Follower Read
In TiDB, to ensure high availability and data safety, TiKV stores multiple replicas for each Region, one of which is the leader and the others are followers. By default, all read and write requests are processed by the leader. The Follower Read feature enables TiDB to read data from follower replicas of a Region while maintaining strong consistency, thereby reducing the read workload on the leader and improving the overall read throughput of the cluster.
When performing Follower Read, TiDB selects an appropriate replica based on the topology information. Specifically, TiDB uses the zone label to identify local replicas: if the zone label of a TiDB node is the same as that of the target TiKV node, TiDB considers the replica as a local replica. For more information, see Schedule Replicas by Topology Labels.
By enabling followers to handle read requests, Follower Read achieves the following goals:
- Distribute read hotspots and reduce the leader workload.
- Prioritize local replica reads in multi-AZ or multi-datacenter deployments to minimize cross-AZ traffic.
Usage scenarios
Follower Read is suitable for the following scenarios:
- Applications with heavy read requests or significant read hotspots.
- Multi-AZ deployments where you want to prioritize reading from local replicas to reduce cross-AZ bandwidth usage.
- Read-write separation architectures that you want to further improve overall read performance.
Usage
To enable TiDB's Follower Read feature, modify the value of the tidb_replica_read variable as follows:
set [session | global] tidb_replica_read = '<target value>';
Scope: SESSION | GLOBAL
Default: leader
This variable defines the expected data read mode. Starting from v8.5.4 and v9.0.0, this variable only takes effect on read-only SQL statements.
In scenarios where you need to reduce cross-AZ traffic by reading from local replicas, the following configurations are recommended:
leader: the default value, providing the best performance.closest-adaptive: minimizes cross-AZ traffic while keeping performance loss to a minimum.closest-replicas: maximizes cross-AZ traffic savings but might cause some performance degradation.
If you are using other configurations, refer to the following table to modify them to the recommended configurations:
| Current configuration | Recommended configuration |
|---|---|
follower | closest-replicas |
leader-and-follower | closest-replicas |
prefer-leader | closest-adaptive |
learner | closest-replicas |
If you want to use a more precise read replica selection policy, refer to the full list of available configurations as follows:
When you set the value of
tidb_replica_readtoleaderor an empty string, TiDB maintains its default behavior and sends all read operations to the leader replica to perform.When you set the value of
tidb_replica_readtofollower, TiDB selects a follower replica of the Region to perform read operations. If the Region has learner replicas, TiDB also considers them for reads with the same priority. If no available follower or learner replicas exist for the current Region, TiDB reads from the leader replica.When the value of
tidb_replica_readis set toleader-and-follower, TiDB can select any replicas to perform read operations. In this mode, read requests are load balanced between the leader, follower, and learner.When the value of
tidb_replica_readis set toprefer-leader, TiDB prefers to select the leader replica to perform read operations. If the leader replica is obviously slow in processing read operations (such as caused by disk or network performance jitter), TiDB will select other available follower replicas to perform read operations.When the value of
tidb_replica_readis set toclosest-replicas, TiDB prefers to select a replica in the same availability zone to perform read operations, which can be a leader, a follower, or a learner. If there is no replica in the same availability zone, TiDB reads from the leader replica.When the value of
tidb_replica_readis set toclosest-adaptive:- If the estimated result of a read request is greater than or equal to the value of
tidb_adaptive_closest_read_threshold, TiDB prefers to select a replica in the same availability zone for read operations. To avoid unbalanced distribution of read traffic across availability zones, TiDB dynamically detects the distribution of availability zones for all online TiDB and TiKV nodes. In each availability zone, the number of TiDB nodes whoseclosest-adaptiveconfiguration takes effect is limited, which is always the same as the number of TiDB nodes in the availability zone with the fewest TiDB nodes, and the other TiDB nodes automatically read from the leader replica. For example, if TiDB nodes are distributed across 3 availability zones (A, B, and C), where A and B each contains 3 TiDB nodes and C contains only 2 TiDB nodes, the number of TiDB nodes whoseclosest-adaptiveconfiguration takes effect in each availability zone is 2, and the other TiDB node in each of the A and B availability zones automatically selects the leader replica for read operations. - If the estimated result of a read request is less than the value of
tidb_adaptive_closest_read_threshold, TiDB can only select the leader replica for read operations.
- If the estimated result of a read request is greater than or equal to the value of
When you set the value of
tidb_replica_readtolearner, TiDB reads data from the learner replica. If no learner replica is available for the current Region, TiDB reads from an available leader or follower replica.
