:29092,EXTERNAL://0.0.0.0:39092 inter.broker.listener.name=INTERNAL advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://{broker-node1-ip}:9092,EXTERNAL://b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093 controller.listener.names=CONTROLLER listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,EXTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL log.dirs=./data# broker-node2 ~/config/server.properties # 1. Replace {broker-node1-ip}, {broker-node2-ip}, {broker-node3-ip} with the actual IP addresses. # 2. Configure EXTERNAL in "advertised.listeners" based on the "Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern" in the "Prerequisites" section. # 2.1 The pattern is "<broker_id>.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:<port>". # 2.2 So the EXTERNAL can be "b2.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9094". Replace <broker_id> with "b" prefix plus "node.id" properties, and replace <port> with a unique port (9094) in the port range of the EXTERNAL advertised listener. process.roles=broker,controller node.id=2 controller.quorum.voters=1@{broker-node1-ip}:29092,2@{broker-node2-ip}:29092,3@{broker-node3-ip}:29092 listeners=INTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9092,CONTROLLER://0.0.0.0:29092,EXTERNAL://0.0.0.0:39092 inter.broker.listener.name=INTERNAL advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://{broker-node2-ip}:9092,EXTERNAL://b2.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9094 controller.listener.names=CONTROLLER listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,EXTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL log.dirs=./data# broker-node3 ~/config/server.properties # 1. Replace {broker-node1-ip}, {broker-node2-ip}, {broker-node3-ip} with the actual IP addresses. # 2. Configure EXTERNAL in "advertised.listeners" based on the "Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern" in the "Prerequisites" section. # 2.1 The pattern is "<broker_id>.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:<port>". # 2.2 So the EXTERNAL can be "b3.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9095". Replace <broker_id> with "b" prefix plus "node.id" properties, and replace <port> with a unique port (9095) in the port range of the EXTERNAL advertised listener. process.roles=broker,controller node.id=3 controller.quorum.voters=1@{broker-node1-ip}:29092,2@{broker-node2-ip}:29092,3@{broker-node3-ip}:29092 listeners=INTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9092,CONTROLLER://0.0.0.0:29092,EXTERNAL://0.0.0.0:39092 inter.broker.listener.name=INTERNAL advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://{broker-node3-ip}:9092,EXTERNAL://b3.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9095 controller.listener.names=CONTROLLER listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,EXTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL log.dirs=./dataCreate a script, and then execute it to start the Kafka broker in each broker node.
#!/bin/bash # Get the directory of the current script SCRIPT_DIR="$(cd "$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)" # Set JAVA_HOME to the Java installation within the script directory export JAVA_HOME="$SCRIPT_DIR/jdk-22.0.2" # Define the vars KAFKA_DIR="$SCRIPT_DIR/kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin" KAFKA_STORAGE_CMD=$KAFKA_DIR/kafka-storage.sh KAFKA_START_CMD=$KAFKA_DIR/kafka-server-start.sh KAFKA_DATA_DIR=$SCRIPT_DIR/data KAFKA_LOG_DIR=$SCRIPT_DIR/log KAFKA_CONFIG_DIR=$SCRIPT_DIR/config # Cleanup step, which makes it easy for multiple experiments # Find all Kafka process IDs KAFKA_PIDS=$(ps aux | grep 'kafka.Kafka' | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}') if [ -z "$KAFKA_PIDS" ]; then echo "No Kafka processes are running." else # Kill each Kafka process echo "Killing Kafka processes with PIDs: $KAFKA_PIDS" for PID in $KAFKA_PIDS; do kill -9 $PID echo "Killed Kafka process with PID: $PID" done echo "All Kafka processes have been killed." fi rm -rf $KAFKA_DATA_DIR mkdir -p $KAFKA_DATA_DIR rm -rf $KAFKA_LOG_DIR mkdir -p $KAFKA_LOG_DIR # Magic id: BRl69zcmTFmiPaoaANybiw. You can use your own magic ID. $KAFKA_STORAGE_CMD format -t "BRl69zcmTFmiPaoaANybiw" -c "$KAFKA_CONFIG_DIR/server.properties" > $KAFKA_LOG_DIR/server_format.log LOG_DIR=$KAFKA_LOG_DIR nohup $KAFKA_START_CMD "$KAFKA_CONFIG_DIR/server.properties" &
5. Test the Kafka cluster in the bastion node
Test the Kafka bootstrap.
