Manage TiCDC Cluster and Replication Tasks
This document describes how to upgrade TiCDC cluster and modify the configuration of TiCDC cluster using TiUP, and how to manage the TiCDC cluster and replication tasks using the command-line tool cdc cli and the HTTP interface.
Upgrade TiCDC using TiUP
This section introduces how to upgrade the TiCDC cluster using TiUP. In the following example, assume that you need to upgrade TiCDC and the entire TiDB cluster to v5.0.6.
tiup update --self && \
tiup update --all && \
tiup cluster upgrade <cluster-name> v5.0.6
Notes for upgrade
- The
changefeedconfiguration has changed in TiCDC v4.0.2. See Compatibility notes for the configuration file for details. - If you encounter any issues, see Upgrade TiDB using TiUP - FAQ.
Modify TiCDC configuration using TiUP
This section introduces how to modify the configuration of TiCDC cluster using the tiup cluster edit-config command of TiUP. The following example changes the value of gc-ttl from the default 86400 to 3600, namely, one hour.
First, execute the following command. You need to replace <cluster-name> with your actual cluster name.
tiup cluster edit-config <cluster-name>
Then, enter the vi editor page and modify the cdc configuraion under server-configs. The configuration is shown below:
server_configs:
tidb: {}
tikv: {}
pd: {}
tiflash: {}
tiflash-learner: {}
pump: {}
drainer: {}
cdc:
gc-ttl: 3600
After the modification, execute the tiup cluster reload -R cdc command to reload the configuration.
Use TLS
For details about using encrypted data transmission (TLS), see Enable TLS Between TiDB Components.
Use cdc cli to manage cluster status and data replication task
This section introduces how to use cdc cli to manage a TiCDC cluster and data replication tasks. cdc cli is the cli sub-command executed using the cdc binary. The following interface description assumes that:
clicommands are executed directly using thecdcbinary;- PD listens on
10.0.10.25and the port is2379.
If you deploy TiCDC using TiUP, replace cdc cli in the following commands with tiup ctl:<cluster-version> cdc.
Manage TiCDC service progress (capture)
Query the
capturelist:cdc cli capture list --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379[ { "id": "806e3a1b-0e31-477f-9dd6-f3f2c570abdd", "is-owner": true, "address": "127.0.0.1:8300" }, { "id": "ea2a4203-56fe-43a6-b442-7b295f458ebc", "is-owner": false, "address": "127.0.0.1:8301" } ]id: The ID of the service process.is-owner: Indicates whether the service process is the owner node.address: The address via which the service process provides interface to the outside.
Manage replication tasks (changefeed)
State transfer of replication tasks
This feature is available in TiDB v5.1.2 and later versions.
The state of a replication task represents the running status of the replication task. During the running of TiCDC, replication tasks might fail with errors, be manually paused, resumed, or reach the specified TargetTs. These behaviors can lead to the change of the replication task state. This section describes the states of TiCDC replication tasks and the transfer relationships between states.

The states in the above state transfer diagram are described as follows:
Normal: The replication task runs normally and the checkpoint-ts proceeds normally.Stopped: The replication task is stopped, because the user manually pauses the changefeed. The changefeed in this state blocks GC operations.Error: The replication task returns an error. The replication cannot continue due to some recoverable errors. The changefeed in this state keeps trying to resume until the state transfers toNormal. The changefeed in this state blocks GC operations.Finished: The replication task is finished and has reached the presetTargetTs. The changefeed in this state does not block GC operations.Failed: The replication task fails. Due to some unrecoverable errors, the replication task cannot resume and cannot be recovered. The changefeed in this state does not block GC operations.
The numbers in the above state transfer diagram are described as follows.
- ① Execute the
changefeed pausecommand. - ② Execute the
changefeed resumecommand to resume the replication task. - ③ Recoverable errors occur during the
changefeedoperation, and the operation is resumed automatically. - ④ Execute the
changefeed resumecommand to resume the replication task. - ⑤ Unrecoverable errors occur during the
changefeedoperation. - ⑥
changefeedhas reached the presetTargetTs, and the replication is automatically stopped. - ⑦
changefeedsuspended longer than the duration specified bygc-ttl, and cannot be resumed. - ⑧
changefeedexperienced an unrecoverable error when trying to execute automatic recovery.
