TiFlash の分散型ストレージとコンピューティングアーキテクチャおよび S3 サポート
デフォルトでは、 TiFlash は結合されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャを使用して展開され、各TiFlashノードはstorageとコンピューティング ノードの両方として機能します。 TiDB v7.0.0 以降、 TiFlash は分散storageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャをサポートし、Amazon S3 または S3 互換のオブジェクトstorage(MinIO など) にデータを保存できるようになります。
アーキテクチャの概要
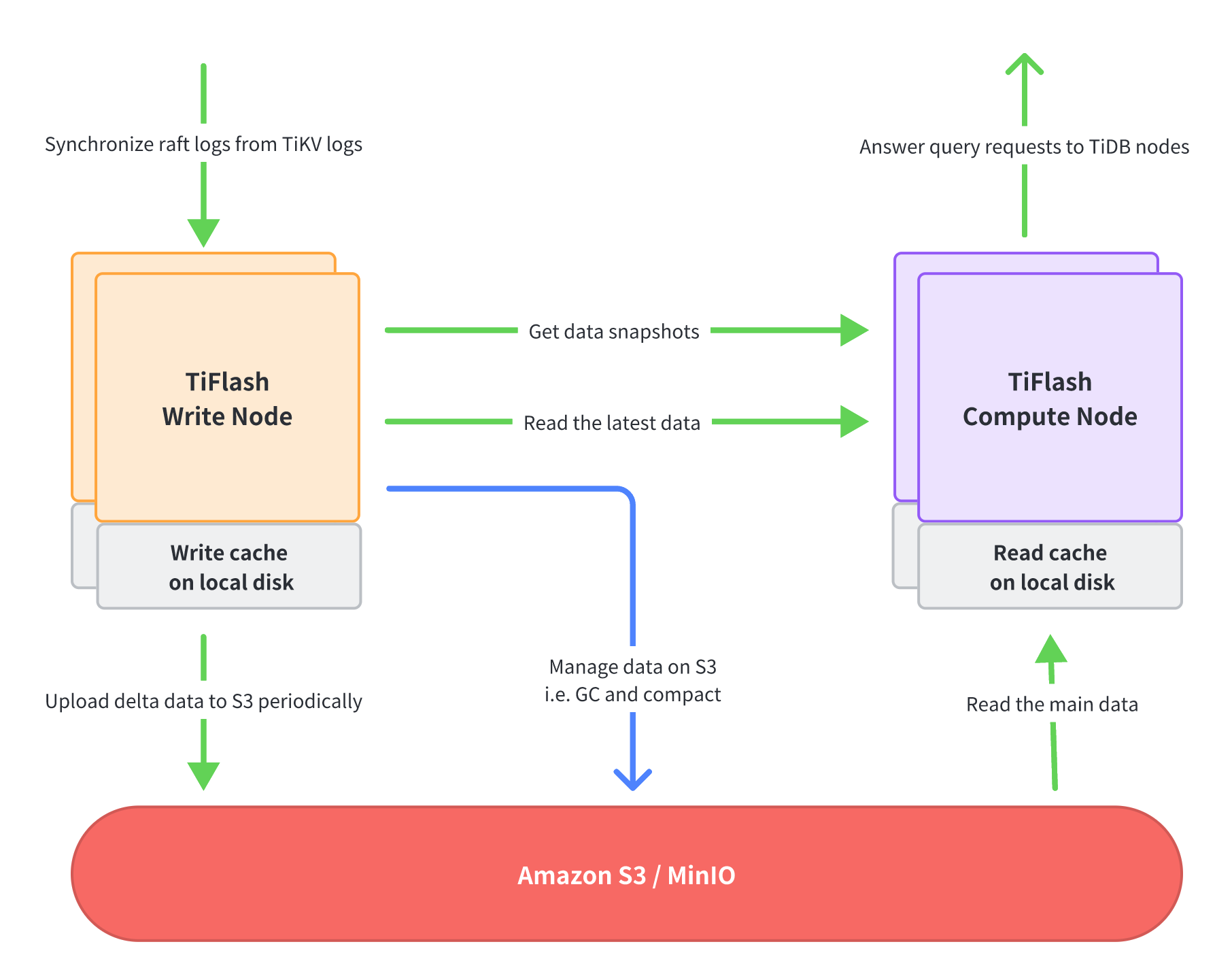
分離されたstorageおよびコンピューティングアーキテクチャでは、 TiFlashプロセスのさまざまな機能が分割され、書き込みノードとコンピューティング ノードの 2 種類のノードに割り当てられます。これら 2 種類のノードは個別にデプロイし、独立してスケーリングできます。つまり、デプロイする書き込みノードと計算ノードの数を必要に応じて決定できます。
TiFlash書き込みノード
Write NodeはTiKVからRaftログデータを受け取り、カラムナ形式に変換し、一定期間内の更新データを定期的にパッケージ化してS3にアップロードします。さらに、書き込みノードは、クエリのパフォーマンスを向上させるためにデータを継続的に整理したり、不要なデータを削除したりするなど、S3 上のデータを管理します。
書き込みノードは、メモリの過度の使用を避けるために、ローカル ディスク (通常は NVMe SSD) を使用して最新の書き込みデータをキャッシュします。
TiFlashコンピューティング ノード
コンピューティング ノードは、TiDB ノードから送信されたクエリ リクエストを実行します。まず書き込みノードにアクセスしてデータのスナップショットを取得し、次に書き込みノードから最新のデータ (つまり、まだ S3 にアップロードされていないデータ) を読み取り、残りのデータの大部分を S3 から読み取ります。
コンピューティング ノードは、リモートの場所 (書き込みノードまたは S3) から同じデータを繰り返し読み取ることを回避し、クエリのパフォーマンスを向上させるために、データ ファイルのキャッシュとしてローカル ディスク (通常は NVMe SSD) を使用します。
計算ノードはステートレスであり、そのスケーリング速度は第 2 レベルです。この機能を使用すると、次のようにコストを削減できます。
- クエリのワークロードが低い場合は、計算ノードの数を減らしてコストを節約します。クエリがない場合は、すべての計算ノードを停止することもできます。
- クエリのワークロードが増加した場合は、クエリのパフォーマンスを確保するためにコンピューティング ノードの数をすぐに増やします。
シナリオ
TiFlash の分散storageおよびコンピューティングアーキテクチャは、コスト効率の高いデータ分析サービスに適しています。このアーキテクチャでは、storageとコンピューティング リソースを必要に応じて個別に拡張できるため、次のシナリオで大きなメリットが得られます。
データの量は多くなりますが、頻繁にクエリされるのは少量のデータだけです。データの大部分はコールド データであり、クエリされることはほとんどありません。現時点では、頻繁にクエリされるデータは通常、高速クエリ パフォーマンスを提供するためにコンピューティング ノードのローカル SSD にキャッシュされますが、他のコールド データのほとんどは、storageコストを節約するために低コストの S3 またはその他のオブジェクトstorageに保存されます。
コンピューティング リソースの需要には明らかな山と谷があります。たとえば、集中的な調整クエリは通常夜間に実行されるため、大量のコンピューティング リソースが必要になります。この場合、夜間に一時的にコンピューティング ノードを追加することを検討できます。また、通常のクエリ タスクを完了するために必要な計算ノードの数が少なくなる場合もあります。
前提条件
TiFlashデータを保存するための Amazon S3 バケットを準備します。
既存のバケットを使用することもできますが、TiDB クラスターごとに専用のキー プレフィックスを予約する必要があります。 S3 バケットの詳細については、 AWS ドキュメントを参照してください。
MinIOなど、他の S3 互換オブジェクトstorageを使用することもできます。
TiFlashで使用される S3 API は次のとおりです。
- PutObject
- GetObject
- コピーオブジェクト
- オブジェクトの削除
- リストオブジェクトV2
- GetObjectTagging
- PutBucketライフサイクル
削除されたデータをクリーンアップするために、準備された S3 バケットにライフサイクルを追加します。
"ID": "tiflash-clean", "Expiration": { "Days": 1 }, "Filter": { "And": { "Tags": [ { "Value": "tiflash_deleted", "Key": "true" } ] } }TiDB クラスター内にTiFlashノードがないことを確認してください。存在する場合は、すべてのテーブルのTiFlashレプリカ数を
0に設定し、すべてのTiFlashノードを削除します。例えば:SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TIFLASH_REPLICA; # Query all tables with TiFlash replicas ALTER TABLE table_name SET TIFLASH REPLICA 0; # Set the TiFlash replica count of all tables to `0`tiup cluster scale-in mycuster -R tiflash # Remove all TiFlash nodes tiup cluster display mycluster # Wait for all TiFlash nodes to enter the Tombstone state tiup cluster prune mycluster # Remove all TiFlash nodes in the Tombstone state
