Access TiDB Dashboard
TiDB Dashboard is a visualized tool introduced since TiDB v4.0 and is used to monitor and diagnose TiDB clusters. For details, see TiDB Dashboard.
This document describes how to access TiDB Dashboard on Kubernetes.
- In a test environment, you can access TiDB Dashboard by port forward.
- In a production environment, it is recommended to access TiDB Dashboard by Ingress. You can also enable the TLS transfer. See Use Ingress with TLS for details.
- To access TiDB Dashboard without a domain name, you can use NodePort Service.
In this document, you can use the Discovery service to access TiDB Dashboard. TiDB Operator starts a Discovery service for each TiDB cluster. The Discovery service can return the corresponding startup parameters for each PD Pod to support the startup of the PD cluster. The Discovery service can also send proxy requests to the TiDB Dashboard.
Prerequisites
To access TiDB Dashboard smoothly on Kubernetes, you need to use TiDB Operator v1.1.1 (or later versions) and the TiDB cluster (v4.0.1 or later versions).
You need to configure the TidbCluster object file as follows to enable quick access to TiDB Dashboard:
apiVersion: pingcap.com/v1alpha1
kind: TidbCluster
metadata:
name: basic
spec:
pd:
config: |
[dashboard]
internal-proxy = true
Method 1. Access TiDB Dashboard by port forward
TiDB Dashboard is built in the PD component in TiDB 4.0 and later versions. You can refer to the following example to quickly deploy a TiDB cluster on Kubernetes.
Deploy the following example
.yamlfile into the Kubernetes cluster by running thekubectl apply -fcommand:apiVersion: pingcap.com/v1alpha1 kind: TidbCluster metadata: name: basic spec: version: v6.1.0 timezone: UTC pvReclaimPolicy: Delete pd: enableDashboardInternalProxy: true baseImage: pingcap/pd maxFailoverCount: 0 replicas: 1 requests: storage: "10Gi" config: {} tikv: baseImage: pingcap/tikv maxFailoverCount: 0 replicas: 1 requests: storage: "100Gi" config: {} tidb: baseImage: pingcap/tidb maxFailoverCount: 0 replicas: 1 service: type: ClusterIP config: {}After the cluster is created, expose TiDB Dashboard to the local machine by running the following command:
kubectl port-forward svc/basic-discovery -n ${namespace} 10262:10262By default,
port-forwardbinds to the IP address 127.0.0.1. If you need to use another IP address to access the machine running theport-forwardcommand, you can add the--addressoption and specify the IP address to be bound.Visit http://localhost:10262/dashboard in your browser to access TiDB Dashboard.
Method 2. Access TiDB Dashboard by Ingress
In important production environments, it is recommended to expose the TiDB Dashboard service using Ingress.
Prerequisites
Before using Ingress, install the Ingress controller in your Kubernetes cluster. Otherwise, simply creating Ingress resources does not take effect.
To deploy the Ingress controller, refer to ingress-nginx. You can also choose from various Ingress controllers.
Use Ingress
You can expose the TiDB Dashboard service outside the Kubernetes cluster by using Ingress. In this way, the service can be accessed outside Kubernetes via http/https. For more details, see Ingress.
The following is an .yaml example of accessing TiDB Dashboard using Ingress:
Deploy the following
.yamlfile to the Kubernetes cluster by running thekubectl apply -fcommand:apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: access-dashboard namespace: ${namespace} spec: rules: - host: ${host} http: paths: - backend: serviceName: ${cluster_name}-discovery servicePort: 10262 path: /dashboardAfter Ingress is deployed, you can access TiDB Dashboard via http://${host}/dashboard outside the Kubernetes cluster.
Use Ingress with TLS
Ingress supports TLS. See Ingress TLS. The following example shows how to use Ingress TLS:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: access-dashboard
namespace: ${namespace}
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- ${host}
secretName: testsecret-tls
rules:
- host: ${host}
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: ${cluster_name}-discovery
servicePort: 10262
path: /dashboard
In the above file, testsecret-tls contains tls.crt and tls.key needed for example.com.