export JAVA_HOME=~/jdk-22.0.2 # Bootstrap from INTERNAL listener ./kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin/kafka-broker-api-versions.sh --bootstrap-server {one_of_broker_ip}:9092 | grep 9092 # Expected output (the actual order might be different) {broker-node1-ip}:9092 (id: 1 rack: null) -> ( {broker-node2-ip}:9092 (id: 2 rack: null) -> ( {broker-node3-ip}:9092 (id: 3 rack: null) -> ( # Bootstrap from EXTERNAL listener ./kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin/kafka-broker-api-versions.sh --bootstrap-server {one_of_broker_ip}:39092 # Expected output for the last 3 lines (the actual order might be different) # The difference in the output from "bootstrap from INTERNAL listener" is that exceptions or errors might occur because advertised listeners cannot be resolved in Kafka VPC. # We will make them resolvable in TiDB Cloud side and make it route to the right broker when you create a changefeed connect to this Kafka cluster by Private Service Connect. b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093 (id: 1 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException b2.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9094 (id: 2 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException b3.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9095 (id: 3 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectExceptionCreate a producer script
produce.shin the bastion node.#!/bin/bash BROKER_LIST=$1 # "{broker_address1},{broker_address2}..." # Get the directory of the current script SCRIPT_DIR="$(cd "$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)" # Set JAVA_HOME to the Java installation within the script directory export JAVA_HOME="$SCRIPT_DIR/jdk-22.0.2" # Define the Kafka directory KAFKA_DIR="$SCRIPT_DIR/kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin" TOPIC="test-topic" # Create a topic if it does not exist create_topic() { echo "Creating topic if it does not exist..." $KAFKA_DIR/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic $TOPIC --bootstrap-server $BROKER_LIST --if-not-exists --partitions 3 --replication-factor 3 } # Produce messages to the topic produce_messages() { echo "Producing messages to the topic..." for ((chrono=1; chrono <= 10; chrono++)); do message="Test message "$chrono echo "Create "$message echo $message | $KAFKA_DIR/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list $BROKER_LIST --topic $TOPIC done } create_topic produce_messagesCreate a consumer script
consume.shin the bastion node.#!/bin/bash BROKER_LIST=$1 # "{broker_address1},{broker_address2}..." # Get the directory of the current script SCRIPT_DIR="$(cd "$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)" # Set JAVA_HOME to the Java installation within the script directory export JAVA_HOME="$SCRIPT_DIR/jdk-22.0.2" # Define the Kafka directory KAFKA_DIR="$SCRIPT_DIR/kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin" TOPIC="test-topic" CONSUMER_GROUP="test-group" # Consume messages from the topic consume_messages() { echo "Consuming messages from the topic..." $KAFKA_DIR/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server $BROKER_LIST --topic $TOPIC --from-beginning --timeout-ms 5000 --consumer-property group.id=$CONSUMER_GROUP } consume_messagesExecute
produce.shandconsume.shto verify that the Kafka cluster is running. These scripts will also be reused for later network connection testing. The script will create a topic with--partitions 3 --replication-factor 3. Ensure that all three brokers contain data. Ensure that the scripts will connect to all three brokers to guarantee that network connection will be tested.# Test write message. ./produce.sh {one_of_broker_ip}:9092# Expected output Creating topic if it does not exist... Producing messages to the topic... Create Test message 1 >>Create Test message 2 >>Create Test message 3 >>Create Test message 4 >>Create Test message 5 >>Create Test message 6 >>Create Test message 7 >>Create Test message 8 >>Create Test message 9 >>Create Test message 10# Test read message ./consume.sh {one_of_broker_ip}:9092# Expected example output (the actual message order might be different) Consuming messages from the topic... Test message 3 Test message 4 Test message 5 Test message 9 Test message 10 Test message 6 Test message 8 Test message 1 Test message 2 Test message 7 [2024-11-01 08:54:27,547] ERROR Error processing message, terminating consumer process: (kafka.tools.ConsoleConsumer$) org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TimeoutException Processed a total of 10 messages
Reconfigure a running Kafka cluster
Ensure that your Kafka cluster is deployed in the same region as the TiDB cluster. It is recommended that the zones are also in the same region to reduce cross-zone traffic.