Create a replication task
Execute the following commands to create a replication task:
cdc cli changefeed create --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --sink-uri="mysql://root:123456@127.0.0.1:3306/" --changefeed-id="simple-replication-task" --sort-engine="unified"
Create changefeed successfully!
ID: simple-replication-task
Info: {"sink-uri":"mysql://root:123456@127.0.0.1:3306/","opts":{},"create-time":"2020-03-12T22:04:08.103600025+08:00","start-ts":415241823337054209,"target-ts":0,"admin-job-type":0,"sort-engine":"unified","sort-dir":".","config":{"case-sensitive":true,"filter":{"rules":["*.*"],"ignore-txn-start-ts":null,"ddl-allow-list":null},"mounter":{"worker-num":16},"sink":{"dispatchers":null,"protocol":"default"},"cyclic-replication":{"enable":false,"replica-id":0,"filter-replica-ids":null,"id-buckets":0,"sync-ddl":false},"scheduler":{"type":"table-number","polling-time":-1}},"state":"normal","history":null,"error":null}
--changefeed-id: The ID of the replication task. The format must match the^[a-zA-Z0-9]+(\-[a-zA-Z0-9]+)*$regular expression. If this ID is not specified, TiCDC automatically generates a UUID (the version 4 format) as the ID.--sink-uri: The downstream address of the replication task. Configure--sink-uriaccording to the following format. Currently, the scheme supportsmysql/tidb/kafka/pulsar/s3/local.[scheme]://[userinfo@][host]:[port][/path]?[query_parameters]When a URI contains special characters, you need to process these special characters using URL encoding.
--start-ts: Specifies the starting TSO of thechangefeed. From this TSO, the TiCDC cluster starts pulling data. The default value is the current time.--target-ts: Specifies the ending TSO of thechangefeed. To this TSO, the TiCDC cluster stops pulling data. The default value is empty, which means that TiCDC does not automatically stop pulling data.--sort-engine: Specifies the sorting engine for thechangefeed. Because TiDB and TiKV adopt distributed architectures, TiCDC must sort the data changes before writing them to the sink. This option supportsunified(by default)/memory/file.unified: Whenunifiedis used, TiCDC prefers data sorting in memory. If the memory is insufficient, TiCDC automatically uses the disk to store the temporary data. This is the default value of--sort-enginein TiDB v5.0.memory: Sorts data changes in memory. It is NOT recommended to use it, because memory overflow might occur when a large amount of data is replicated.file: Entirely uses the disk to store the temporary data. This feature is deprecated. It is NOT recommended to use it in any situation.
--sort-dir: Specifies the temporary file directory of the sorting engine. In TiDB v5.0, it is NOT recommended to use this option in the commandcdc cli changefeed create. You are recommended to use this option in the commandcdc serverto set the temporary file directory. The default value of this option is/tmp/cdc_sort. When the unified sorter is enabled, if the default directory/tmp/cdc_sorton the sever is not writable or there is not enough space, you need to manually specify a directory insort-dir. If the directory specified insort-diris not writable,changefeedstops automatically.--config: Specifies the configuration file of thechangefeed.