This is an example of testsecret-tls:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: testsecret-tls
namespace: default
data:
tls.crt: base64 encoded cert
tls.key: base64 encoded key
type: kubernetes.io/tls
After Ingress is deployed, visit https://{host}/dashboard to access TiDB Dashboard.
Method 3. Use NodePort Service
Because ingress can only be accessed with a domain name, it might be difficult to use ingress in some scenarios. In this case, to access and use TiDB Dashboard, you can add a Service of NodePort type.
The following is an .yaml example using the Service of NodePort type to access the TiDB Dashboard. To deploy the following .yaml file into the Kubernetes cluster, you can run the kubectl apply -f command:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: access-dashboard
namespace: ${namespace}
spec:
ports:
- name: dashboard
port: 10262
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 10262
type: NodePort
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/component: discovery
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ${cluster_name}
app.kubernetes.io/name: tidb-cluster
After deploying the Service, you can access TiDB Dashboard via https://{nodeIP}:{nodePort}/dashboard. By default, nodePort is randomly assigned by Kubernetes. You can also specify an available port in the .yaml file.
Note that if there is more than one PD Pod in the cluster, you need to set spec.pd.config.dashboard.internal-proxy: true in the TidbCluster CR to ensure normal access to TiDB Dashboard.
Enable Continuous Profiling
With Continuous Profiling, you can collect continuous performance data of TiDB, PD, TiKV, and TiFlash instances, and have the nodes monitored day and night without restarting any of them. The data collected can be displayed in various forms, for example, on a flame graph or a directed acyclic graph. The data displayed visually shows what internal operations are performed on the instances during the performance profiling period and the corresponding proportions. With such data, you can quickly learn the CPU resource consumption of these instances.
To enable this feature, you need to deploy TidbNGMonitoring CR using TiDB Operator v1.3.0 or later versions.
Deploy TidbMonitor CR.
If your TiDB cluster is earlier than v5.4.0, see Deploy Monitoring and Alerts for a TiDB Cluster to deploy TidbMonitor CR.
If your TiDB cluster is v5.4.0 or later, skip this step.
Deploy TidbNGMonitoring CR.
Run the following command to deploy TidbNGMonitoring CR. In this command,
${cluster_name}is the name of the TidbCluster CR and${cluster_ns}is the namespace of this CR.cat << EOF | kubectl apply -n ${ns} -f - apiVersion: pingcap.com/v1alpha1 kind: TidbNGMonitoring metadata: name: ${name} spec: clusters: - name: ${cluster_name} namespace: ${cluster_ns} ngMonitoring: requests: storage: 10Gi version: v6.1.0 # storageClassName: default baseImage: pingcap/ng-monitoring EOFFor more configuration items of the TidbNGMonitoring CR, see example in tidb-operator.
