TiFlash Overview
TiFlash is the key component that makes TiDB essentially an Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing (HTAP) database. As a columnar storage extension of TiKV, TiFlash provides both good isolation level and strong consistency guarantee.
In TiFlash, the columnar replicas are asynchronously replicated according to the Raft Learner consensus algorithm. When these replicas are read, the Snapshot Isolation level of consistency is achieved by validating Raft index and multi-version concurrency control (MVCC).
Architecture
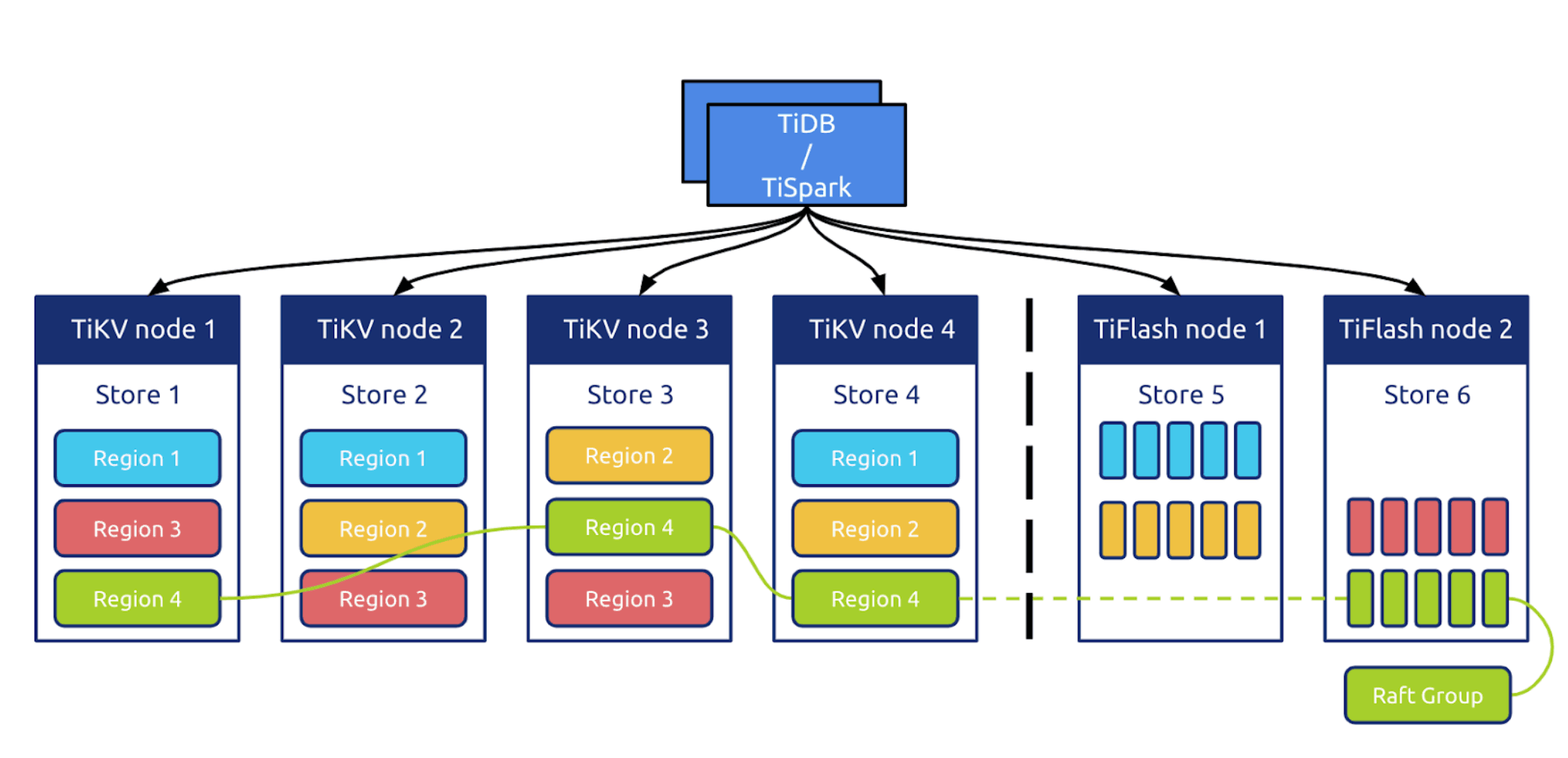
The above figure is the architecture of TiDB in its HTAP form, including TiFlash nodes.
TiFlash provides the columnar storage, with a layer of coprocessors efficiently implemented by ClickHouse. Similar to TiKV, TiFlash also has a Multi-Raft system, which supports replicating and distributing data in the unit of Region (see Data Storage for details).
TiFlash conducts real-time replication of data in the TiKV nodes at a low cost that does not block writes in TiKV. Meanwhile, it provides the same read consistency as in TiKV and ensures that the latest data is read. The Region replica in TiFlash is logically identical to those in TiKV, and is split and merged along with the Leader replica in TiKV at the same time.
TiFlash is compatible with both TiDB and TiSpark, which enables you to freely choose between these two computing engines.
It is recommended that you deploy TiFlash in different nodes from TiKV to ensure workload isolation. It is also acceptable to deploy TiFlash and TiKV in the same node if no business isolation is required.
Currently, data cannot be written directly into TiFlash. You need to write data in TiKV and then replicate it to TiFlash, because it connects to the TiDB cluster as a Learner role. TiFlash supports data replication in the unit of table, but no data is replicated by default after deployment. To replicate data of a specified table, see Create TiFlash replicas for tables.
TiFlash has three components: the columnar storage module, tiflash proxy, and pd buddy. tiflash proxy is responsible for the communication using the Multi-Raft consensus algorithm. pd buddy works with PD to replicate data from TiKV to TiFlash in the unit of table.
When TiDB receives the DDL command to create replicas in TiFlash, the pd buddy component acquires the information of the table to be replicated via the status port of TiDB, and sends the information to PD. Then PD performs the corresponding data scheduling according to the information provided by pd buddy.
Key features
TiFlash has the following key features:
Asynchronous replication
The replica in TiFlash is asynchronously replicated as a special role, Raft Learner. This means when the TiFlash node is down or high network latency occurs, applications in TiKV can still proceed normally.
This replication mechanism inherits two advantages of TiKV: automatic load balancing and high availability.
- TiFlash does not rely on additional replication channels, but directly receives data from TiKV in a many-to-many manner.
- As long as the data is not lost in TiKV, you can restore the replica in TiFlash at any time.
Consistency
TiFlash provides the same Snapshot Isolation level of consistency as TiKV, and ensures that the latest data is read, which means that you can read the data previously written in TiKV. Such consistency is achieved by validating the data replication progress.
Every time TiFlash receives a read request, the Region replica sends a progress validation request (a lightweight RPC request) to the Leader replica. TiFlash performs the read operation only after the current replication progress includes the data covered by the timestamp of the read request.
Intelligent choice
TiDB can automatically choose to use TiFlash (column-wise) or TiKV (row-wise), or use both of them in one query to ensure the best performance.
This selection mechanism is similar to that of TiDB which chooses different indexes to execute query. TiDB optimizer makes the appropriate choice based on statistics of the read cost.
Computing acceleration
TiFlash accelerates the computing of TiDB in two ways:
- The columnar storage engine is more efficient in performing read operation.
- TiFlash shares part of the computing workload of TiDB.
TiFlash shares the computing workload in the same way as the TiKV Coprocessor does: TiDB pushes down the computing that can be completed in the storage layer. Whether the computing can be pushed down depends on the support of TiFlash. For details, see Supported pushdown calculations.