TiDB Pessimistic Transaction Mode
To make the usage of TiDB closer to traditional databases and reduce the cost of migration, starting from v3.0, TiDB supports the pessimistic transaction mode on top of the optimistic transaction model. This document describes the features of the TiDB pessimistic transaction mode.
Switch transaction mode
You can set the transaction mode by configuring the tidb_txn_mode system variable. The following command sets all explicit transactions (that is, non-autocommit transactions) executed by newly created sessions in the cluster to the pessimistic transaction mode:
SET GLOBAL tidb_txn_mode = 'pessimistic';
You can also explicitly enable the pessimistic transaction mode by executing the following SQL statements:
BEGIN PESSIMISTIC;
BEGIN /*T! PESSIMISTIC */;
The BEGIN PESSIMISTIC; and BEGIN OPTIMISTIC; statements take precedence over the tidb_txn_mode system variable. Transactions started with these two statements ignore the system variable and support using both the pessimistic and optimistic transaction modes.
Behaviors
Pessimistic transactions in TiDB behave similarly to those in MySQL. See the minor differences in Difference with MySQL InnoDB.
For pessimistic transactions, TiDB introduces snapshot read and current read.
Snapshot read: it is an unlocked read that reads a version committed before the transaction starts. The read in the
SELECTstatement is a snapshot read.Current read: it is a locked read that reads the latest committed version. The read in the
UPDATE,DELETE,INSERT, orSELECT FOR UPDATEstatement is a current read.The following examples provide a detailed description of snapshot read and current read.
Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 CREATE TABLE t (a INT); INSERT INTO T VALUES(1); BEGIN PESSIMISTIC; UPDATE t SET a = a + 1; BEGIN PESSIMISTIC; SELECT * FROM t; -- Use the snapshot read to read the version committed before the current transaction starts. The result returns a=1. BEGIN PESSIMISTIC; SELECT * FROM t FOR UPDATE; -- Use the current read. Wait for the lock. COMMIT; -- Release the lock. The SELECT FOR UPDATE operation of session 3 obtains the lock and TiDB uses the current read to read the latest committed version. The result returns a=2. SELECT * FROM t; -- Use the snapshot read to read the version committed before the current transaction starts. The result returns a=1.
When you execute
UPDATE,DELETEorINSERTstatements, the latest committed data is read, data is modified, and a pessimistic lock is applied on the modified rows.For
SELECT FOR UPDATEstatements, a pessimistic lock is applied on the latest version of the committed data, instead of on the modified rows.Locks will be released when the transaction is committed or rolled back. Other transactions attempting to modify the data are blocked and have to wait for the lock to be released. Transactions attempting to read the data are not blocked, because TiDB uses multi-version concurrency control (MVCC).
You can set the system variable
tidb_constraint_check_in_place_pessimisticto control whether to skip the pessimistic locks with unique constraint checks. See constraints for details.If several transactions are trying to acquire each other's respective locks, a deadlock will occur. This is automatically detected, and one of the transactions will randomly be terminated with a MySQL-compatible error code
1213returned.Transactions will wait up to
innodb_lock_wait_timeoutseconds (default: 50) to acquire new locks. When this timeout is reached, a MySQL-compatible error code1205is returned. If multiple transactions are waiting for the same lock, the order of priority is approximately based on thestart tsof the transaction.TiDB supports both the optimistic transaction mode and pessimistic transaction mode in the same cluster. You can specify either mode for transaction execution.
TiDB supports the
FOR UPDATE NOWAITsyntax and does not block and wait for locks to be released. Instead, a MySQL-compatible error code3572is returned.If the
Point GetandBatch Point Getoperators do not read data, they still lock the given primary key or unique key, which blocks other transactions from locking or writing data to the same primary key or unique key.TiDB supports the
FOR UPDATE OF TABLESsyntax. For a statement that joins multiple tables, TiDB only applies pessimistic locks on the rows that are associated with the tables inOF TABLES.
Difference with MySQL InnoDB
When TiDB executes DML or
SELECT FOR UPDATEstatements that use range in the WHERE clause, concurrent DML statements within the range are not blocked.For example:
CREATE TABLE t1 ( id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, pad1 VARCHAR(100) ); INSERT INTO t1 (id) VALUES (1),(5),(10);BEGIN /*T! PESSIMISTIC */; SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE id BETWEEN 1 AND 10 FOR UPDATE;BEGIN /*T! PESSIMISTIC */; INSERT INTO t1 (id) VALUES (6); -- blocks only in MySQL UPDATE t1 SET pad1='new value' WHERE id = 5; -- blocks waiting in both MySQL and TiDBThis behavior is because TiDB does not currently support gap locking.