Basic monitoring
You can check the TiDB > KV Request > Read Req Traffic panel (New in v8.5.4 and v9.0.0) to determine whether to enable Follower Read and observe the traffic reduction effect after enabling it.
Implementation mechanism
Before the Follower Read feature was introduced, TiDB applied the strong leader principle and submitted all read and write requests to the leader node of a Region to handle. Although TiKV can distribute Regions evenly on multiple physical nodes, for each Region, only the leader can provide external services. The other followers cannot handle read requests, and they only receive the data replicated from the leader at all times and prepare for voting to elect a leader in case of a failover.
Follower Read includes a set of load balancing mechanisms that offload TiKV read requests from the leader replica to a follower replica in a Region. To allow data reading from the follower node without violating linearizability or affecting Snapshot Isolation in TiDB, the follower node needs to use ReadIndex of the Raft protocol to ensure that the read request can read the latest data that has been committed on the leader node. At the TiDB level, the Follower Read feature simply needs to send the read request of a Region to a follower replica based on the load balancing policy.
Strongly consistent reads
When the follower node processes a read request, it first uses ReadIndex of the Raft protocol to interact with the leader of the Region, to obtain the latest commit index of the current Raft group. After the latest commit index of the leader is applied locally to the follower, the processing of a read request starts.
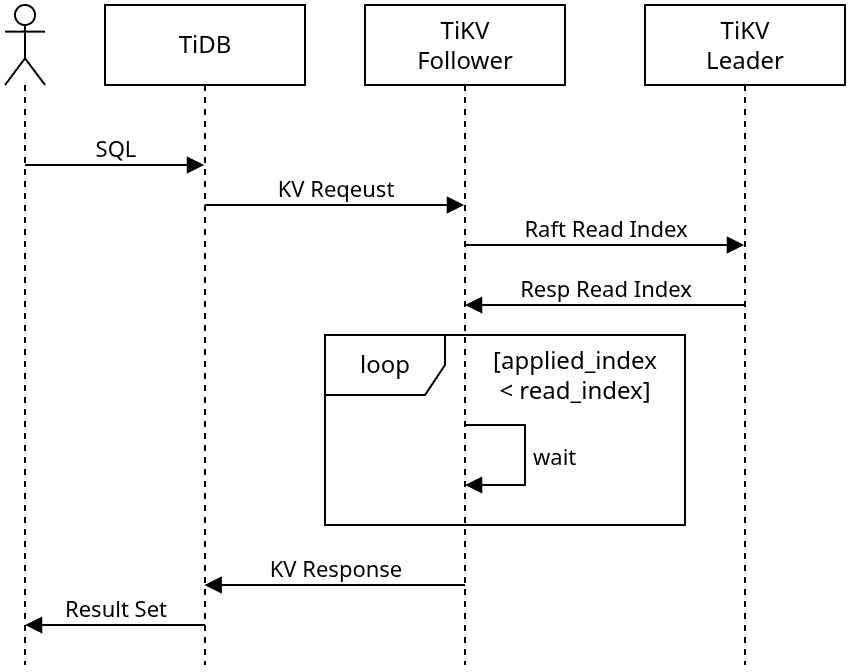
Follower replica selection strategy
The Follower Read feature does not affect TiDB's Snapshot Isolation transaction isolation level. TiDB selects a replica based on the tidb_replica_read configuration for the first read attempt. From the second retry onward, TiDB prioritizes ensuring successful reads. Therefore, when the selected follower node becomes inaccessible or has other errors, TiDB switches to the leader for service.
leader
- Always selects the leader replica for reads, regardless of its location.
closest-replicas
- When the replica in the same AZ as TiDB is the leader node, TiDB does not perform Follower Read from it.
- When the replica in the same AZ as TiDB is a follower node, TiDB performs Follower Read from it.
closest-adaptive
- If the estimated result is not large enough, TiDB uses the
leaderpolicy and does not perform Follower Read. - If the estimated result is large enough, TiDB uses the
closest-replicaspolicy.
Follower Read performance overhead
To ensure strong data consistency, Follower Read performs a ReadIndex operation regardless of how much data is read, which inevitably consumes additional TiKV CPU resources. Therefore, in small-query scenarios (such as point queries), the performance loss of Follower Read is relatively more obvious. Moreover, because the traffic reduced by local reads for small queries is limited, Follower Read is more recommended for large queries or batch reading scenarios.
When tidb_replica_read is set to closest-adaptive, TiDB does not perform Follower Read for small queries. As a result, under various workloads, the additional CPU overhead on TiKV is typically no more than 10% compared with the leader policy.