TiDB Binlog Cluster Overview
This document introduces the architecture and the deployment of the cluster version of TiDB Binlog.
TiDB Binlog is a tool used to collect binlog data from TiDB and provide near real-time backup and replication to downstream platforms.
TiDB Binlog has the following features:
- Data replication: replicate the data in the TiDB cluster to other databases
- Real-time backup and restoration: back up the data in the TiDB cluster and restore the TiDB cluster when the cluster fails
TiDB Binlog architecture
The TiDB Binlog architecture is as follows:
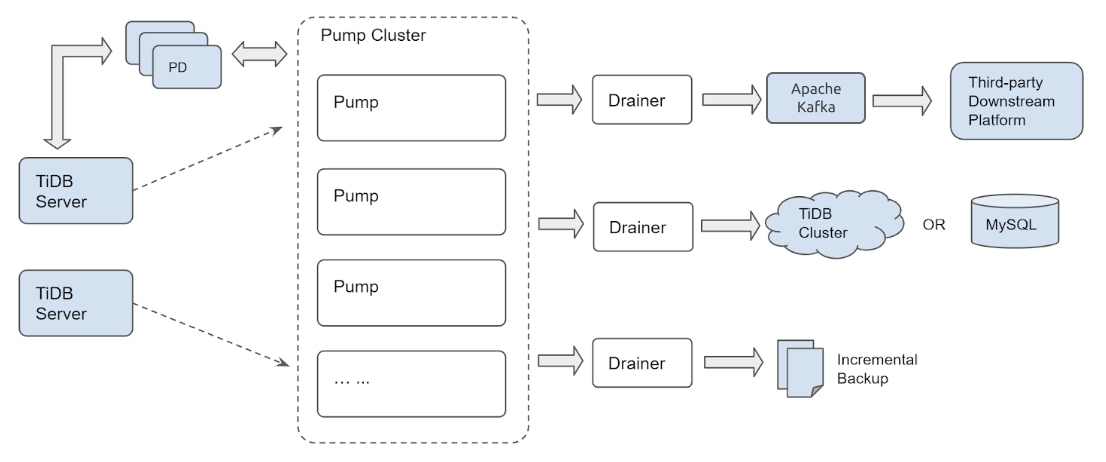
The TiDB Binlog cluster is composed of Pump and Drainer.
Pump
Pump is used to record the binlogs generated in TiDB, sort the binlogs based on the commit time of the transaction, and send binlogs to Drainer for consumption.
Drainer
Drainer collects and merges binlogs from each Pump, converts the binlog to SQL or data of a specific format, and replicates the data to a specific downstream platform.
binlogctl guide
binlogctl is an operations tool for TiDB Binlog with the following features:
- Obtaining the current
tsoof TiDB cluster - Checking the Pump/Drainer state
- Modifying the Pump/Drainer state
- Pausing or closing Pump/Drainer
Main features
- Multiple Pumps form a cluster which can scale out horizontally
- TiDB uses the built-in Pump Client to send the binlog to each Pump
- Pump stores binlogs and sends the binlogs to Drainer in order
- Drainer reads binlogs of each Pump, merges and sorts the binlogs, and sends the binlogs downstream
- Drainer supports relay log. By the relay log, Drainer ensures that the downstream clusters are in a consistent state.
Notes
You need to use TiDB v2.0.8-binlog, v2.1.0-rc.5 or a later version. Older versions of TiDB cluster are not compatible with the cluster version of TiDB Binlog.
Drainer supports replicating binlogs to MySQL, TiDB, Kafka or local files. If you need to replicate binlogs to other Drainer unsuppored destinations, you can set Drainer to replicate the binlog to Kafka and read the data in Kafka for customized processing according to binlog consumer protocol. See Binlog Consumer Client User Guide.
To use TiDB Binlog for recovering incremental data, set the config
db-typetofile(local files in the proto buffer format). Drainer converts the binlog to data in the specified proto buffer format and writes the data to local files. In this way, you can use Reparo to recover data incrementally.Pay attention to the value of
db-type:- If your TiDB version is earlier than 2.1.9, set
db-type="pb". - If your TiDB version is 2.1.9 or later, set
db-type="file"ordb-type="pb".
- If your TiDB version is earlier than 2.1.9, set
If the downstream is MySQL, MariaDB, or another TiDB cluster, you can use sync-diff-inspector to verify the data after data replication.