TiDB does not support
SELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODE.TiDB does not support the
SELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODEsyntax by default. You can enabletidb_enable_noop_functionsto make TiDB compatible with theSELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODEsyntax. ExecutingSELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODEhas the same effect as that without the lock, so it does not block read or write operations of other transactions.Starting from v8.3.0, TiDB supports using the
tidb_enable_shared_lock_promotionsystem variable to enable theSELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODEstatement to add locks. However, note that the lock added at this time is not a true shared lock, but an exclusive lock, which is consistent withSELECT FOR UPDATE. If you want to block writes to prevent data from being modified by write transactions in parallel during reads while keeping TiDB compatible with theSELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODEsyntax, you can enable this variable. Enabling this variable takes effect on theSELECT LOCK IN SHARE MODEstatement, regardless of whethertidb_enable_noop_functionsis enabled or not.DDL may result in failure of the pessimistic transaction commit.
When DDL is executed in MySQL, it might be blocked by the transaction that is being executed. However, in this scenario, the DDL operation is not blocked in TiDB, which leads to failure of the pessimistic transaction commit:
ERROR 1105 (HY000): Information schema is changed. [try again later]. TiDB executes theTRUNCATE TABLEstatement during the transaction execution, which might result in thetable doesn't existerror.After executing
START TRANSACTION WITH CONSISTENT SNAPSHOT, MySQL can still read the tables that are created later in other transactions, while TiDB cannot.The autocommit transactions prefer the optimistic locking.