1. Configure the EXTERNAL listener for brokers
The following configuration applies to a Kafka KRaft cluster. The ZK mode configuration is similar.
Plan configuration changes.
- Configure an EXTERNAL listener for every broker for external access from TiDB Cloud. Select a unique port as the EXTERNAL port, for example,
39092. - Configure an EXTERNAL advertised listener based on Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern you get from TiDB Cloud for every broker node to help TiDB Cloud differentiate between different brokers. Different EXTERNAL advertised listeners help Kafka clients from TiDB Cloud side route requests to the right broker.
<port>differentiates brokers from Kafka Private Service Connect access points. Plan a port range for EXTERNAL advertised listeners of all brokers, for example,range from 9093. These ports do not have to be actual ports listened to by brokers. They are ports listened to by the load balancer for Private Service Connect that will forward requests to different brokers.- It is recommended to configure different broker IDs for different brokers to make it easy for troubleshooting.
- Configure an EXTERNAL listener for every broker for external access from TiDB Cloud. Select a unique port as the EXTERNAL port, for example,
Use SSH to log in to each broker node. Modify the configuration file of each broker with the following content:
# Add EXTERNAL listener listeners=INTERNAL:...,EXTERNAL://0.0.0.0:39092 # Add EXTERNAL advertised listeners based on the "Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern" in the "Prerequisites" section # 1. The pattern is "<broker_id>.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:<port>". # 2. So the EXTERNAL can be "bx.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:xxxx". Replace <broker_id> with "b" prefix plus "node.id" properties, and replace <port> with a unique port in the port range of the EXTERNAL advertised listener. # For example advertised.listeners=...,EXTERNAL://b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093 # Configure EXTERNAL map listener.security.protocol.map=...,EXTERNAL:PLAINTEXTAfter you reconfigure all the brokers, restart your Kafka brokers one by one.
2. Test EXTERNAL listener settings in your internal network
You can download Kafka and OpenJDK in your Kafka client node.
# Download Kafka and OpenJDK, and then extract the files. You can choose the binary version based on your preference.
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/3.7.1/kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz
tar -zxf kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz
wget https://download.java.net/java/GA/jdk22.0.2/c9ecb94cd31b495da20a27d4581645e8/9/GPL/openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz
tar -zxf openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz
Execute the following script to test if the bootstrap works as expected.
export JAVA_HOME=~/jdk-22.0.2
# Bootstrap from the EXTERNAL listener
./kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin/kafka-broker-api-versions.sh --bootstrap-server {one_of_broker_ip}:39092
# Expected output for the last 3 lines (the actual order might be different)
# There will be some exceptions or errors because advertised listeners cannot be resolved in your Kafka network.
# We will make them resolvable in TiDB Cloud side and make it route to the right broker when you create a changefeed connect to this Kafka cluster by Private Service Connect.
b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093 (id: 1 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException
b2.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9094 (id: 2 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException
b3.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9095 (id: 3 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException
Step 2. Expose the Kafka cluster as Private Service Connect
Go to the Network endpoint group page. Create a network endpoint group as follows:
- Name:
kafka-neg - Network endpoint group type:
Port Mapping NEG(Regional)- Region:
us-west1 - Network:
kafka-vpc - Subnet:
brokers-subnet
- Region:
- Name:
Go to the detail page of the network endpoint group, and add the network endpoints to configure the port mapping to broker nodes.
- Network endpoint 1
- Instance:
broker-node1 - VM Port:
39092 - Client Port:
9093
- Instance:
- Network endpoint 2
- Instance:
broker-node2 - VM Port:
39092 - Client Port:
9094
- Instance:
- Network endpoint 3
- Instance:
broker-node3 - VM Port:
39092 - Client Port:
9095
- Instance:
- Network endpoint 1
Go to the Load balancing page. Create a load balancer as follows:
- Type of load balancer:
Network Load Balancer - Proxy or Passthrough:
Passthrough - Public facing or internal:
Internal - Load Balancer name:
kafka-lb - Region:
us-west1 - Network:
kafka-vpc - Backend configuration
- Backend type:
Port mapping network endpoint group - Protocol:
TCP - Port mapping network endpoint group:
kafka-neg
- Backend type:
- Frontend configuration
- Subnetwork:
brokers-subnet - Ports:
All
- Subnetwork:
- Type of load balancer:
Go to Private Service Connect > PUBLISH SERVICE.
