Two Data Centers in One City Deployment
This document introduces the deployment mode of two data centers (DCs) in one city, including the architecture, configuration, how to enable this deployment mode, and how to use replicas in this mode.
In a self-hosted environment, TiDB usually adopts the multi-data-center deployment solution to ensure high availability and disaster recovery capability. The multi-data-center deployment solution includes multiple deployment modes, such as three data centers in two cities and three data centers in one city. This document introduces the deployment mode of two data centers in one city. Deployed in this mode, TiDB can also meet the requirements of high availability and disaster recovery, with a lower cost. This deployment solution adopts Data Replication Auto Synchronous mode, or the DR Auto-Sync mode.
Under the mode of two data centers in one city, the two data centers are less than 50 kilometers apart. They are usually located in the same city or in two adjacent cities. The network latency between the two data centers is lower than 1.5 milliseconds and the bandwidth is higher than 10 Gbps.
Deployment architecture
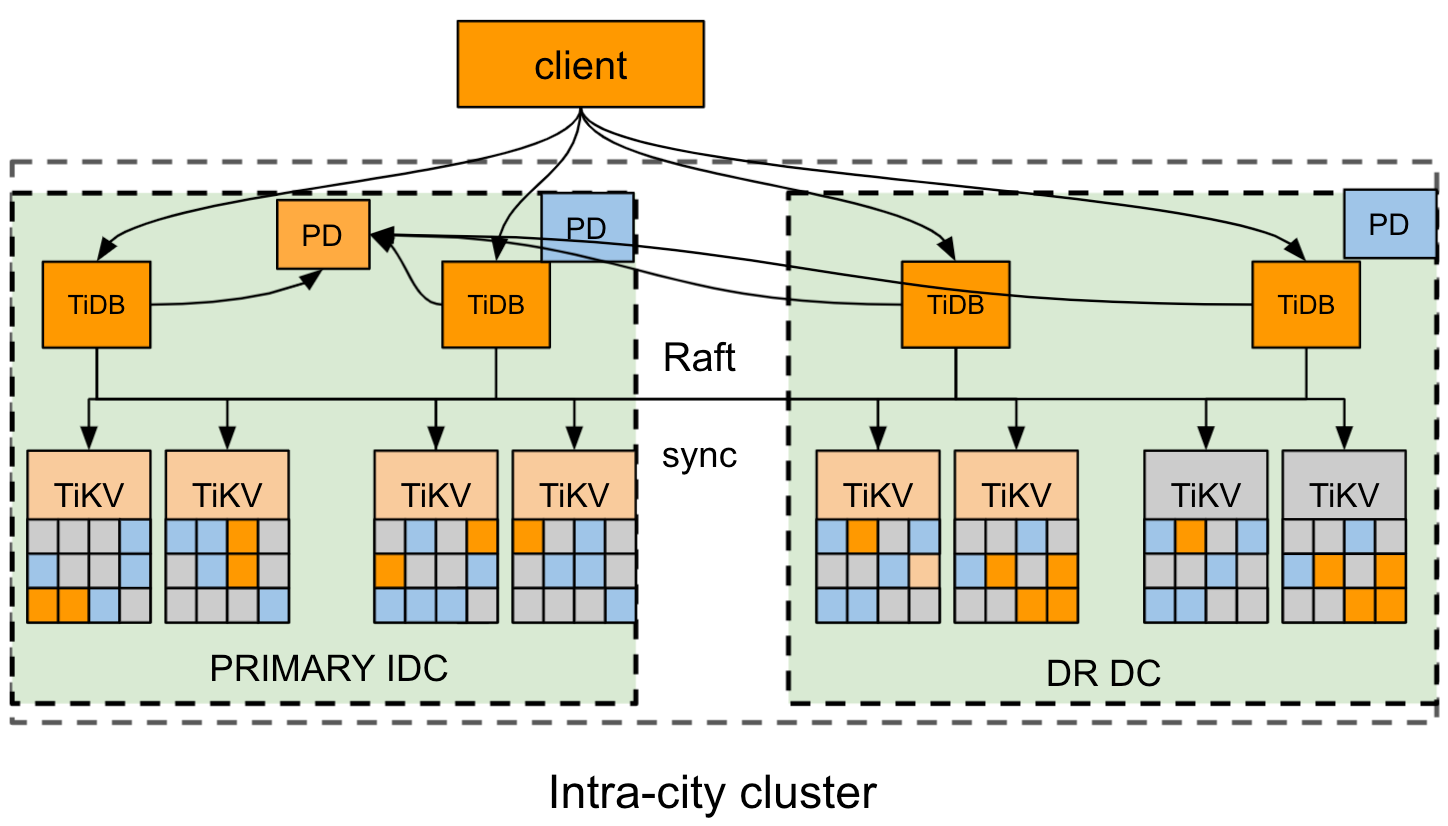
This section takes the example of a city where two data centers IDC1 and IDC2 are located respectively in the east and west.
