TiDB Operator Architecture
This document introduces the architecture of TiDB Operator and how it works.
Architecture
The following diagram shows an overview of the TiDB Operator architecture:
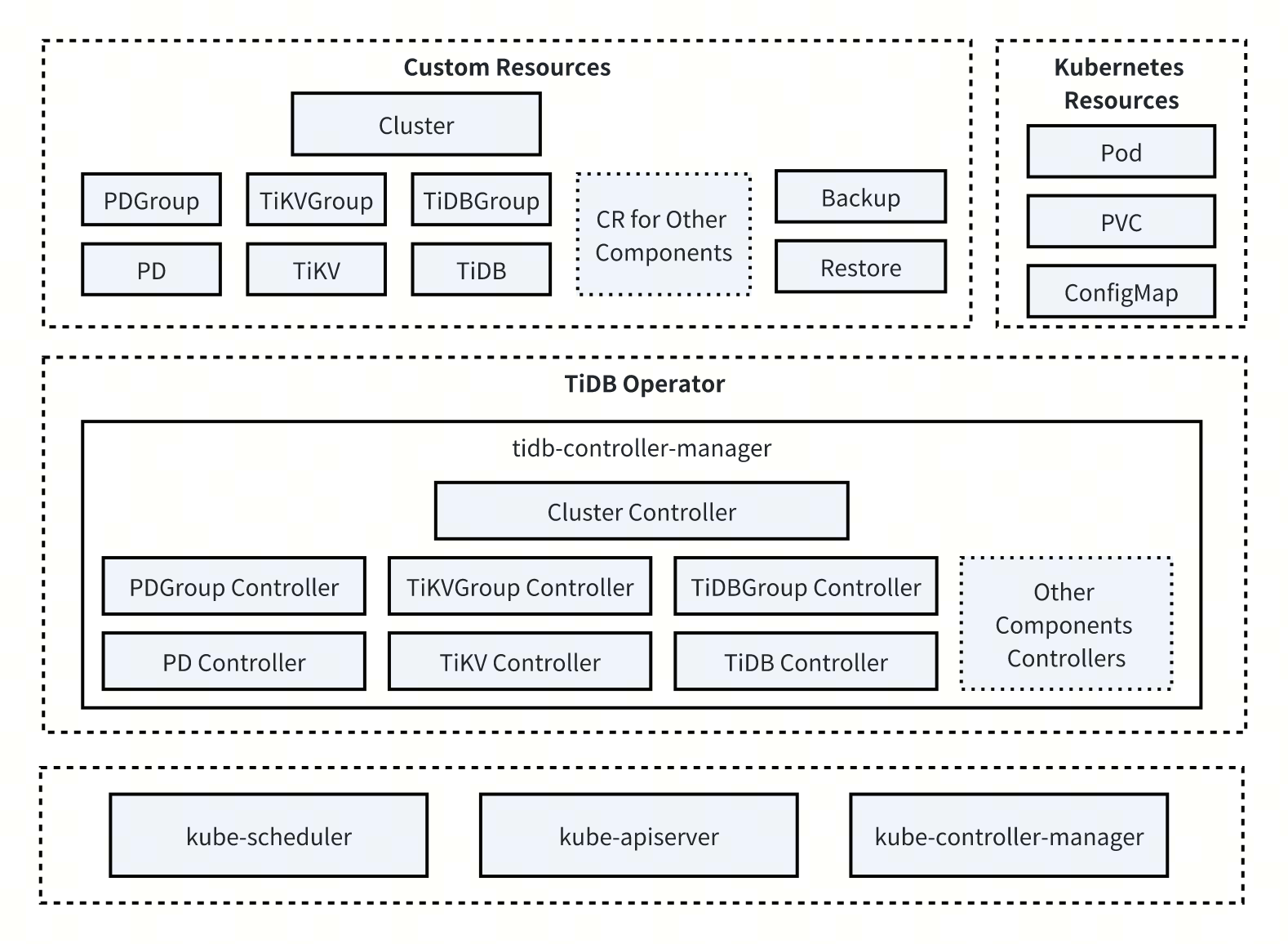
The diagram includes several resource objects defined by Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs), such as Cluster, PDGroup, PD, TiKVGroup, TiKV, TiDBGroup, TiDB, Backup, and Restore. The following describes some of these resources:
Cluster: represents a complete TiDB cluster. It contains shared configuration and feature flags for the TiDB cluster and reflects the overall cluster status. This CRD is designed as the "namespace" for the TiDB cluster, and all components in the cluster must reference aClusterCR.ComponentGroup: describes a group of TiDB cluster components with the same configuration. For example:PDGroup: a group of PD instances with the same configuration.TiKVGroup: a group of TiKV instances with the same configuration.TiDBGroup: a group of TiDB instances with the same configuration.