- Load Balancer Type:
Internal passthrough Network Load Balancer - Internal load balancer:
kafka-lb - Service name:
kafka-psc - Subnets:
RESERVE NEW SUBNET- Name:
psc-subnet - VPC Network:
kafka-vpc - Region:
us-west1 - IPv4 range:
10.128.0.0/18
- Name:
- Accepted projects: the Google Cloud project of TiDB Cloud you got in Prerequisites, for example,
tidbcloud-prod-000.
- Load Balancer Type:
Navigate to the detail page of the
kafka-psc. Note down the Service attachment, for example,projects/tidbcloud-dp-stg-000/regions/us-west1/serviceAttachments/kafka-psc. You will use it in TiDB Cloud to connect to this PSC.Go to the detail page of the VPC network
kafka-vpc. Add a firewall rule to allow PSC traffic to all brokers.- Name:
allow-psc-traffic - Direction of traffic:
Ingress - Action on match:
Allow - Targets:
All instances in the network - Source filter:
IPv4 ranges - Source IPv4 ranges:
10.128.0.0/18. The range of psc-subnet. - Protocols and ports: Allow all
- Name:
Step 3. Connect from TiDB Cloud
Go back to the TiDB Cloud console to create a changefeed for the cluster to connect to the Kafka cluster by Private Service Connect. For more information, see Sink to Apache Kafka.
When you proceed to Configure the changefeed target > Connectivity Method > Private Service Connect, fill in the following fields with corresponding values and other fields as needed.
- Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern:
abc. It is the same as the unique random string you use to generate Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern in Prerequisites. - Service Attachment: the Kafka service attachment of PSC, for example,
projects/tidbcloud-dp-stg-000/regions/us-west1/serviceAttachments/kafka-psc. - Bootstrap Ports:
9092,9093,9094
- Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern:
Proceed with the steps in Sink to Apache Kafka.
Set up self-hosted Kafka Private Service Connect by Kafka-proxy
Expose each Kafka broker to TiDB Cloud VPC with a unique port by using the Kafka-proxy dynamic port mapping mechanism. The following diagram shows how it works.
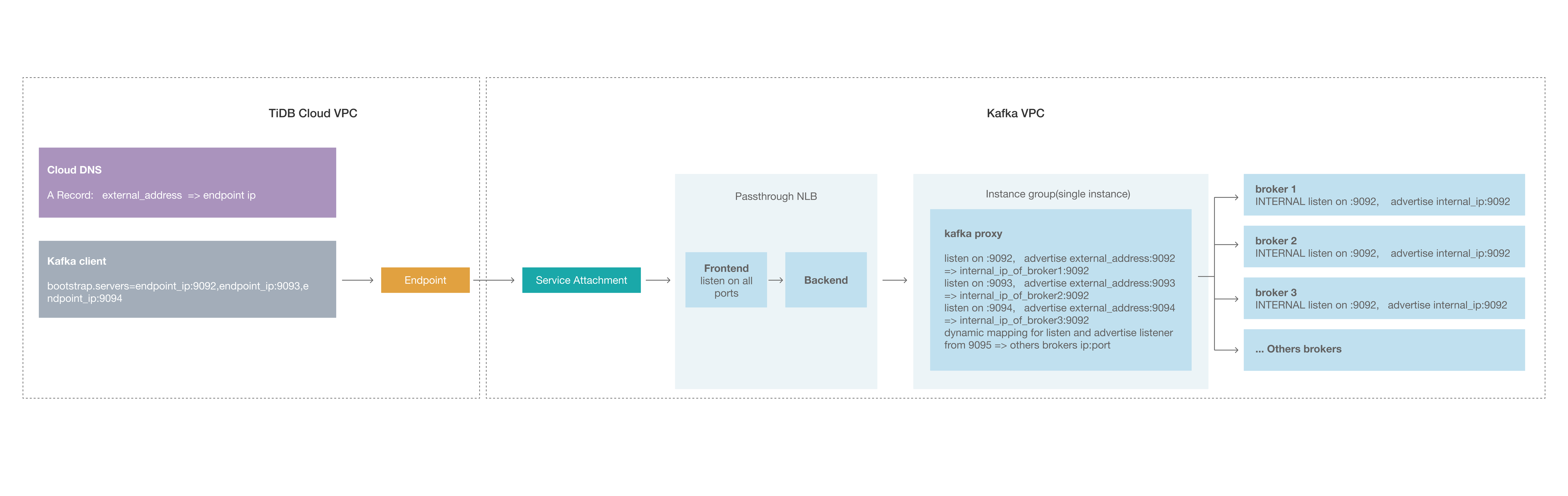
Step 1. Set up Kafka-proxy
Assume that you already have a Kafka cluster running in the same region as the TiDB cluster. You can connect to the Kafka cluster from your VPC network. The Kafka cluster can be self-hosted or provided by third-party providers, such as Confluent.