使用法
デフォルトでは、 TiUP は結合されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャにTiFlashを展開します。 TiFlash を分散storageおよびコンピューティングアーキテクチャに導入する必要がある場合は、次の手順に従って手動構成を行ってください。
次の構成でTiFlashトポロジ構成ファイル (
scale-out.topo.yamlなど) を準備します。tiflash_servers: # In the TiFlash topology configuration file, the `storage.s3` configuration indicates that the disaggregated storage and compute architecture is used for deployment. # If `flash.disaggregated_mode: tiflash_compute` is configured for a node, it is a Compute Node. # If `flash.disaggregated_mode: tiflash_write` is configured for a node, it is a Write Node. # 172.31.8.1~2 are TiFlash Write Nodes - host: 172.31.8.1 config: flash.disaggregated_mode: tiflash_write # This is a Write Node storage.s3.endpoint: http://s3.{region}.amazonaws.com # S3 endpoint address storage.s3.bucket: mybucket # TiFlash stores all data in this bucket storage.s3.root: /cluster1_data # Root directory where data is stored in the S3 bucket storage.s3.access_key_id: {ACCESS_KEY_ID} # Access S3 with ACCESS_KEY_ID storage.s3.secret_access_key: {SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} # Access S3 with SECRET_ACCESS_KEY storage.main.dir: ["/data1/tiflash/data"] # Local data directory of the Write Node. Configure it in the same way as the directory configuration of the coupled storage and compute architecture - host: 172.31.8.2 config: flash.disaggregated_mode: tiflash_write # This is a Write Node storage.s3.endpoint: http://s3.{region}.amazonaws.com # S3 endpoint address storage.s3.bucket: mybucket # TiFlash stores all data in this bucket storage.s3.root: /cluster1_data # Root directory where data is stored in the S3 bucket storage.s3.access_key_id: {ACCESS_KEY_ID} # Access S3 with ACCESS_KEY_ID storage.s3.secret_access_key: {SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} # Access S3 with SECRET_ACCESS_KEY storage.main.dir: ["/data1/tiflash/data"] # Local data directory of the Write Node. Configure it in the same way as the directory configuration of the coupled storage and compute architecture # 172.31.9.1~2 are TiFlash Compute Nodes - host: 172.31.9.1 config: flash.disaggregated_mode: tiflash_compute # This is a Compute Node storage.s3.endpoint: http://s3.{region}.amazonaws.com # S3 endpoint address storage.s3.bucket: mybucket # TiFlash stores all data in this bucket storage.s3.root: /cluster1_data # Root directory where data is stored in the S3 bucket storage.s3.access_key_id: {ACCESS_KEY_ID} # Access S3 with ACCESS_KEY_ID storage.s3.secret_access_key: {SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} # Access S3 with SECRET_ACCESS_KEY storage.main.dir: ["/data1/tiflash/data"] # Local