Component: describes an individual TiDB cluster component. For example:PD: a single PD instance.TiKV: a single TiKV instance.TiDB: a single TiDB instance.
Backup: describes a backup task for the TiDB cluster.Restore: describes a restore task for the TiDB cluster.
Control flow
TiDB Operator uses a declarative API to automate cluster management by continuously monitoring user-defined resources. The core workflow is as follows:
- The user creates
Clusterand other component Custom Resource (CR) objects throughkubectl, such asPDGroup,TiKVGroup, andTiDBGroup. - TiDB Operator continuously watches these CRs and dynamically adjusts the corresponding
Pod,PVC, andConfigMapobjects based on the actual cluster state.
Through this control (reconciliation) loop, TiDB Operator can automatically perform cluster node health checks and failure recovery. Operations such as deployment, upgrades, and scaling can also be completed with one action by modifying the Cluster and other component CRs.
The following diagram shows the control flow using TiKV as an example:
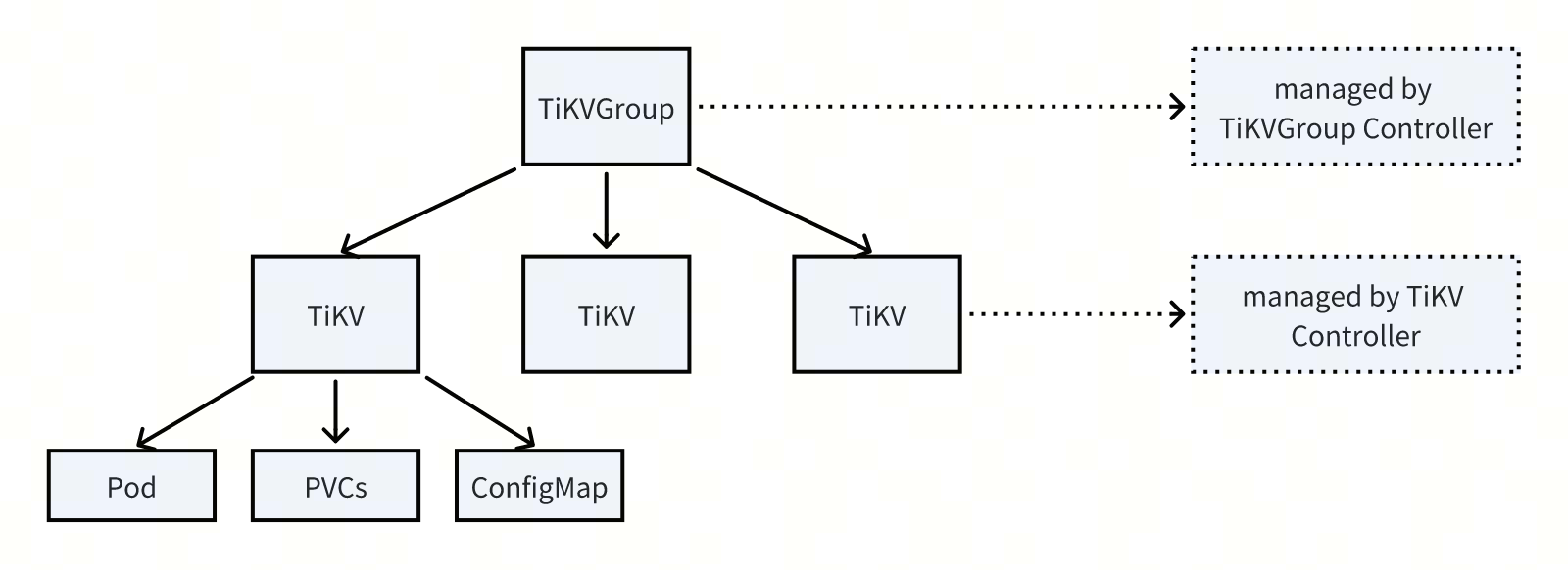
In this workflow:
- TiKVGroup Controller: watches the
TiKVGroupCR and creates or updates the correspondingTiKVCR based on its configuration. - TiKV Controller: watches the
TiKVCR and creates or updates related resources such as Pod, PVC, and ConfigMap based on the configuration in the CR.