When using the pessimistic model, the autocommit transactions first try to commit the statement using the optimistic model that has less overhead. If a write conflict occurs, the pessimistic model is used for transaction retry. Therefore, if
tidb_retry_limitis set to0, the autocommit transaction still reports theWrite Conflicterror when a write conflict occurs.The autocommit
SELECT FOR UPDATEstatement does not wait for lock.The data read by
EMBEDDED SELECTin the statement is not locked.Open transactions in TiDB do not block garbage collection (GC). By default, this limits the maximum execution time of pessimistic transactions to 1 hour. You can modify this limit by editing
max-txn-ttlunder[performance]in the TiDB configuration file.
Isolation level
TiDB supports the following two isolation levels in the pessimistic transaction mode:
Repeatable Read by default, which is the same as MySQL.
Read Committed. You can set this isolation level using the
SET TRANSACTIONstatement.
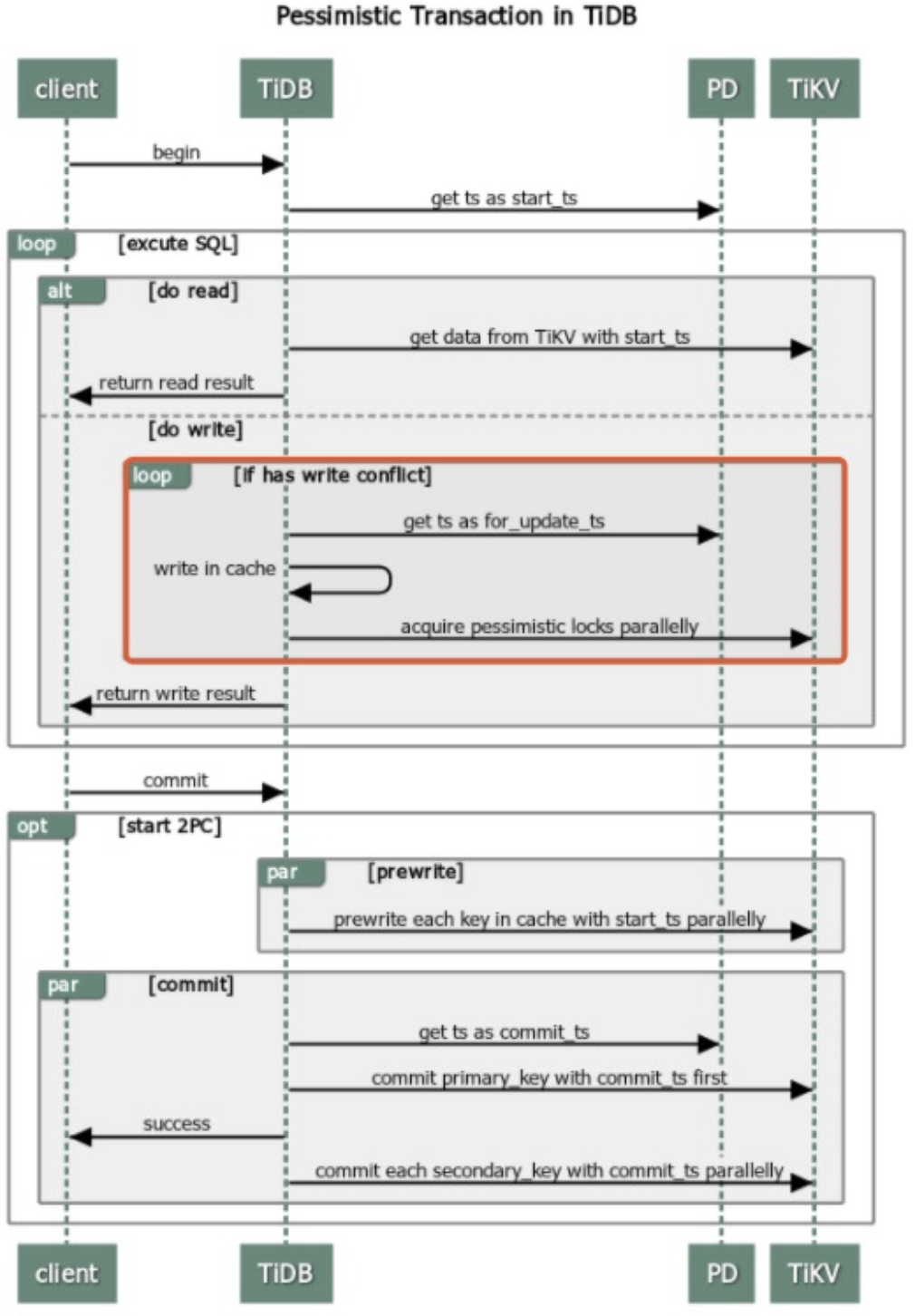
Pessimistic transaction commit process
In the transaction commit process, pessimistic transactions and optimistic transactions have the same logic. Both transactions adopt the two-phase commit (2PC) mode. The important adaptation of pessimistic transactions is DML execution.
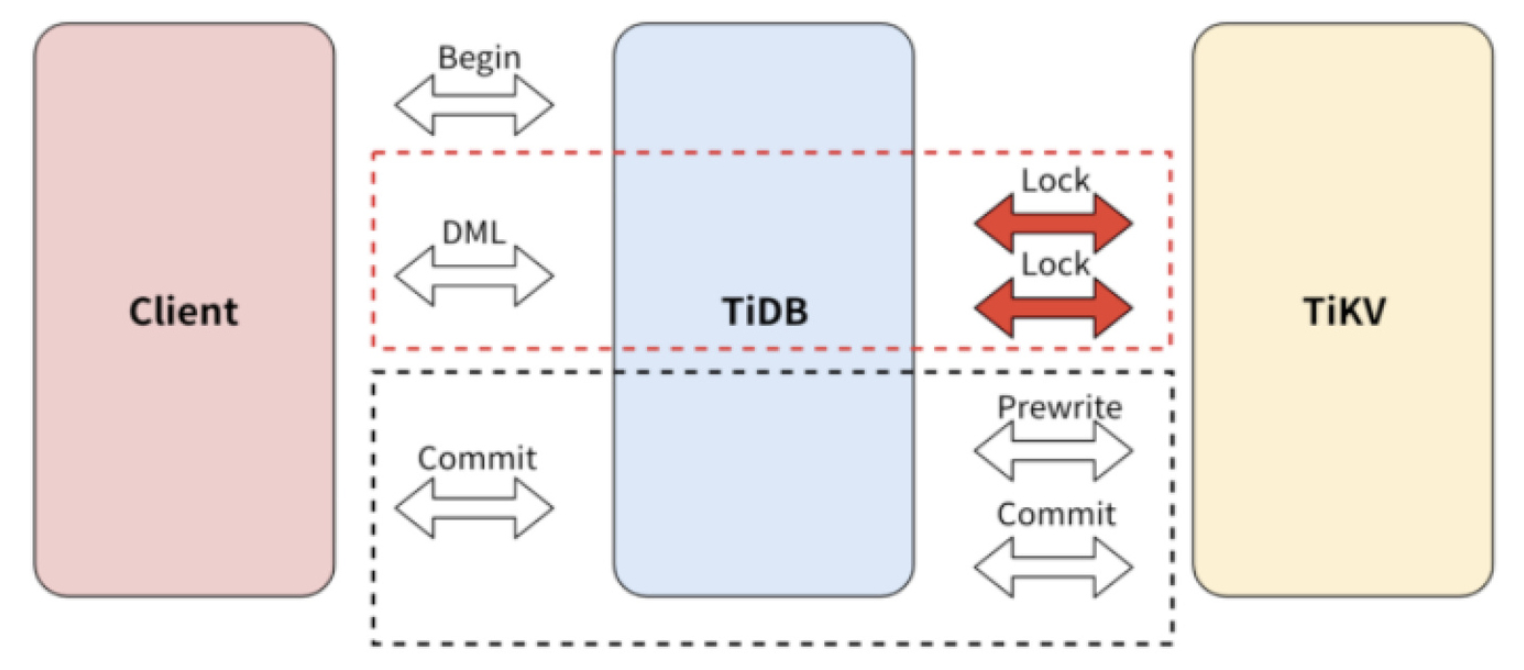
The pessimistic transaction adds an Acquire Pessimistic Lock phase before 2PC. This phase includes the following steps:
- (Same as the optimistic transaction mode) TiDB receives the
beginrequest from the client, and the current timestamp is this transaction's start_ts. - When the TiDB server receives a writing request from the client, the TiDB server initiates a pessimistic lock request to the TiKV server, and the lock is persisted to the TiKV server.
