Connect to a TiDB Cloud Premium Instance via AWS PrivateLink
This document describes how to connect to your TiDB Cloud Premium instance via AWS PrivateLink.
TiDB Cloud supports highly secure and one-way access to the TiDB Cloud service hosted in an AWS VPC via AWS PrivateLink, as if the service were in your own VPC. A private endpoint is exposed in your VPC and you can create a connection to the TiDB Cloud service via the endpoint with permission.
Powered by AWS PrivateLink, the endpoint connection is secure and private, and does not expose your data to the public internet. In addition, the endpoint connection supports CIDR overlap and is easier for network management.
The architecture of the private endpoint is as follows:
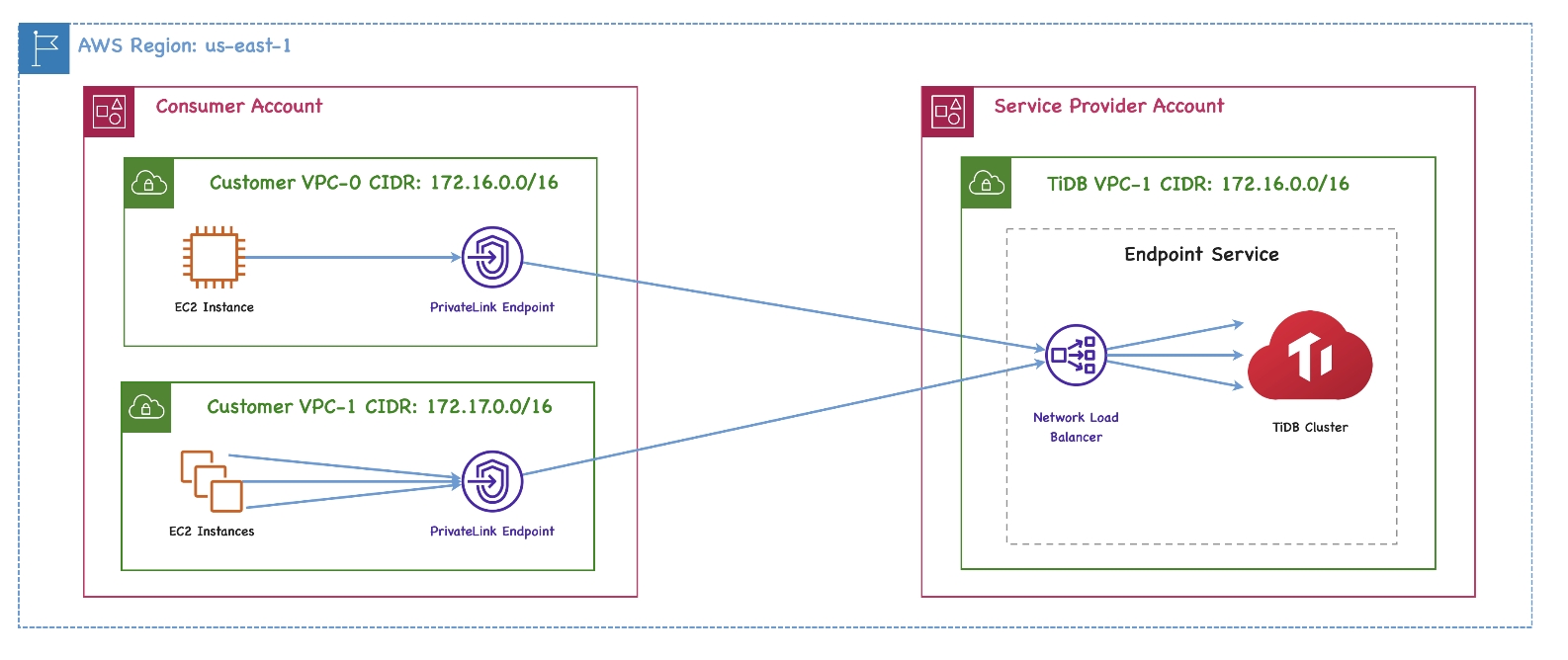
For more detailed definitions of the private endpoint and endpoint service, see the following AWS documents:
Restrictions
- Only users with the
Organization Ownerrole can create private endpoint connections. - The private endpoint and the TiDB instance you want to connect to must be located in the same region.
Prerequisites
Make sure that DNS hostnames and DNS resolution are both enabled in your AWS VPC settings. They are disabled by default when you create a VPC in the AWS Management Console.
Set up a private endpoint connection and connect to your instance
To connect to your TiDB Cloud Premium instance via a private endpoint, follow these steps:
- Select a TiDB instance
- Create an AWS interface endpoint
- Create a private endpoint connection
- Enable private DNS
- Connect to your TiDB instance
If you have multiple instances, you need to repeat these steps for each instance that you want to connect to using AWS PrivateLink.
Step 1. Select a TiDB instance
- On the TiDB Instances page of your TiDB Cloud web console, click the name of your target TiDB instance to go to its overview page.
- Click Connect in the upper-right corner. A connection dialog is displayed.