Configure sink URI with mysql/tidb
Sample configuration:
--sink-uri="mysql://root:123456@127.0.0.1:3306/?worker-count=16&max-txn-row=5000"
The following are descriptions of parameters and parameter values that can be configured for the sink URI with mysql/tidb:
| Parameter/Parameter Value | Description |
|---|---|
root | The username of the downstream database |
123456 | The password of the downstream database |
127.0.0.1 | The IP address of the downstream database |
3306 | The port for the downstream data |
worker-count | The number of SQL statements that can be concurrently executed to the downstream (optional, 16 by default) |
max-txn-row | The size of a transaction batch that can be executed to the downstream (optional, 256 by default) |
ssl-ca | The path of the CA certificate file needed to connect to the downstream MySQL instance (optional) |
ssl-cert | The path of the certificate file needed to connect to the downstream MySQL instance (optional) |
ssl-key | The path of the certificate key file needed to connect to the downstream MySQL instance (optional) |
time-zone | The time zone used when connecting to the downstream MySQL instance, which is effective since v4.0.8. This is an optional parameter. If this parameter is not specified, the time zone of TiCDC service processes is used. If this parameter is set to an empty value, no time zone is specified when TiCDC connects to the downstream MySQL instance and the default time zone of the downstream is used. |
Configure sink URI with kafka
Sample configuration:
--sink-uri="kafka://127.0.0.1:9092/cdc-test?kafka-version=2.4.0&partition-num=6&max-message-bytes=67108864&replication-factor=1"
The following are descriptions of parameters and parameter values that can be configured for the sink URI with kafka:
| Parameter/Parameter Value | Description |
|---|---|
127.0.0.1 | The IP address of the downstream Kafka services |
9092 | The port for the downstream Kafka |
cdc-test | The name of the Kafka topic |
kafka-version | The version of the downstream Kafka (optional, 2.4.0 by default. Currently, the earliest supported Kafka version is 0.11.0.2 and the latest one is 2.7.0. This value needs to be consistent with the actual version of the downstream Kafka.) |
kafka-client-id | Specifies the Kafka client ID of the replication task (optional, TiCDC_sarama_producer_replication ID by default) |
partition-num | The number of the downstream Kafka partitions (Optional. The value must be no greater than the actual number of partitions. If you do not configure this parameter, the partition number is obtained automatically.) |
max-message-bytes | The maximum size of data that is sent to Kafka broker each time (optional, 10MB by default) |
replication-factor | The number of Kafka message replicas that can be saved (optional, 1 by default) |
compression | The compression algorithm used when sending messages (value options are none, lz4, gzip, snappy, and zstd; none by default). |
protocol | The protocol with which messages are output to Kafka. The value options are default, canal, avro, and maxwell (default by default) |
auto-create-topic | Determines whether TiCDC creates the topic automatically when the topic-name passed in does not exist in the Kafka cluster (optional, true by default) |
max-batch-size | New in v4.0.9. If the message protocol supports outputting multiple data changes to one Kafka message, this parameter specifies the maximum number of data changes in one Kafka message. It currently takes effect only when Kafka's protocol is default. It's optional and 16 by default. From v5.0.1 and later versions, the default value has changed from 4096 to 16. |
ca | The path of the CA certificate file needed to connect to the downstream Kafka instance (optional) |
cert | The path of the certificate file needed to connect to the downstream Kafka instance (optional) |
key | The path of the certificate key file needed to connect to the downstream Kafka instance (optional) |
sasl-user | The identity (authcid) of SASL/SCRAM authentication needed to connect to the downstream Kafka instance (optional) |
sasl-password | The password of SASL/SCRAM authentication needed to connect to the downstream Kafka instance (optional) |
sasl-mechanism | The name of SASL/SCRAM authentication needed to connect to the downstream Kafka instance (optional) |
Integrate TiCDC with Kafka Connect (Confluent Platform)
Sample configuration:
--sink-uri="kafka://127.0.0.1:9092/cdc-test?kafka-version=2.4.0&protocol=avro&partition-num=6&max-message-bytes=67108864&replication-factor=1"
--opts registry="http://127.0.0.1:8081"
To use the data connectors provided by Confluent to stream data to relational or non-relational databases, you should use the avro protocol and provide a URL for Confluent Schema Registry in opts. Note that the avro protocol and Confluent integration are experimental.
For detailed integration guide, see Quick Start Guide on Integrating TiDB with Confluent Platform.