The architecture of the cluster deployment is as follows:
- The TiDB cluster is deployed to two DCs in one city: the primary IDC1 in the east, and the disaster recovery (DR) IDC2 in the west.
- The cluster has 4 replicas: 2 Voter replicas in IDC1, 1 Voter replica and 1 Learner replica in IDC2. For the TiKV component, each rack has a proper label.
- The Raft protocol is adopted to ensure consistency and high availability of data, which is transparent to users.
This deployment solution defines three statuses to control and identify the replication status of the cluster, which restricts the replication mode of TiKV. The replication mode of the cluster can automatically and adaptively switch between the three statuses. For details, see the Status switch section.
- sync: Synchronous replication mode. In this mode, at least one replica in the disaster recovery (DR) data center synchronizes with the primary data center. The Raft algorithm ensures that each log is replicated to the DR based on the label.
- async: Asynchronous replication mode. In this mode, the DR data center is not fully synchronized with the primary data center. The Raft algorithm follows the majority protocol to replicate logs.
- sync-recover: Synchronous recovery mode. In this mode, the DR data center is not fully synchronized with the primary data center. Raft gradually switches to the label replication mode and then reports the label information to PD.
Configuration
Example
The following tiup topology.yaml example file is a typical topology configuration for the two data centers in one city deployment mode:
# # Global variables are applied to all deployments and used as the default value of
# # the deployments if a specific deployment value is missing.
global:
user: "tidb"
ssh_port: 22
deploy_dir: "/data/tidb_cluster/tidb-deploy"
data_dir: "/data/tidb_cluster/tidb-data"
server_configs:
pd:
replication.location-labels: ["zone","rack","host"]
pd_servers:
- host: 10.63.10.10
name: "pd-10"
- host: 10.63.10.11
name: "pd-11"
- host: 10.63.10.12
name: "pd-12"
tidb_servers:
- host: 10.63.10.10
- host: 10.63.10.11
- host: 10.63.10.12
tikv_servers:
- host: 10.63.10.30
config:
server.labels: { zone: "east", rack: "east-1", host: "30" }
- host: 10.63.10.31
config:
server.labels: { zone: "east", rack: "east-2", host: "31" }
- host: 10.63.10.32
config:
server.labels: { zone: "west", rack: "west-1", host: "32" }
- host: 10.63.10.33
config:
server.labels: { zone: "west", rack: "west-2", host: "33" }
monitoring_servers:
- host: 10.63.10.60
grafana_servers:
- host: 10.63.10.60
alertmanager_servers:
- host: 10.63.10.60
Placement Rules
To deploy a cluster based on the planned topology, you need to use Placement Rules to determine the locations of the cluster replicas. Taking the deployment of 4 replicas (2 Voter replicas are at the primary center, 1 Voter replica and 1 Learner replica are at the DR center) as an example, you can use the Placement Rules to configure the replicas as follows:
cat rule.json
[
{
"group_id": "pd",
"group_index": 0,
"group_override": false,
"rules": [
{
"group_id": "pd",
"id": "zone-east",
"start_key": "",
"end_key": "",
"role": "voter",
"count": 2,
"label_constraints": [
{
"key": "zone",
"op": "in",
"values": [
"east"
]
}
],
"location_labels": [
"zone",
"rack",
"host"
]
},
{
"group_id": "pd",
"id": "zone-west",
"start_key": "",
"end_key": "",
"role": "voter",
"count": 1,
"label_constraints": [
{
"key": "zone",
"op": "in",
"values": [
"west"
]
}
],
"location_labels": [
"zone",
"rack",
"host"
]
},
{
"group_id": "pd",
"id": "zone-west",
"start_key": "",
"end_key": "",
"role": "learner",
"count": 1,
"label_constraints": [
{
"key": "zone",
"op": "in",
"values": [
"west"
]
}
],
"location_labels": [
"zone",
"rack",
"host"
]
}
]
}
]
To use the configurations in rule.json, run the following command to back up the existing configuration to the default.json file and overwrite the existing configuration with rule.json:
pd-ctl config placement-rules rule-bundle load --out="default.json"
pd-ctl config placement-rules rule-bundle save --in="rule.json"
If you need to roll back to the previous configuration, you can restore the backup file default.json or write the following JSON file manually and overwrite the current configuration with this JSON file:
cat default.json
[
{
"group_id": "pd",
"group_index": 0,
"group_override": false,
"rules": [
{
"group_id": "pd",
"id": "default",
"start_key": "",
"end_key": "",
"role": "voter",
"count": 3
}
]
}
]
Enable the DR Auto-Sync mode
The replication mode is controlled by PD. You can configure the replication mode in the PD configuration file using one of the following methods:
Method 1: Configure the PD configuration file, and then deploy a cluster.