- In the Connection Type drop-down list, select Private Endpoint, and then click Create Private Endpoint Connection.
Step 2. Create an AWS interface endpoint
If you see the TiDB Private Link Service is ready message, the corresponding endpoint service is ready. You can provide the following information to create the endpoint.
Fill in the Your VPC ID and Your Subnet IDs fields. You can find these IDs from your AWS Management Console. For multiple subnets, enter the IDs separated by spaces.
Click Generate Command to get the following endpoint creation command.
aws ec2 create-vpc-endpoint --vpc-id ${your_vpc_id} --region ${your_region} --service-name ${your_endpoint_service_name} --vpc-endpoint-type Interface --subnet-ids ${your_application_subnet_ids}
Then, you can create an AWS interface endpoint either using the AWS CLI or using the AWS Management Console.
To use the AWS CLI to create a VPC interface endpoint, perform the following steps:
- Copy the generated command and run it in your terminal.
- Record the VPC endpoint ID you just created.
To use the AWS Management Console to create a VPC interface endpoint, perform the following steps:
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon VPC console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/.
Click Endpoints in the navigation pane, and then click Create Endpoint in the upper-right corner.
The Create endpoint page is displayed.
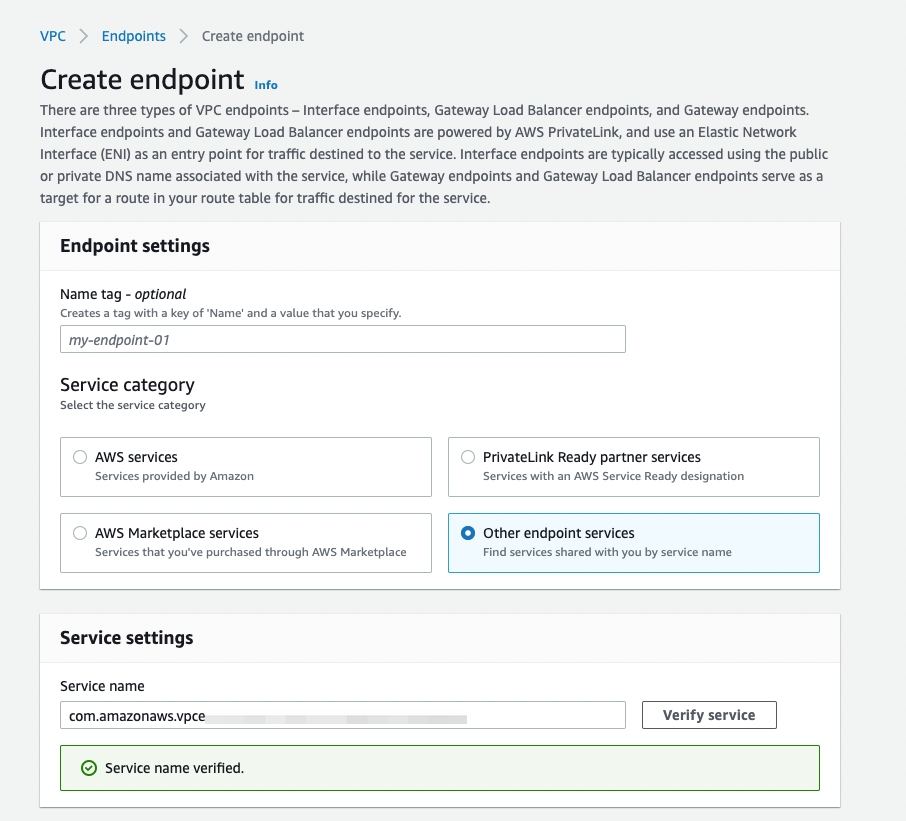
In the Endpoint settings area, fill in a name tag if needed, and then select the Endpoint services that use NLBs and GWLBs option.
In the Service settings area, enter the service name
${your_endpoint_service_name}from the generated command (--service-name ${your_endpoint_service_name}).Click Verify service.
In the Network settings area, select your VPC in the drop-down list.
In the Subnets area, select the availability zones where your TiDB instance is located.
In the Security groups area, select your security group properly.
Click Create endpoint.
Step 3. Create a private endpoint connection
- Go back to the TiDB Cloud console.
- On the Create AWS Private Endpoint Connection page, enter your VPC endpoint ID.
- Click Create Private Endpoint Connection.
Step 4. Enable private DNS
Enable private DNS in AWS. You can either use the AWS CLI or the AWS Management Console.
To enable private DNS using your AWS CLI, copy the following aws ec2 modify-vpc-endpoint command from the Create Private Endpoint Connection page and run it in your AWS CLI.
aws ec2 modify-vpc-endpoint --vpc-endpoint-id ${your_vpc_endpoint_id} --private-dns-enabled
Alternatively, you can find the command on the Networking page of your instance. Locate the private endpoint and click ... > Enable DNS in the Action column.