Configure sink URI with pulsar
Sample configuration:
--sink-uri="pulsar://127.0.0.1:6650/cdc-test?connectionTimeout=2s"
The following are descriptions of parameters that can be configured for the sink URI with pulsar:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
connectionTimeout | The timeout for establishing a connection to the downstream Pulsar, which is optional and defaults to 30 (seconds) |
operationTimeout | The timeout for performing an operation on the downstream Pulsar, which is optional and defaults to 30 (seconds) |
tlsTrustCertsFilePath | The path of the CA certificate file needed to connect to the downstream Pulsar instance (optional) |
tlsAllowInsecureConnection | Determines whether to allow unencrypted connection after TLS is enabled (optional) |
tlsValidateHostname | Determines whether to verify the host name of the certificate from the downstream Pulsar (optional) |
maxConnectionsPerBroker | The maximum number of connections allowed to a single downstream Pulsar broker, which is optional and defaults to 1 |
auth.tls | Uses the TLS mode to verify the downstream Pulsar (optional). For example, auth=tls&auth.tlsCertFile=/path/to/cert&auth.tlsKeyFile=/path/to/key. |
auth.token | Uses the token mode to verify the downstream Pulsar (optional). For example, auth=token&auth.token=secret-token or auth=token&auth.file=path/to/secret-token-file. |
name | The name of Pulsar producer in TiCDC (optional) |
maxPendingMessages | Sets the maximum size of the pending message queue, which is optional and defaults to 1000. For example, pending for the confirmation message from Pulsar. |
disableBatching | Disables automatically sending messages in batches (optional) |
batchingMaxPublishDelay | Sets the duration within which the messages sent are batched (default: 10ms) |
compressionType | Sets the compression algorithm used for sending messages (optional). The value options are NONE,LZ4, ZLIB, and ZSTD. (NONE by default) |
hashingScheme | The hash algorithm used for choosing the partition to which a message is sent (optional). The value options are JavaStringHash (default) and Murmur3. |
properties.* | The customized properties added to the Pulsar producer in TiCDC (optional). For example, properties.location=Hangzhou. |
For more parameters of Pulsar, see pulsar-client-go ClientOptions and pulsar-client-go ProducerOptions.
Use the task configuration file
For more replication configuration (for example, specify replicating a single table), see Task configuration file.
You can use a configuration file to create a replication task in the following way:
cdc cli changefeed create --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --sink-uri="mysql://root:123456@127.0.0.1:3306/" --config changefeed.toml
In the command above, changefeed.toml is the configuration file for the replication task.
Query the replication task list
Execute the following command to query the replication task list:
cdc cli changefeed list --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379
[{
"id": "simple-replication-task",
"summary": {
"state": "normal",
"tso": 417886179132964865,
"checkpoint": "2020-07-07 16:07:44.881",
"error": null
}
}]
checkpointindicates that TiCDC has already replicated data before this time point to the downstream.stateindicates the state of the replication task.normal: The replication task runs normally.stopped: The replication task is stopped (manually paused or stopped by an error).removed: The replication task is removed. Tasks of this state are displayed only when you have specified the--alloption. To see these tasks when this option is not specified, execute thechangefeed querycommand.finished: The replication task is finished (data is replicated to thetarget-ts). Tasks of this state are displayed only when you have specified the--alloption. To see these tasks when this option is not specified, execute thechangefeed querycommand.
Query a specific replication task
To query a specific replication task, execute the changefeed query command. The query result includes the task information and the task state. You can specify the --simple or -s argument to simplify the query result that will only include the basic replication state and the checkpoint information. If you do not specify this argument, detailed task configuration, replication states, and replication table information are output.
cdc cli changefeed query -s --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id=simple-replication-task
{
"state": "normal",
"tso": 419035700154597378,
"checkpoint": "2020-08-27 10:12:19.579",
"error": null
}
In the command and result above:
stateis the replication state of the currentchangefeed. Each state must be consistent with the state inchangefeed list.tsorepresents the largest transaction TSO in the currentchangefeedthat has been successfully replicated to the downstream.checkpointrepresents the corresponding time of the largest transaction TSO in the currentchangefeedthat has been successfully replicated to the downstream.errorrecords whether an error has occurred in the currentchangefeed.