[replication-mode] replication-mode = "dr-auto-sync" [replication-mode.dr-auto-sync] label-key = "zone" primary = "east" dr = "west" primary-replicas = 2 dr-replicas = 1 wait-store-timeout = "1m" wait-sync-timeout = "1m"Method 2: If you have deployed a cluster, use pd-ctl commands to modify the configurations of PD.
config set replication-mode dr-auto-sync config set replication-mode dr-auto-sync label-key zone config set replication-mode dr-auto-sync primary east config set replication-mode dr-auto-sync dr west config set replication-mode dr-auto-sync primary-replicas 2 config set replication-mode dr-auto-sync dr-replicas 1
Descriptions of configuration items:
replication-modeis the replication mode to be enabled. In the above example, it is set todr-auto-sync. By default, the majority protocol is used.label-keyis used to distinguish different data centers and needs to match Placement Rules. In this example, the primary data center is "east" and the DR data center is "west".primary-replicasis the number of Voter replicas in the primary data center.dr-replicasis the number of Voter replicas in the DR data center.wait-store-timeoutis the waiting time for switching to asynchronous replication mode when network isolation or failure occurs. If the time of network failure exceeds the waiting time, asynchronous replication mode is enabled. The default waiting time is 60 seconds.
To check the current replication status of the cluster, use the following API:
curl http://pd_ip:pd_port/pd/api/v1/replication_mode/status
{
"mode": "dr-auto-sync",
"dr-auto-sync": {
"label-key": "zone",
"state": "sync"
}
}
Status switch
The replication mode of a cluster can automatically and adaptively switch between three statuses:
- When the cluster is normal, the synchronous replication mode is enabled to maximize the data integrity of the disaster recovery data center.
- When the network connection between the two data centers fails or the DR data center breaks down, after a pre-set protective interval, the cluster enables the asynchronous replication mode to ensure the availability of the application.
- When the network reconnects or the DR data center recovers, the TiKV node joins the cluster again and gradually replicates the data. Finally, the cluster switches to the synchronous replication mode.
The details for the status switch are as follows:
Initialization: At the initialization stage, the cluster is in the synchronous replication mode. PD sends the status information to TiKV, and all TiKV nodes strictly follow the synchronous replication mode to work.
Switch from sync to async: PD regularly checks the heartbeat information of TiKV to judge whether the TiKV node fails or is disconnected. If the number of failed nodes exceeds the number of replicas of the primary data center (
primary-replicas) and the DR data center (dr-replicas), the synchronous replication mode can no longer serve the data replication and it is necessary to switch the status. When the failure or disconnect time exceeds the time set bywait-store-timeout, PD switches the status of the cluster to the async mode. Then PD sends the status of async to all TiKV nodes, and the replication mode for TiKV switches from two-center replication to the native Raft majority.Switch from async to sync: PD regularly checks the heartbeat information of TiKV to judge whether the TiKV node is reconnected. If the number of failed nodes is less than the number of replicas of the primary data center (
primary-replicas) and the DR data center (dr-replicas), the synchronous replication mode can be enabled again. PD first switches the status of the cluster to sync-recover and sends the status information to all TiKV nodes. All Regions of TiKV gradually switch to the two-data-center synchronous replication mode and then report the heartbeat information to PD. PD records the status of TiKV Regions and calculates the recovery progress. When all TiKV Regions finish the switching, PD switches the replication mode to sync.
Disaster recovery
This section introduces the disaster recovery solution of the two data centers in one city deployment.
When a disaster occurs to a cluster in the synchronous replication mode, you can perform data recovery with RPO = 0:
If the primary data center fails and most of the Voter replicas are lost, but complete data exists in the DR data center, the lost data can be recovered from the DR data center. At this time, manual intervention is required with professional tools. You can contact the TiDB team for a recovery solution.
If the DR center fails and a few Voter replicas are lost, the cluster automatically switches to the asynchronous replication mode.
When a disaster occurs to a cluster that is not in the synchronous replication mode and you cannot perform data recovery with RPO = 0:
- If most of the Voter replicas are lost, manual intervention is required with professional tools. You can contact the TiDB team for a recovery solution.