使用 TiFlash MPP 模式
本文介绍了 Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) 模式的 TiFlash 以及如何使用它。
TiFlash 支持使用 MPP 模式执行查询,该模式引入了跨节点数据交换(数据洗牌过程)到计算中。TiDB 会通过优化器的成本估算自动判断是否选择 MPP 模式。你可以通过修改 tidb_allow_mpp 和 tidb_enforce_mpp 的值来改变选择策略。
下图展示了 MPP 模式的工作原理。
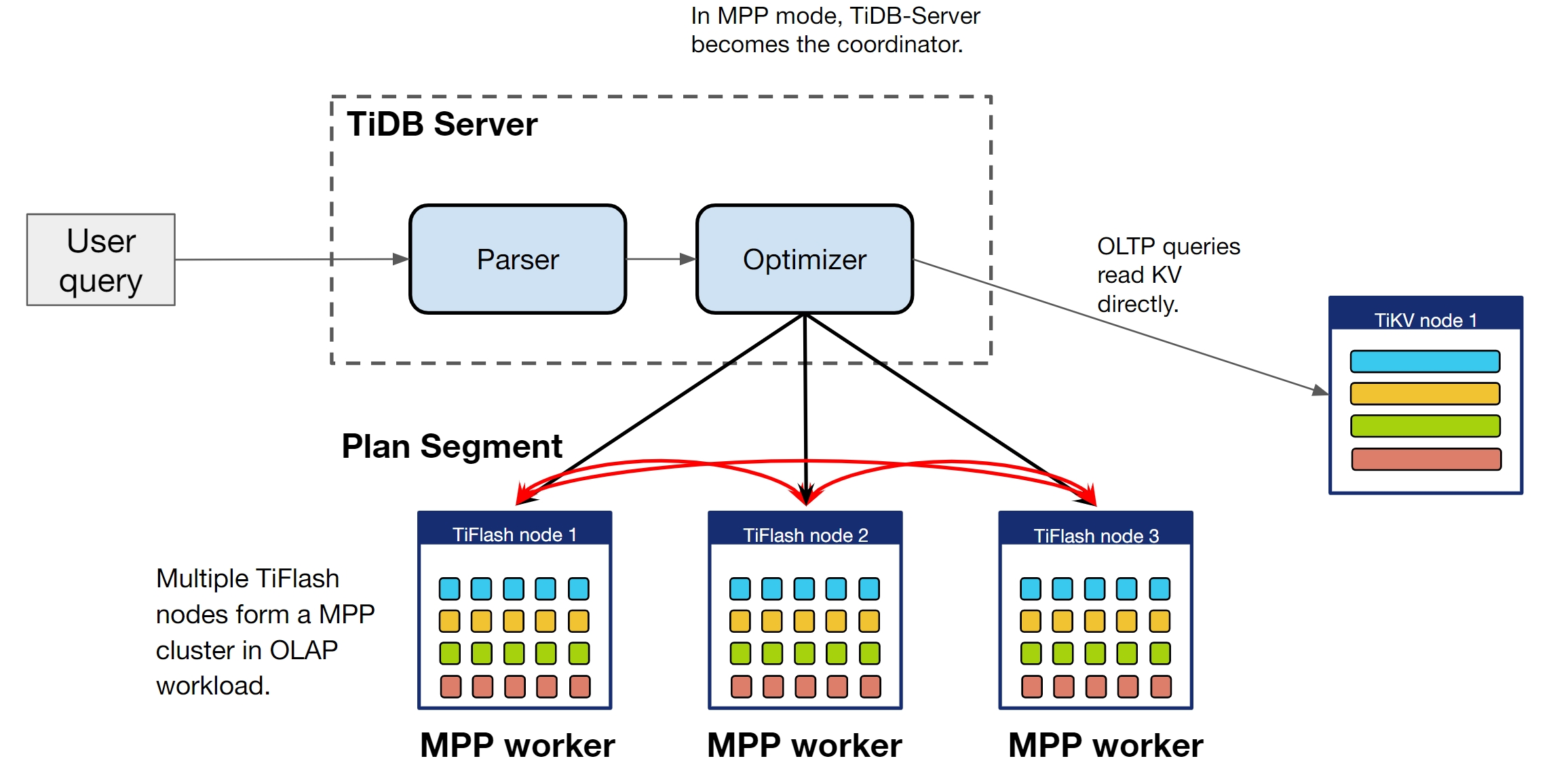
控制是否选择 MPP 模式
tidb_allow_mpp 变量控制 TiDB 是否可以选择 MPP 模式执行查询。tidb_enforce_mpp 变量控制是否忽略优化器的成本估算,强制使用 TiFlash 的 MPP 模式执行查询。
这两个变量所有取值对应的结果如下:
| tidb_allow_mpp=off | tidb_allow_mpp=on(默认) | |
|---|---|---|
| tidb_enforce_mpp=off(默认) | 不使用 MPP 模式。 | 根据成本估算由优化器选择 MPP 模式(默认)。 |
| tidb_enforce_mpp=on | 不使用 MPP 模式。 | TiDB 忽略成本估算,强制选择 MPP 模式。 |
例如,如果你不想使用 MPP 模式,可以执行以下语句:
set @@session.tidb_allow_mpp=0;
如果你希望 TiDB 的基于成本的优化器自动决定是否使用 MPP 模式(默认),可以执行:
set @@session.tidb_allow_mpp=1;
set @@session.tidb_enforce_mpp=0;
如果你希望 TiDB 忽略优化器的成本估算,强制选择 MPP 模式,可以执行:
set @@session.tidb_allow_mpp=1;
set @@session.tidb_enforce_mpp=1;
MPP 模式的算法支持
MPP 模式支持以下物理算法:Broadcast Hash Join、Shuffled Hash Join、Shuffled Hash Aggregation、Union All、TopN 和 Limit。优化器会自动判断在某个查询中使用哪种算法。要查看具体的执行计划,可以执行 EXPLAIN 语句。如果 EXPLAIN 的结果中显示有 ExchangeSender 和 ExchangeReceiver 操作符,说明 MPP 模式已生效。
以下示例以 TPC-H 测试集中的表结构为例:
explain select count(*) from customer c join nation n on c.c_nationkey=n.n_nationkey;
+------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| HashAgg_23 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#16)->Column#15 |
| └─TableReader_25 | 1.00 | root | | data:ExchangeSender_24 |
| └─ExchangeSender_24 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | ExchangeType: PassThrough |
| └─HashAgg_12 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#16 |
| └─HashJoin_17 | 3000000.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | inner join, equal:[eq(tpch.nation.n_nationkey, tpch.customer.c_nationkey)] |
| ├─ExchangeReceiver_21(Build) | 25.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | |
| │ └─ExchangeSender_20 | 25.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | ExchangeType: Broadcast |
| │ └─TableFullScan_18 | 25.00 | mpp[tiflash] | table:n | keep order:false |
| └─TableFullScan_22(Probe) | 3000000.00 | mpp[tiflash] | table:c | keep order:false |
+------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
在示例执行计划中,包含了 ExchangeReceiver 和 ExchangeSender 操作符。执行计划表明,在读取 nation 表后,ExchangeSender 操作符会将表广播到每个节点,HashJoin 和 HashAgg 操作在 nation 表和 customer 表上执行,最后将结果返回给 TiDB。
TiFlash 提供以下 3 个全局/会话变量,用于控制是否使用 Broadcast Hash Join:
tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_size:值的单位为字节。如果表的大小(以字节为单位)小于该变量的值,则使用 Broadcast Hash Join 算法,否则使用 Shuffled Hash Join。tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_count:值的单位为行数。如果连接操作的对象属于子查询,优化器无法估算子查询结果集的大小,因此以结果集中的行数为准。如果子查询的估算行数小于该变量的值,则使用 Broadcast Hash Join,否则使用 Shuffled Hash Join。tidb_prefer_broadcast_join_by_exchange_data_size:控制是否优先选择网络传输开销较小的算法。如果启用该变量,TiDB 会分别估算Broadcast Hash Join和Shuffled Hash Join需要交换的数据大小,然后选择较小的那个。启用后,tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_count和tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_size不再生效。
在 MPP 模式下访问分区表
要在 MPP 模式下访问分区表,首先需要启用 动态裁剪模式。
示例:
mysql> DROP TABLE if exists test.employees;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE TABLE test.employees
(id int NOT NULL,
fname varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
lname varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
hired date NOT NULL DEFAULT '1970-01-01',
separated date DEFAULT '9999-12-31',
job_code int DEFAULT NULL,
store_id int NOT NULL) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_bin
PARTITION BY RANGE (store_id)