cdc cli changefeed query --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id=simple-replication-task
{
"info": {
"sink-uri": "mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/?max-txn-row=20\u0026worker-number=4",
"opts": {},
"create-time": "2020-08-27T10:33:41.687983832+08:00",
"start-ts": 419036036249681921,
"target-ts": 0,
"admin-job-type": 0,
"sort-engine": "unified",
"sort-dir": ".",
"config": {
"case-sensitive": true,
"enable-old-value": false,
"filter": {
"rules": [
"*.*"
],
"ignore-txn-start-ts": null,
"ddl-allow-list": null
},
"mounter": {
"worker-num": 16
},
"sink": {
"dispatchers": null,
"protocol": "default"
},
"cyclic-replication": {
"enable": false,
"replica-id": 0,
"filter-replica-ids": null,
"id-buckets": 0,
"sync-ddl": false
},
"scheduler": {
"type": "table-number",
"polling-time": -1
}
},
"state": "normal",
"history": null,
"error": null
},
"status": {
"resolved-ts": 419036036249681921,
"checkpoint-ts": 419036036249681921,
"admin-job-type": 0
},
"count": 0,
"task-status": [
{
"capture-id": "97173367-75dc-490c-ae2d-4e990f90da0f",
"status": {
"tables": {
"47": {
"start-ts": 419036036249681921,
"mark-table-id": 0
}
},
"operation": null,
"admin-job-type": 0
}
}
]
}
In the command and result above:
infois the replication configuration of the queriedchangefeed.statusis the replication state of the queriedchangefeed.resolved-ts: The largest transactionTSin the currentchangefeed. Note that thisTShas been successfully sent from TiKV to TiCDC.checkpoint-ts: The largest transactionTSin the currentchangefeed. Note that thisTShas been successfully written to the downstream.admin-job-type: The status of achangefeed:0: The state is normal.1: The task is paused. When the task is paused, all replicatedprocessors exit. The configuration and the replication status of the task are retained, so you can resume the task fromcheckpiont-ts.2: The task is resumed. The replication task resumes fromcheckpoint-ts.3: The task is removed. When the task is removed, all replicatedprocessors are ended, and the configuration information of the replication task is cleared up. Only the replication status is retained for later queries.
task-statusindicates the state of each replication sub-task in the queriedchangefeed.
Pause a replication task
Execute the following command to pause a replication task:
cdc cli changefeed pause --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id simple-replication-task
In the above command:
--changefeed-id=uuidrepresents the ID of thechangefeedthat corresponds to the replication task you want to pause.
Resume a replication task
Execute the following command to resume a paused replication task:
cdc cli changefeed resume --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id simple-replication-task
In the above command:
--changefeed-id=uuidrepresents the ID of thechangefeedthat corresponds to the replication task you want to resume.
Remove a replication task
Execute the following command to remove a replication task:
cdc cli changefeed remove --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id simple-replication-task
In the above command:
--changefeed-id=uuidrepresents the ID of thechangefeedthat corresponds to the replication task you want to remove.
After the replication task is removed, the state information of the task will be retained for 24 hours, mainly used for recording the replication checkpoint. Within this 24 hours, you cannot create a replication task of the same name.
If you want to completely remove the task information, you can specify the --force or -f argument in the command. Then all information of the changefeed will be removed, and you can immediately create a changefeed of the same name.
cdc cli changefeed remove --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id simple-replication-task --force
Update task configuration
Starting from v4.0.4, TiCDC supports modifying the configuration of the replication task (not dynamically). To modify the changefeed configuration, pause the task, modify the configuration, and then resume the task.
cdc cli changefeed pause -c test-cf --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379
cdc cli changefeed update -c test-cf --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --sink-uri="mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/?max-txn-row=20&worker-number=8" --config=changefeed.toml
cdc cli changefeed resume -c test-cf --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379
Currently, you can modify the following configuration items:
sink-uriof thechangefeed.- The
changefeedconfiguration file and all configuration items in the file. - Whether to use the file sorting feature and the sorting directory.
- The
target-tsof thechangefeed.