Go to the Instance groups page, and create an instance group for Kafka-proxy.
- Name:
kafka-proxy-ig - Instance template:
- Name:
kafka-proxy-tpl - Location:
Regional - Region:
us-west1 - Machine type:
e2-medium. You can choose your own machine type based on your workload. - Network: your VPC network that can connect to the Kafka cluster.
- Subnetwork: your subnet that can connect to the Kafka cluster.
- External IPv4 address:
Ephemeral. Enable Internet access to make it easy to configure Kafka-proxy. You can select None in your production environment and log in to the node in your way.
- Name:
- Location:
Single zone - Region:
us-west1 - Zone: choose one of your broker's zones.
- Autoscaling mode:
Off - Minimum number of instances:
1 - Maximum number of instances:
1. Kafka-proxy does not support the cluster mode, so only one instance can be deployed. Each Kafka-proxy randomly maps local ports to the ports of the broker, resulting in different mappings across proxies. Deploying multiple Kafka-proxies behind a load balancer can cause issues. If a Kafka client connects to one proxy and then accesses a broker through another, the request might be routed to the wrong broker.
- Name:
Go to the detail page of the node in kafka-proxy-ig. Click SSH to log in to the node. Download the binaries:
# You can choose another version wget https://github.com/grepplabs/kafka-proxy/releases/download/v0.3.11/kafka-proxy-v0.3.11-linux-amd64.tar.gz tar -zxf kafka-proxy-v0.3.11-linux-amd64.tar.gzRun Kafka-proxy and connect to Kafka brokers.
# There are three kinds of parameters that need to feed to the Kafka-proxy # 1. --bootstrap-server-mapping defines the bootstrap mapping. Suggest that you configure three mappings, one for each zone for resilience. # a) Kafka broker address; # b) Local address for the broker in Kafka-proxy; # c) Advertised listener for the broker if Kafka clients bootstrap from Kafka-proxy # 2. --dynamic-sequential-min-port defines the start port of the random mapping for other brokers # 3. --dynamic-advertised-listener defines advertised listener address for other brokers based on the pattern obtained from the "Prerequisites" section # a) The pattern: <broker_id>.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:<port> # b) Make sure to replace <broker_id> with a fixed lowercase string, for example, "brokers". You can use your own string. This step will help TiDB Cloud route requests properly. # c) Remove ":<port>" # d) The advertised listener address would be: brokers.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com ./kafka-proxy server \ --bootstrap-server-mapping "{address_of_broker1},0.0.0.0:9092,b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9092" \ --bootstrap-server-mapping "{address_of_broker2},0.0.0.0:9093,b2.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093" \ --bootstrap-server-mapping "{address_of_broker3},0.0.0.0:9094,b3.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9094" \ --dynamic-sequential-min-port=9095 \ --dynamic-advertised-listener=brokers.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com > ./kafka_proxy.log 2>&1 &Test bootstrap in the Kafka-proxy node.
# Download Kafka and OpenJDK, and then extract the files. You can choose the binary version based on your preference. wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/3.7.1/kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz tar -zxf kafka_2.13-3.7.1.tgz wget https://download.java.net/java/GA/jdk22.0.2/c9ecb94cd31b495da20a27d4581645e8/9/GPL/openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz tar -zxf openjdk-22.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz export JAVA_HOME=~/jdk-22.0.2 ./kafka_2.13-3.7.1/bin/kafka-broker-api-versions.sh --bootstrap-server 0.0.0.0:9092 # Expected output of the last few lines (the actual order might be different) # There might be exceptions or errors because advertised listeners cannot be resolved in your network. # We will make them resolvable in TiDB Cloud side and make it route to the right broker when you create a changefeed connect to this Kafka cluster by Private Service Connect. b1.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9092 (id: 1 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException b2.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9093 (id: 2 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException b3.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9094 (id: 3 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException brokers.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9095 (id: 4 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException brokers.abc.us-west1.gcp.3199745.tidbcloud.com:9096 (id: 5 rack: null) -> ERROR: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.DisconnectException ...