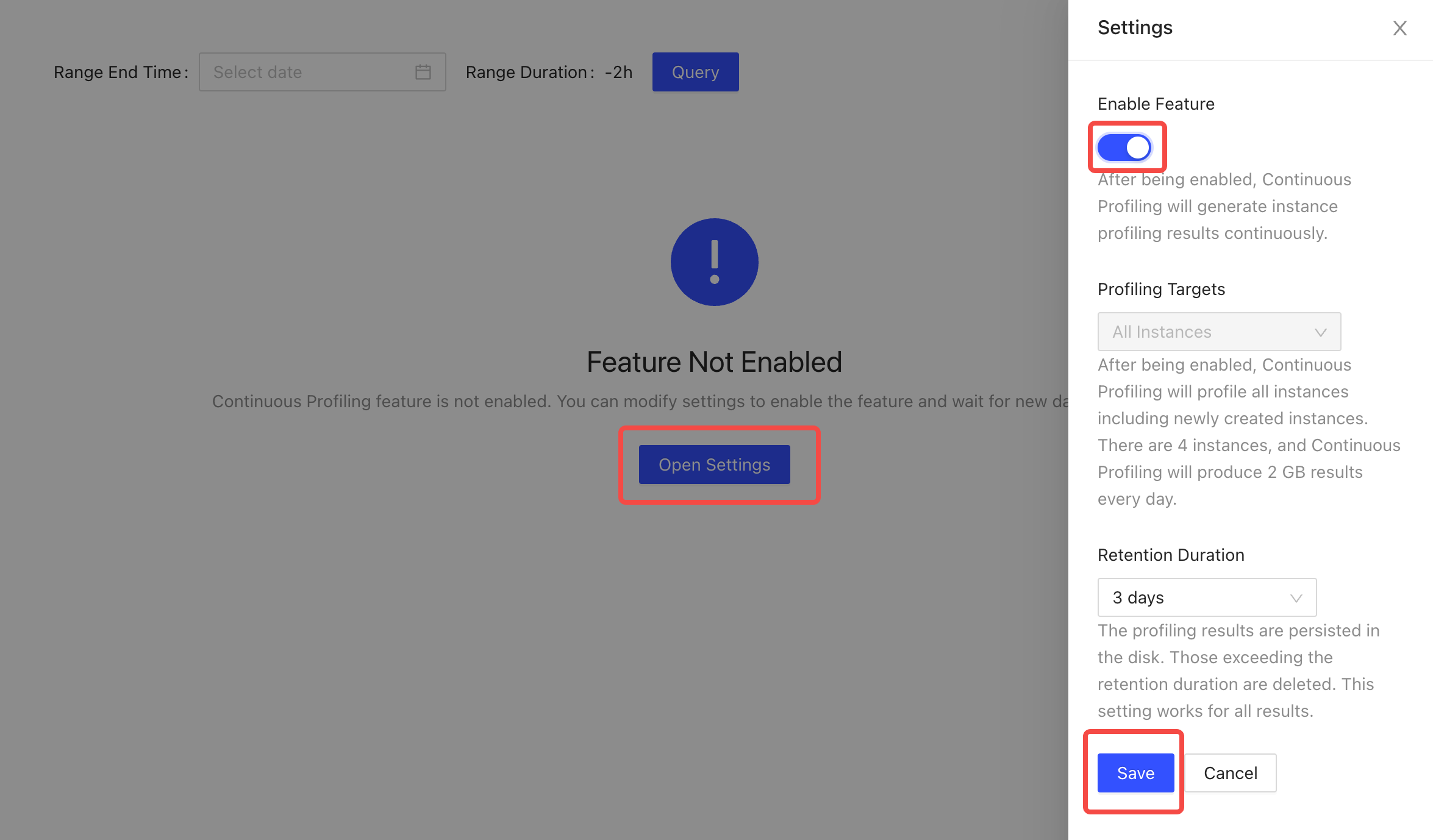
Enable Continuous Profiling.
On TiDB Dashboard, click Advanced Debugging > Profiling Instances > Continuous Profiling.
In the displayed window, click Open Settings. Switch on the button under Enable Feature on the right. Modify the value of Retention Duration as required or retain the default value.
Click Save to enable this feature.
For more operations of the Continuous Profiling function, see TiDB Dashboard Instance Profiling - Continuous Profiling.
Unsupported TiDB Dashboard features
Due to the special environment of Kubernetes, some features of TiDB Dashboard are not supported in TiDB Operator, including:
In Overview -> Monitor & Alert -> View Metrics, the link does not direct to the Grafana monitoring dashboard. If you need to access Grafana, refer to Access the Grafana monitoring dashboard.
The log search feature is unavailable. If you need to view the log of a component, execute
kubectl logs ${pod_name} -n {namespace}. You can also view logs using the log service of the Kubernetes cluster.In Cluster Info -> Hosts, the Disk Usage cannot display correctly. You can view the disk usage of each component by viewing the component dashboards in the TidbMonitor dashboard. You can also view the disk usage of Kubernetes nodes by deploying a Kubernetes host monitoring system.