Manage processing units of replication sub-tasks (processor)
Query the
processorlist:cdc cli processor list --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379[ { "id": "9f84ff74-abf9-407f-a6e2-56aa35b33888", "capture-id": "b293999a-4168-4988-a4f4-35d9589b226b", "changefeed-id": "simple-replication-task" } ]Query a specific
changefeedwhich corresponds to the status of a specific replication task:cdc cli processor query --pd=http://10.0.10.25:2379 --changefeed-id=simple-replication-task --capture-id=b293999a-4168-4988-a4f4-35d9589b226b{ "status": { "tables": { "56": { # ID of the replication table, corresponding to tidb_table_id of a table in TiDB "start-ts": 417474117955485702, "mark-table-id": 0 # ID of mark tables in the cyclic replication, corresponding to tidb_table_id of mark tables in TiDB } }, "operation": null, "admin-job-type": 0 }, "position": { "checkpoint-ts": 417474143881789441, "resolved-ts": 417474143881789441, "count": 0 } }In the command above:
status.tables: Each key number represents the ID of the replication table, corresponding totidb_table_idof a table in TiDB.mark-table-id: The ID of mark tables in the cyclic replication, corresponding totidb_table_idof mark tables in TiDB.resolved-ts: The largest TSO among the sorted data in the current processor.checkpoint-ts: The largest TSO that has been successfully written to the downstream in the current processor.
Use HTTP interface to manage cluster status and data replication task
Currently, the HTTP interface provides some basic features for query and maintenance.
In the following examples, suppose that the TiCDC server listens on 127.0.0.1, and the port is 8300 (you can specify the IP and port in --addr=ip:port when starting the TiCDC server).
Get the TiCDC server status
Use the following command to get the TiCDC server status:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8300/status
{
"version": "0.0.1",
"git_hash": "863f8ea889b144244ff53593a45c47ad22d37396",
"id": "6d92386a-73fc-43f3-89de-4e337a42b766", # capture id
"pid": 12102 # cdc server pid
}
Evict the owner node
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8300/capture/owner/resign
The above command takes effect only for requesting on the owner node.
{
"status": true,
"message": ""
}
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8301/capture/owner/resign
For nodes other than owner nodes, executing the above command will return the following error.
election: not leader
Manually schedule a table to other node
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8300/capture/owner/move_table -d 'cf-id=cf060953-036c-4f31-899f-5afa0ad0c2f9&target-cp-id=6f19a6d9-0f8c-4dc9-b299-3ba7c0f216f5&table-id=49'
Parameter description:
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
cf-id | The ID of the changefeed to be scheduled |
target-cp-id | The ID of the target capture |
table-id | The ID of the table to be scheduled |
For nodes other than owner nodes, executing the above command will return the following error.
{
"status": true,
"message": ""
}
Dynamically change the log level of TiCDC server
curl -X POST -d '"debug"' http://127.0.0.1:8301/admin/log
In the command above, the POST parameter indicates the new log level. The zap-provided log level options are supported: "debug", "info", "warn", "error", "dpanic", "panic", and "fatal". This interface parameter is JSON-encoded and you need to pay attention to the use of quotation marks. For example: '"debug"'.
Task configuration file
This section introduces the configuration of a replication task.
# Specifies whether the database names and tables in the configuration file are case-sensitive.
# The default value is true.
# This configuration item affects configurations related to filter and sink.
case-sensitive = true
# Specifies whether to output the old value. New in v4.0.5. Since v5.0, the default value is `true`.
enable-old-value = true
[filter]
# Ignores the transaction of specified start_ts.
ignore-txn-start-ts = [1, 2]
# Filter rules.
# Filter syntax: https://docs.pingcap.com/tidb/stable/table-filter#syntax.
rules = ['*.*', '!test.*']
[mounter]
# mounter thread counts, which is used to decode the TiKV output data.
worker-num = 16
[sink]
# For the sink of MQ type, you can use dispatchers to configure the event dispatcher.
# Supports four dispatchers: default, ts, rowid, and table.
# The dispatcher rules are as follows:
# - default: When multiple unique indexes (including the primary key) exist or the Old Value feature is enabled, events are dispatched in the table mode. When only one unique index (or the primary key) exists, events are dispatched in the rowid mode.