Step 2. Expose Kafka-proxy as Private Service Connect Service
Go to the Load balancing page, and create a load balancer.
- Type of load balancer:
Network Load Balancer - Proxy or Passthrough:
Passthrough - Public facing or internal:
Internal - Load Balancer name:
kafka-proxy-lb - Region:
us-west1 - Network: your network
- Backend configuration
- Backend type:
Instance group - Protocol:
TCP - Instance group:
kafka-proxy-ig
- Backend type:
- Frontend configuration
- Subnetwork: your subnet
- Ports:
All - Heath check:
- Name:
kafka-proxy-hc - Scope:
Regional - Protocol:
TCP - Port:
9092. You can select one of the bootstrap ports in Kafka-proxy.
- Name:
- Type of load balancer:
Go to Private Service Connect > PUBLISH SERVICE.
- Load Balancer Type:
Internal passthrough Network Load Balancer - Internal load balancer:
kafka-proxy-lb - Service name:
kafka-proxy-psc - Subnets:
RESERVE NEW SUBNET- Name:
proxy-psc-subnet - VPC Network: your network
- Region:
us-west1 - IPv4 range: set the CIDR based on your network planning
- Name:
- Accepted projects: the Google Cloud project of TiDB Cloud you get in Prerequisites, for example,
tidbcloud-prod-000.
- Load Balancer Type:
Navigate to the detail page of the kafka-proxy-psc. Note down the
Service attachment, for example,projects/tidbcloud-dp-stg-000/regions/us-west1/serviceAttachments/kafka-proxy-psc, which will be used in TiDB Cloud to connect to this PSC.Go to the detail page of your VPC network. Add a firewall rule to allow the PSC traffic for all brokers.
- Name:
allow-proxy-psc-traffic - Direction of traffic:
Ingress - Action on match:
Allow - Targets: All instances in the network
- Source filter:
IPv4 ranges - Source IPv4 ranges: the CIDR of proxy-psc-subnet
- Protocols and ports: Allow all
- Name:
Step 3. Connect from TiDB Cloud
Return to the TiDB Cloud console and create a changefeed for the cluster to connect to the Kafka cluster by Private Service Connect. For more information, see Sink to Apache Kafka.
After you proceed to the Configure the changefeed target > Connectivity Method > Private Service Connect, fill in the following fields with corresponding values and other fields as needed.
- Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern:
abc. The same as the unique random string you use to generate Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern in Prerequisites. - Service Attachment: the kafka-proxy service attachment of PSC, for example,
projects/tidbcloud-dp-stg-000/regions/us-west1/serviceAttachments/kafka-proxy-psc. - Bootstrap Ports:
9092,9093,9094
- Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern:
Continue to follow the guideline in Sink to Apache Kafka.
FAQ
How to connect to the same Kafka Private Service Connect service from two different TiDB Cloud projects?
If you have already followed the steps in this document and successfully set up the connection from the first project, and you want to set up a second connection from the second project, you can connect to the same Kafka Private Service Connect service from two different TiDB Cloud projects as follows:
If you set up Kafka PSC by PSC port mapping, do the following:
Follow instructions from the beginning of this document. When you proceed to Step 1. Set up Kafka Cluster, follow the Reconfigure a running Kafka cluster section to create another group of EXTERNAL listeners and advertised listeners. You can name it as
EXTERNAL2. Note that the port range ofEXTERNAL2cannot overlap with the EXTERNAL.After reconfiguring the brokers, add another group of Network endpoints to the Network endpoint group, which maps the ports range to the
EXTERNAL2listener.Configure the TiDB Cloud connection with the following input to create the new changefeed:
- New Bootstrap ports
- New Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern
- The same Service Attachment
If you set up self-hosted Kafka Private Service Connect by Kafka-proxy, create a new Kafka-proxy PSC from the beginning with a new Kafka Advertised Listener Pattern.