data directory of the Compute Node. Configure it in the same way as the directory configuration of the coupled storage and compute architecture storage.remote.cache.dir: /data1/tiflash/cache # Local data cache directory of the Compute Node storage.remote.cache.capacity: 858993459200 # 800 GiB - host: 172.31.9.2 config: flash.disaggregated_mode: tiflash_compute # This is a Compute Node storage.s3.endpoint: http://s3.{region}.amazonaws.com # S3 endpoint address storage.s3.bucket: mybucket # TiFlash stores all data in this bucket storage.s3.root: /cluster1_data # Root directory where data is stored in the S3 bucket storage.s3.access_key_id: {ACCESS_KEY_ID} # Access S3 with ACCESS_KEY_ID storage.s3.secret_access_key: {SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} # Access S3 with SECRET_ACCESS_KEY storage.main.dir: ["/data1/tiflash/data"] # Local data directory of the Compute Node. Configure it in the same way as the directory configuration of the coupled storage and compute architecture storage.remote.cache.dir: /data1/tiflash/cache # Local data cache directory of the Compute Node storage.remote.cache.capacity: 858993459200 # 800 GiBなお、上記
ACCESS_KEY_IDとSECRET_ACCESS_KEYは設定ファイルに直接記述します。環境変数を使用してそれらを個別に構成することも選択できます。両方の方法が設定されている場合は、環境変数の方が優先されます。環境変数を使用して
ACCESS_KEY_IDとSECRET_ACCESS_KEY構成するには、 TiFlashプロセスがデプロイされているすべてのマシンでTiFlashプロセスを開始するユーザー環境 (通常はtidb) に切り替えてから、~/.bash_profileを変更して次の構成を追加します。export S3_ACCESS_KEY_ID={ACCESS_KEY_ID} export S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY={SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}storage.s3.endpointhttpまたはhttpsモードを使用した S3 への接続をサポートしており、URL を直接変更することでモードを設定できます。たとえば、https://s3.{region}.amazonaws.com。
TiFlashノードを追加し、 TiFlashレプリカの数をリセットします。
tiup cluster scale-out mycluster ./scale-out.topo.yamlALTER TABLE table_name SET TIFLASH REPLICA 1;TiDB 構成を変更して、分離されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャを使用してTiFlashをクエリします。
TiDB 構成ファイルを編集モードで開きます。
tiup cluster edit-config mycluster次の構成項目を TiDB 構成ファイルに追加します。
server_configs: tidb: disaggregated-tiflash: true # Query TiFlash using the disaggregated storage and compute architectureTiDB を再起動します。
tiup cluster reload mycluster -R tidb
制限
- TiFlash は、分散されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャと結合されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャ間のインプレース切り替えをサポートしていません。アーキテクチャを切り替える前に、既存のTiFlashノードをすべて削除する必要があります。
- あるアーキテクチャから別のアーキテクチャに移行した後、すべてのTiFlashデータを再度レプリケートする必要があります。
- 同じ TiDB クラスター内では、同じアーキテクチャを持つTiFlashノードのみが許可されます。 2 つのアーキテクチャを 1 つのクラスター内で共存させることはできません。
- 分離されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャは、S3 API を使用したオブジェクトstorageのみをサポートしますが、結合されたstorageとコンピューティングアーキテクチャはローカルstorageのみをサポートします。
- S3storageを使用する場合、 TiFlashノードは自身のノードにないファイルのキーを取得できないため、 保存時の暗号化機能は使用できません。