# - ts: Use the commitTs of the row change to create Hash and dispatch events.
# - index-value: Use the value of the primary key or the unique index of the table to create Hash and dispatch events.
# - table: Use the schema name of the table and the table name to create Hash and dispatch events.
# The matching syntax of matcher is the same as the filter rule syntax.
dispatchers = [
{matcher = ['test1.*', 'test2.*'], dispatcher = "ts"},
{matcher = ['test3.*', 'test4.*'], dispatcher = "rowid"},
]
# For the sink of MQ type, you can specify the protocol format of the message.
# Currently four protocols are supported: default, canal, avro, and maxwell. The default protocol is TiCDC Open Protocol.
protocol = "default"
[cyclic-replication]
# Whether to enable cyclic replication.
enable = false
# The replica ID of the current TiCDC.
replica-id = 1
# The replica ID to be filtered.
filter-replica-ids = [2,3]
# Whether to replicate DDL statements.
sync-ddl = true
Notes for compatibility
- In TiCDC v4.0.0,
ignore-txn-commit-tsis removed andignore-txn-start-tsis added, which uses start_ts to filter transactions. - In TiCDC v4.0.2,
db-dbs/db-tables/ignore-dbs/ignore-tablesare removed andrulesis added, which uses new filter rules for databases and tables. For detailed filter syntax, see Table Filter.
Cyclic replication
The cyclic replication feature supports replicating data across multiple independent TiDB clusters. For example, TiDB clusters A, cluster B, and cluster C all have a table named test.user_data and write data into this table respectively. With the cyclic replication feature, the data written into test.user_data in one cluster can be replicated to the other two clusters, so that the test.user_data table in the three clusters is consistent with each other.
Usage example
Enable cyclic replication in the three clusters of A, B, and C. Two TiCDC clusters are used for the replication from cluster A to cluster B. Among the three clusters, DDL statements enters cluster A first.
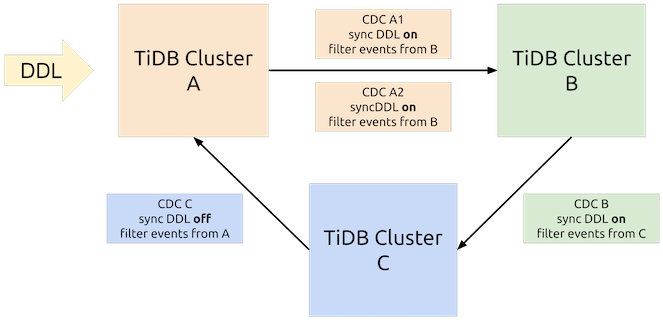
To use the cyclic replication feature, you need to configure the following parameters for the replication task upon the task creation.
--cyclic-replica-id: Specifies the data source (to be written) ID of the upstream cluster. Each cluster ID must be unique.--cyclic-filter-replica-ids: Specifies the data source ID to be filtered, which is usually the downstream cluster ID.--cyclic-sync-ddl: Determines whether to replicate DDL statements to the downstream.
To create a cyclic replication task, take the following steps:
Enable the TiCDC component in TiDB cluster A, cluster B, and cluster C.
# Enables TiCDC in cluster A. cdc server \ --pd="http://${PD_A_HOST}:${PD_A_PORT}" \ --log-file=ticdc_1.log \ --addr=0.0.0.0:8301 \ --advertise-addr=127.0.0.1:8301 # Enables TiCDC in cluster B. cdc server \ --pd="http://${PD_B_HOST}:${PD_B_PORT}" \ --log-file=ticdc_2.log \ --addr=0.0.0.0:8301 \ --advertise-addr=127.0.0.1:8301 # Enables TiCDC in cluster C. cdc server \ --pd="http://${PD_C_HOST}:${PD_C_PORT}" \ --log-file=ticdc_3.log \ --addr=0.0.0.0:8301 \ --advertise-addr=127.0.0.1:8301Create the mark tables used for the cyclic replication in cluster A, cluster B, and cluster C.
# Creates mark tables in cluster A. cdc cli changefeed cyclic create-marktables \ --cyclic-upstream-dsn="root@tcp(${TIDB_A_HOST}:${TIDB_A_PORT})/" \ --pd="http://${PD_A_HOST}:${PD_A_PORT}" # Creates mark tables in cluster B. cdc cli changefeed cyclic create-marktables \ --cyclic-upstream-dsn="root@tcp(${TIDB_B_HOST}:${TIDB_B_PORT})/" \ --pd="http://${PD_B_HOST}:${PD_B_PORT}" # Creates mark tables in cluster C. cdc cli changefeed cyclic create-marktables \ --cyclic-upstream-dsn="root@tcp(${TIDB_C_HOST}:${TIDB_C_PORT})/" \ --pd="http://${PD_C_HOST}:${PD_C_PORT}"Create the cyclic replication task in cluster A, cluster B, and cluster C.