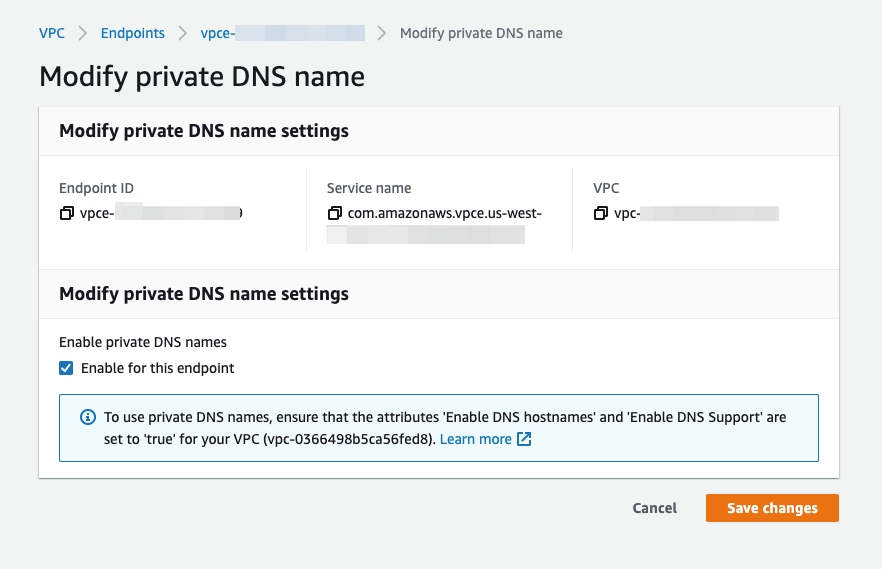
To enable private DNS in your AWS Management Console:
Go to VPC > Endpoints.
Right-click your endpoint ID and select Modify private DNS name.
Select the Enable for this endpoint check box.
Click Save changes.
Step 5. Connect to your TiDB instance
After you have accepted the private endpoint connection, you are redirected back to the connection dialog.
- Wait for the private endpoint connection status to change from System Checking to Active (approximately 5 minutes).
- In the Connect With drop-down list, select your preferred connection method. The corresponding connection string is displayed at the bottom of the dialog.
- Connect to your instance with the connection string.
Private endpoint status reference
When you use private endpoint connections, the statuses of private endpoints and private endpoint services are displayed on the instance-level Networking page:
- Switch to your target instance using the combo box in the upper-left corner.
- Click Settings > Networking in the left navigation pane.
The possible statuses of a private endpoint are explained as follows:
- Not Configured: The endpoint service is created but the private endpoint is not created yet.
- Pending: Waiting for processing.
- Active: Your private endpoint is ready to use. You cannot edit a private endpoint in this status.
- Deleting: The private endpoint is being deleted.
- Failed: The private endpoint creation fails. You can click Edit in that row to retry the creation.
The possible statuses of a private endpoint service are explained as follows:
- Creating: The endpoint service is being created, which takes 3 to 5 minutes.
- Active: The endpoint service is created, regardless of whether the private endpoint is created or not.
- Deleting: The endpoint service or the instance is being deleted, which takes 3 to 5 minutes.
Troubleshooting
I cannot connect to a TiDB instance via a private endpoint after enabling private DNS. Why?
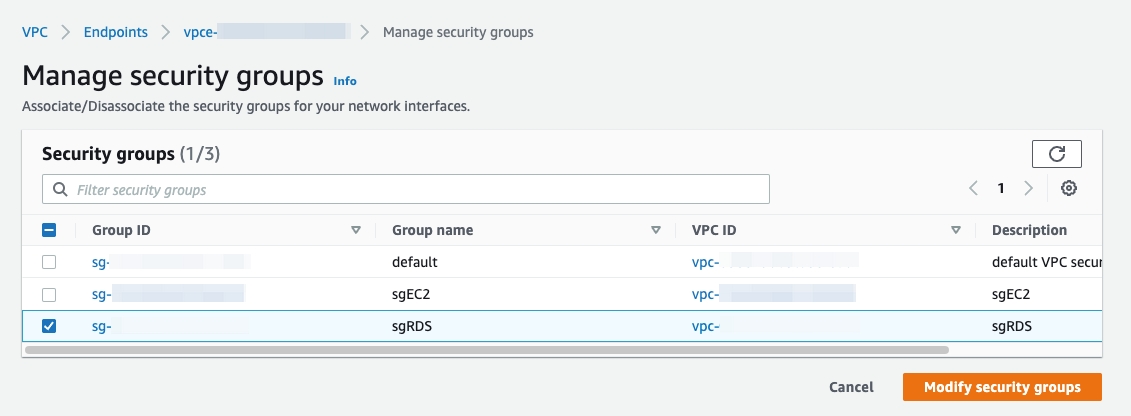
You might need to properly set the security group for your VPC endpoint in the AWS Management Console. To do so, go to VPC > Endpoints, right-click your VPC endpoint, and select Manage security groups. Ensure that the selected security group allows inbound access from your EC2 instances on port 4000 or a customer-defined port.