- (Same as the optimistic transaction mode) When the client sends the commit request, TiDB starts to perform the two-phase commit similar to the optimistic transaction mode.
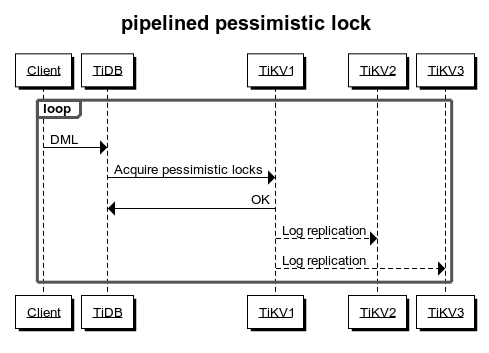
Pipelined locking process
Adding a pessimistic lock requires writing data into TiKV. The response of successfully adding a lock can only be returned to TiDB after commit and apply through Raft. Therefore, compared with optimistic transactions, the pessimistic transaction mode inevitably has higher latency.
To reduce the overhead of locking, TiKV implements the pipelined locking process: when the data meets the requirements for locking, TiKV immediately notifies TiDB to execute subsequent requests and writes into the pessimistic lock asynchronously. This process reduces most latency and significantly improves the performance of pessimistic transactions. However, when network partition occurs in TiKV or a TiKV node is down, the asynchronous write into the pessimistic lock might fail and affect the following aspects:
Other transactions that modify the same data cannot be blocked. If the application logic relies on locking or lock waiting mechanisms, the correctness of the application logic is affected.
There is a low probability that the transaction commit fails, but it does not affect the correctness of the transactions.
If the application logic relies on the locking or lock waiting mechanisms, or if you want to guarantee as much as possible the success rate of transaction commits even in the case of TiKV cluster anomalies, you should disable the pipelined locking feature.
This feature is enabled by default. To disable it, modify the TiKV configuration:
[pessimistic-txn]
pipelined = false
If the TiKV cluster is v4.0.9 or later, you can also dynamically disable this feature by modifying TiKV configuration dynamically:
set config tikv pessimistic-txn.pipelined='false';
In-memory pessimistic lock
In v6.0.0, TiKV introduces the feature of in-memory pessimistic lock. When this feature is enabled, pessimistic locks are usually stored in the memory of the Region leader only, and are not persisted to disk or replicated through Raft to other replicas. This feature can greatly reduce the overhead of acquiring pessimistic locks and improve the throughput of pessimistic transactions.
When the memory usage of in-memory pessimistic locks exceeds the memory threshold of the Region or the TiKV node, the acquisition of pessimistic locks turns to the pipelined locking process. When the Region is merged or the leader is transferred, to avoid the loss of the pessimistic lock, TiKV writes the in-memory pessimistic lock to disk and replicates it to other replicas.
The in-memory pessimistic lock performs similarly to the pipelined locking process, which does not affect the lock acquisition when the cluster is healthy. However, when network isolation occurs in TiKV or a TiKV node is down, the acquired pessimistic lock might be lost.
If the application logic relies on the lock acquiring or lock waiting mechanism, or if you want to guarantee as much as possible the success rate of transaction commits even when the cluster is in an abnormal state, you need to disable the in-memory pessimistic lock feature.
This feature is enabled by default. To disable it, modify the TiKV configuration:
[pessimistic-txn]
in-memory = false
To dynamically disable this feature, modify the TiKV configuration dynamically:
set config tikv pessimistic-txn.in-memory='false';