# Creates the cyclic replication task in cluster A. cdc cli changefeed create \ --sink-uri="mysql://root@${TiDB_B_HOST}/" \ --pd="http://${PD_A_HOST}:${PD_A_PORT}" \ --cyclic-replica-id 1 \ --cyclic-filter-replica-ids 2 \ --cyclic-sync-ddl true # Creates the cyclic replication task in cluster B. cdc cli changefeed create \ --sink-uri="mysql://root@${TiDB_C_HOST}/" \ --pd="http://${PD_B_HOST}:${PD_B_PORT}" \ --cyclic-replica-id 2 \ --cyclic-filter-replica-ids 3 \ --cyclic-sync-ddl true # Creates the cyclic replication task in cluster C. cdc cli changefeed create \ --sink-uri="mysql://root@${TiDB_A_HOST}/" \ --pd="http://${PD_C_HOST}:${PD_C_PORT}" \ --cyclic-replica-id 3 \ --cyclic-filter-replica-ids 1 \ --cyclic-sync-ddl false
Usage notes
- Before creating the cyclic replication task, you must execute
cdc cli changefeed cyclic create-marktablesto create the mark tables for the cyclic replication. - The name of the table with cyclic replication enabled must match the
^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+$regular expression. - Before creating the cyclic replication task, the tables for the task must be created.
- After enabling the cyclic replication, you cannot create a table that will be replicated by the cyclic replication task.
- To avoid causing errors, do not execute DDL statements such as
ADD COLUMN/DROP COLUMNwhen data is written into multiple clusters at the same time. - To perform online DDL operations, ensure the following requirements are met:
- The application is compatible with the table schema before and after executing the DDL operations.
- The TiCDC components of multiple clusters form a one-way DDL replication chain, which is not cyclic. For example, in the example above, only the TiCDC component of cluster C disables
sync-ddl. - DDL operations must be performed on the cluster that is the starting point of the one-way DDL replication chain, such as cluster A in the example above.
Output the historical value of a Row Changed Event New in v4.0.5
In the default configuration, the Row Changed Event of TiCDC Open Protocol output in a replication task only contains the changed value, not the value before the change. Therefore, the output value cannot be used by the consumer ends of TiCDC Open Protocol as the historical value of a Row Changed Event.
Starting from v4.0.5, TiCDC supports outputting the historical value of a Row Changed Event. To enable this feature, specify the following configuration in the changefeed configuration file at the root level:
enable-old-value = true
This feature is enabled by default since v5.0. To learn the output format of the TiCDC Open Protocol after this feature is enabled, see TiCDC Open Protocol - Row Changed Event.
Replicate tables with the new framework for collations enabled
Starting from v4.0.15, v5.0.4, v5.1.1 and v5.2.0, TiCDC supports tables that have enabled new framework for collations.
Replicate tables without a valid index
Since v4.0.8, TiCDC supports replicating tables that have no valid index by modifying the task configuration. To enable this feature, configure in the changefeed configuration file as follows:
enable-old-value = true
force-replicate = true
Unified Sorter
Unified sorter is the sorting engine in TiCDC. This feature is enabled by default in TiDB v5.0.x. It can mitigate OOM problems caused by the following scenarios:
- The data replication task in TiCDC is paused for a long time, during which a large amount of incremental data is accumulated and needs to be replicated.
- The data replication task is started from an early timestamp so it becomes necessary to replicate a large amount of incremental data.
For the changefeeds created using cdc cli after v4.0.13, Unified Sorter is enabled by default; for the changefeeds that have existed before v4.0.13, the previous configuration is used.
To check whether or not the Unified Sorter feature is enabled on a changefeed, you can execute the following example command (assuming the IP address of the PD instance is http://10.0.10.25:2379):
cdc cli --pd="http://10.0.10.25:2379" changefeed query --changefeed-id=simple-replication-task | grep 'sort-engine'
In the output of the above command, if the value of sort-engine is "unified", it means that Unified Sorter is enabled on the changefeed.