(PARTITION p0 VALUES LESS THAN (6),
PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (11),
PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN (16),
PARTITION p3 VALUES LESS THAN (MAXVALUE));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> ALTER table test.employees SET tiflash replica 1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)
mysql> SET tidb_partition_prune_mode=static;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT count(*) FROM test.employees;
+----------------------------------+----------+-------------------+-------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+----------------------------------+----------+-------------------+-------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
| HashAgg_18 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#10)->Column#9 |
| └─PartitionUnion_20 | 4.00 | root | | |
| ├─StreamAgg_35 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#12)->Column#10 |
| │ └─TableReader_36 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_26 |
| │ └─StreamAgg_26 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#12 |
| │ └─TableFullScan_34 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p0 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| ├─StreamAgg_52 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#14)->Column#10 |
| │ └─TableReader_53 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_43 |
| │ └─StreamAgg_43 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#14 |
| │ └─TableFullScan_51 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p1 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| ├─StreamAgg_69 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#16)->Column#10 |
| │ └─TableReader_70 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_60 |
| │ └─StreamAgg_60 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#16 |
| │ └─TableFullScan_68 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p2 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| └─StreamAgg_86 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#18)->Column#10 |
| └─TableReader_87 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_77 |
| └─StreamAgg_77 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#18 |
| └─TableFullScan_85 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p3 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
+----------------------------------+----------+-------------------+-------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
18 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SET tidb_partition_prune_mode=dynamic;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT count(*) FROM test.employees;
+------------------------------+----------+--------------+-----------------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+------------------------------+----------+--------------+-----------------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| HashAgg_17 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#11)->Column#9 |
| └─TableReader_19 | 1.00 | root | partition:all | data:ExchangeSender_18 |
| └─ExchangeSender_18 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | ExchangeType: PassThrough |
| └─HashAgg_8 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#11 |
| └─TableFullScan_16 | 10000.00 | mpp[tiflash] | table:employees | keep order:false, stats:pseudo, PartitionTableScan:true |
+------------------------------+----------+--------------+-----------------+---------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)