TiKV Overview
TiKV is a distributed and transactional key-value database, which provides transactional APIs with ACID compliance. With the implementation of the Raft consensus algorithm and consensus state stored in RocksDB, TiKV guarantees data consistency between multiple replicas and high availability. As the storage layer of the TiDB distributed database, TiKV provides the read and write service, and persist the written data from applications. It also stores the statistics data of the TiDB cluster.
Architecture Overview
TiKV implements the multi-raft-group replica mechanism based on the design of Google Spanner. A Region is a basic unit of the key-value data movement and refers to a data range in a Store. Each Region is replicated to multiple nodes. These multiple replicas form a Raft group. A replica of a Region is called a Peer. Typically there are 3 peers in a Region. One of them is the leader, which provides the read and write services. The PD component balances all the Regions automatically to guarantee that the read and write throughput is balanced among all the nodes in the TiKV cluster. With PD and carefully designed Raft groups, TiKV excels in horizontal scalability and can easily scale to store more than 100 TBs of data.
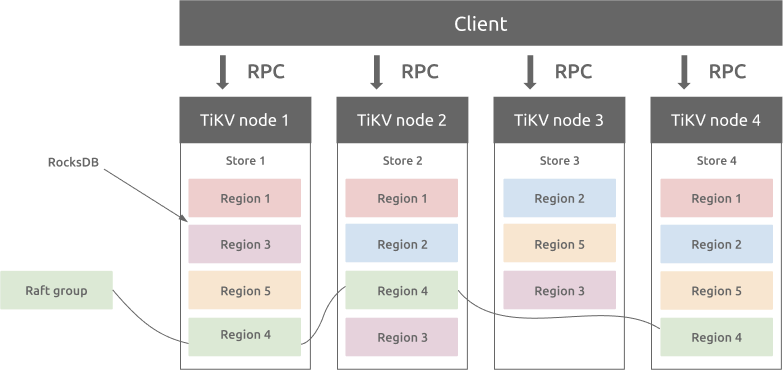
Region and RocksDB
There is a RocksDB database within each Store and it stores data into the local disk. All the Region data are stored in the same RocksDB instance in each Store. All the logs used for the Raft consensus algorithm is stored in another RocksDB instance in each Store. This is because the performance of sequential I/O is better than random I/O. With different RocksDB instances storing raft logs and Region data, TiKV combines all the data write operations of raft logs and TiKV Regions into one I/O operation to improve the performance.
Region and Raft Consensus Algorithm
Data consistency between replicas of a Region is guaranteed by the Raft Consensus Algorithm. Only the leader of the Region can provide the writing service, and only when the data is written to the majority of replicas of a Region, the write operation succeeds.
When the size of a Region exceeds a threshold, which is 144 MB by default, TiKV splits it to two or more Regions. This operation guarantees the size of all the Regions in the cluster is nearly the same, which helps the PD component to balance Regions among nodes in a TiKV cluster. When the size of a Region is smaller than the threshold, TiKV merges the two smaller adjacent Regions into one Region.
When PD moves a replica from one TiKV node to another, it firstly adds a Learner replica on the target node, after the data in the Learner replica is nearly the same as that in the Leader replica, PD changes it to a Follower replica and removes the Follower replica on the source node.
Moving Leader replica from one node to another has a similar mechanism. The difference is that after the Learner replica becomes the Follower replica, there is a "Leader Transfer" operation in which the Follower replica actively proposes an election to elect itself as the Leader. Finally, the new Leader removes the old Leader replica in the source node.
Distributed Transaction
TiKV supports distributed transactions. Users (or TiDB) can write multiple key-value pairs without worrying about whether they belong to the same Region. TiKV uses two-phase commit to achieve ACID constraints. See TiDB Optimistic Transaction Model for details.
TiKV Coprocessor
TiDB pushes some data computation logic to TiKV Coprocessor. TiKV Coprocessor processes the computation for each Region. Each request sent to TiKV Coprocessor only involves the data of one Region.