TiDB TPC-H Performance Test Report -- v4.0 vs. v3.0
Test purpose
This test aims to compare the TPC-H performance of TiDB 4.0 and TiDB 3.0 in the online analytical processing (OLAP) scenario.
Because TiFlash is introduced in TiDB v4.0, which enhances TiDB's Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) capabilities, test objects in this report are as follows:
- TiDB v3.0 that reads data only from TiKV.
- TiDB v4.0 that reads data only from TiKV.
- TiDB v4.0 that reads data from TiKV and TiFlash automatically based on intelligent choice.
Test environment (AWS EC2)
Hardware configuration
| Service type | EC2 type | Instance count |
|---|---|---|
| PD | m5.xlarge | 3 |
| TiDB | c5.4xlarge | 2 |
| TiKV & TiFlash | i3.4xlarge | 3 |
| TPC-H | m5.xlarge | 1 |
Software version
| Service type | Software version |
|---|---|
| PD | 3.0 and 4.0 |
| TiDB | 3.0 and 4.0 |
| TiKV | 3.0 and 4.0 |
| TiFlash | 4.0 |
| tiup-bench | 0.2 |
Parameter configuration
v3.0
For v3.0, TiDB, TiKV, and PD use the default parameter configuration.
Variable configuration
set global tidb_distsql_scan_concurrency = 30;
set global tidb_projection_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_hashagg_partial_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_hashagg_final_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_hash_join_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_index_lookup_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_index_lookup_join_concurrency = 16;
v4.0
For v4.0, TiDB uses the default parameter configuration.
TiKV configuration
readpool.storage.use-unified-pool: false
readpool.coprocessor.use-unified-pool: true
PD configuration
replication.enable-placement-rules: true
TiFlash configuration
logger.level: "info"
learner_config.log-level: "info"
Variable configuration
set global tidb_allow_batch_cop = 1;
set session tidb_opt_distinct_agg_push_down = 1;
set global tidb_distsql_scan_concurrency = 30;
set global tidb_projection_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_hashagg_partial_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_hashagg_final_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_hash_join_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_index_lookup_concurrency = 16;
set global tidb_index_lookup_join_concurrency = 16;
Test plan
Hardware prerequisite
To avoid TiKV and TiFlash racing for disk and I/O resources, mount the two NVMe SSD disks configured on EC2 to /data1 and /data2. Deploy TiKV on /data1 and deploy TiFlash on /data2.
Test process
Deploy TiDB v4.0 and v3.0 using TiUP.
Use the bench tool of TiUP to import the TPC-H data with the scale factor 10.
Execute the following command to import data into v3.0:
tiup bench tpch prepare \ --host ${tidb_v3_host} --port ${tidb_v3_port} --db tpch_10 \ --sf 10 \ --analyze --tidb_build_stats_concurrency 8 --tidb_distsql_scan_concurrency 30Execute the following command to import data into v4.0:
tiup bench tpch prepare \ --host ${tidb_v4_host} --port ${tidb_v4_port} --db tpch_10 --password ${password} \ --sf 10 \ --tiflash \ --analyze --tidb_build_stats_concurrency 8 --tidb_distsql_scan_concurrency 30
Execute the TPC-H queries.
Download the TPC-H SQL query file:
git clone https://github.com/pingcap/tidb-bench.git && cd tpch/queriesExecute TPC-H queries and record the executing time of each query.
- For TiDB v3.0, use the MySQL client to connect to TiDB, execute the queries, and record the execution time of each query.
- For TiDB v4.0, use the MySQL client to connect to TiDB, and choose one of the following operations based on where data is read from:
- If data is read only from TiKV, set
set @@session.tidb_isolation_read_engines = 'tikv,tidb';, execute the queries, and record the execution time of each query. - If data is read from TiKV and TiFlash automatically based on cost-based intelligent choice, set
set @@session.tidb_isolation_read_engines = 'tikv,tiflash,tidb';, execute the query, and record the execution time of each query.
- If data is read only from TiKV, set
Extract and organize the data of query execution time.
