TiDB Lightning Web Interface
TiDB Lightning provides a webpage for viewing the import progress and performing some simple task management. This is called the server mode.
To enable server mode, either start tidb-lightning with the --server-mode flag
./tidb-lightning --server-mode --status-addr :8289
or set the lightning.server-mode setting in the configuration file.
[lightning]
server-mode = true
status-addr = ':8289'
After TiDB Lightning is launched, visit http://127.0.0.1:8289 to control the program (the actual URL depends on the status-addr setting).
In server mode, TiDB Lightning does not start running immediately. Rather, users submit (multiple) tasks via the web interface to import data.
Front page
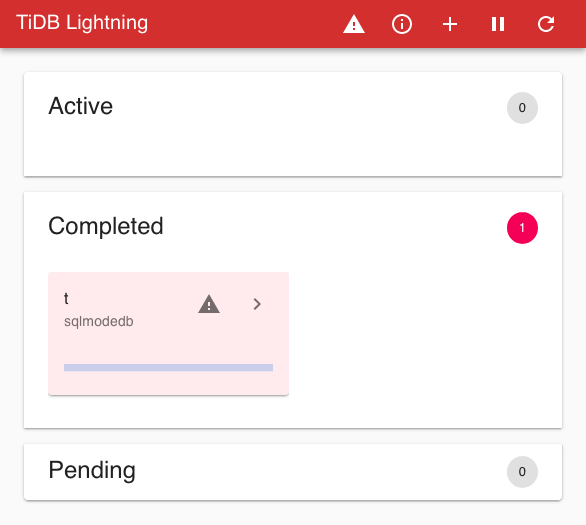
Functions of the title bar, from left to right:
| Icon | Function |
|---|---|
| "TiDB Lightning" | Click to go back to the front page |
| ⚠ | Display any error message from previous task |
| ⓘ | List current and queued tasks; a badge may appear here to indicate number of queued tasks |
| + | Submit a task |
| ⏸/▶ | Pause/resume current execution |
| ⟳ | Configure auto-refresh of the web page |
Three panels below the title bar show all tables in different states:
- Active: these tables are currently being imported
- Completed: these tables have been imported successfully or failed
- Pending: these tables are not yet processed
Each panel contains cards describing the status of the table.
Submit task
Click the + button on the title bar to submit a task.
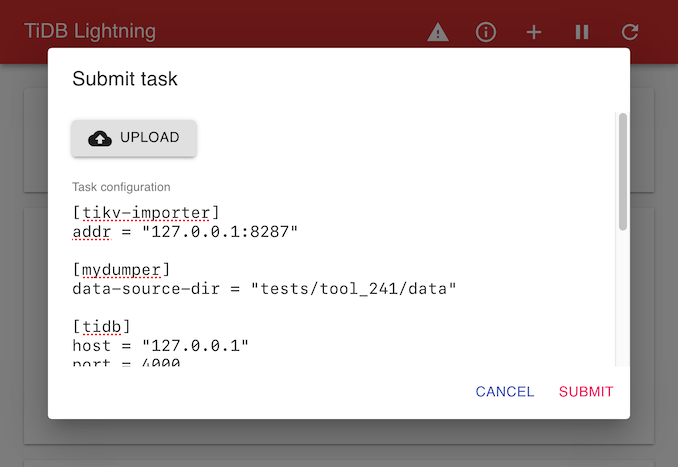
Tasks are TOML files described as task configurations. One could also open a local TOML file by clicking UPLOAD.
Click SUBMIT to run the task. If a task is already running, the new task will be queued and executed after the current task succeeds.
Table progress
Click the > button of a table card on the front page to view the detailed progress of a table.
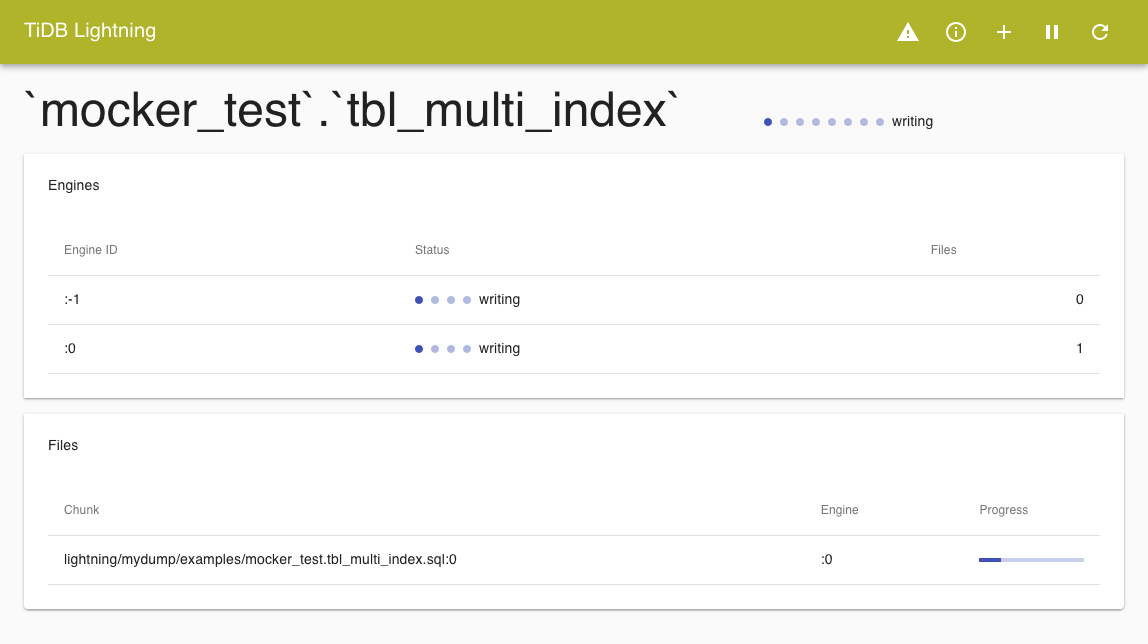
The page shows the import progress of every engine and data files associated with the table.
Click TiDB Lightning on the title bar to go back to the front page.
Task management
Click the ⓘ button on the title bar to manage the current and queued tasks.
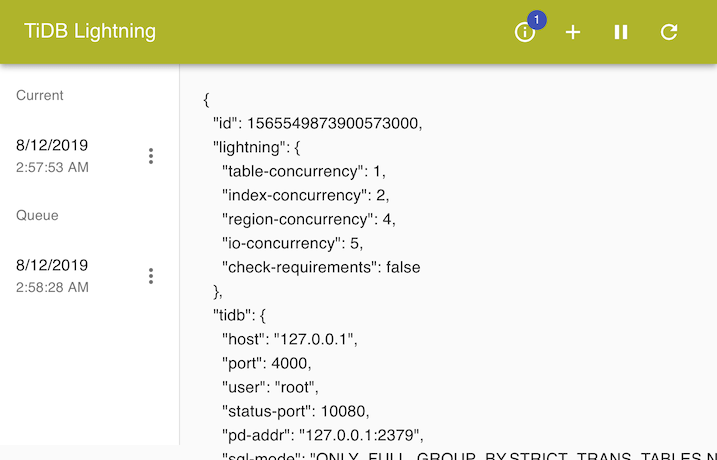
Each task is labeled by the time it was submitted. Clicking the task would show the configuration formatted as JSON.
Manage tasks by clicking the ⋮ button next to a task. You can stop a task immediately, or reorder queued tasks.