Test result
| Query ID | v3.0 | v4.0 TiKV Only | v4.0 TiKV/TiFlash Automatically |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.78 s | 7.45 s | 2.09 s |
| 2 | 3.15 s | 1.71 s | 1.71 s |
| 3 | 6.61 s | 4.10 s | 4.05 s |
| 4 | 2.98 s | 2.56 s | 1.87 s |
| 5 | 20.35 s | 5.71 s | 8.53 s |
| 6 | 4.75 s | 2.44 s | 0.39 s |
| 7 | 7.97 s | 3.72 s | 3.59 s |
| 8 | 5.89 s | 3.22 s | 8.59 s |
| 9 | 34.08 s | 11.87 s | 15.41 s |
| 10 | 4.83 s | 2.75 s | 3.35 s |
| 11 | 3.98 s | 1.60 s | 1.59 s |
| 12 | 5.63 s | 3.40 s | 1.03 s |
| 13 | 5.41 s | 4.56 s | 4.02 s |
| 14 | 5.19 s | 3.10 s | 0.78 s |
| 15 | 10.25 s | 1.82 s | 1.26 s |
| 16 | 2.46 s | 1.51 s | 1.58 s |
| 17 | 23.76 s | 12.38 s | 8.52 s |
| 18 | 17.14 s | 16.38 s | 16.06 s |
| 19 | 5.70 s | 4.59 s | 3.20 s |
| 20 | 4.98 s | 1.89 s | 1.29 s |
| 21 | 11.12 s | 6.23 s | 6.26 s |
| 22 | 4.49 s | 3.05 s | 2.31 s |
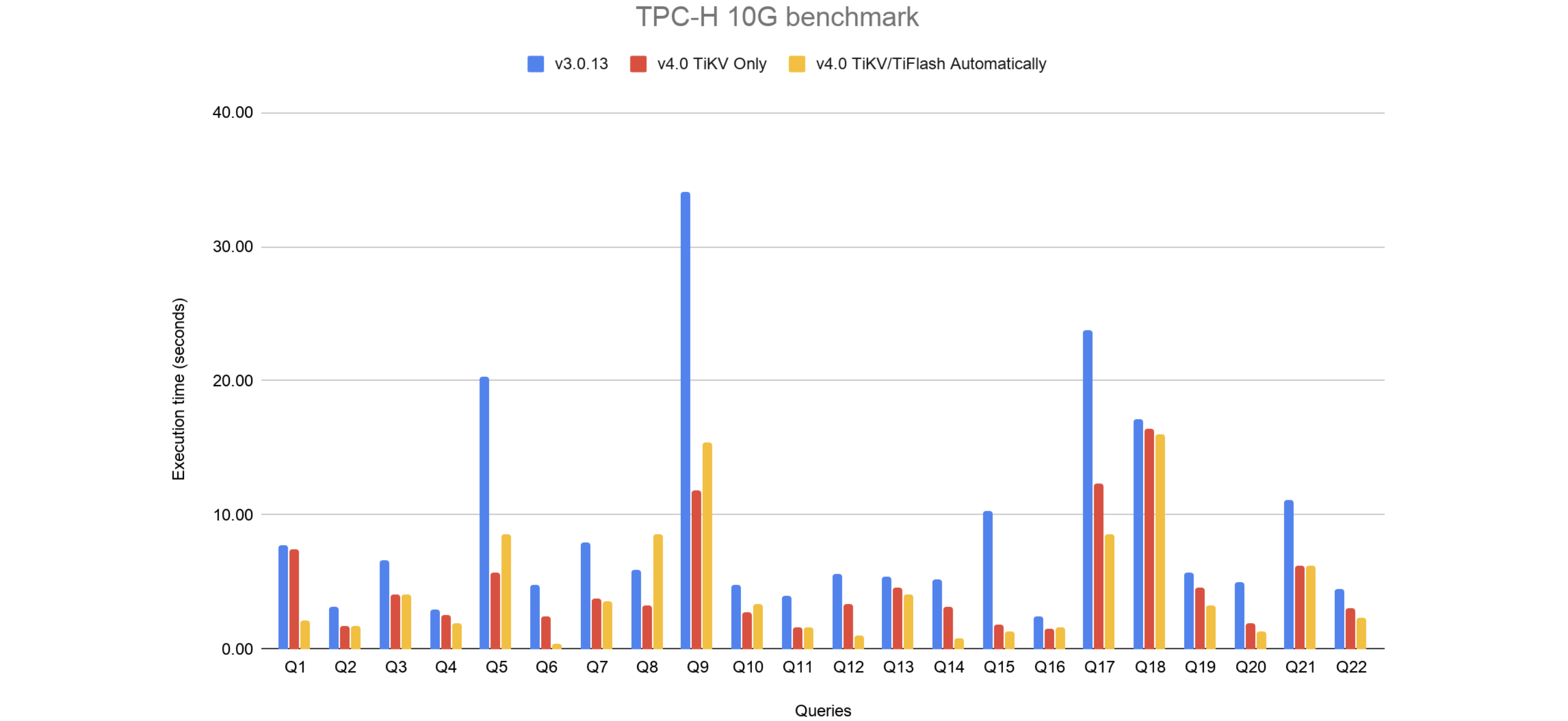
In the performance diagram above:
- Blue lines represent v3.0;
- Red lines represent v4.0 (data read only from TiKV);
- Yellow lines represent v4.0 (data read from TiKV and TiFlash automatically based on intelligent choice).
- The y-axis represents the execution time of the query. The less the time, the better the performance.
Result description:
- v4.0 TiKV Only means that TiDB reads data only from TiKV. The result shows that the TPC-H performance increased after TiDB and TiKV are upgraded to v4.0.
- v4.0 TiKV/TiFlash Automatically means that the TiDB optimizer automatically determines whether to read data from the TiFlash replica according to the cost estimation. The result shows that the TPC-H performance increased in the full HTAP form of v4.0.
From the diagram above, you can see that TPC-H performance increases by about 100% on average over a set of 22 queries.