TiDB Data Migration
TiDB Data Migration (DM) is an integrated data migration task management platform, which supports the full data migration and the incremental data replication from MySQL-compatible databases (such as MySQL, MariaDB, and Aurora MySQL) into TiDB. DM can help simplify the data migration process and reduce the operation cost of data migration.
DM versions
The stable versions of DM include v1.0, v2.0, and v5.3. It is recommended to use DM v5.3 (the latest stable version of DM) and not recommended to use v1.0 (the earliest stable version of DM).
Currently, the DM documentation is independent of the TiDB documentation. To access the DM documentation, click one of the following links:
Basic features
This section describes the basic data migration features provided by DM.
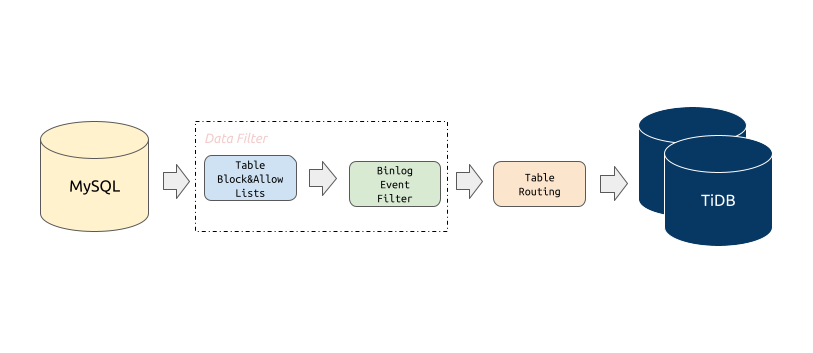
Block and allow lists migration at the schema and table levels
The block and allow lists filtering rule is similar to the replication-rules-db/replication-rules-table feature of MySQL, which can be used to filter or replicate all operations of some databases only or some tables only.
Binlog event filtering
The binlog event filtering feature means that DM can filter certain types of SQL statements from certain tables in the source database. For example, you can filter all INSERT statements in the table test.sbtest or filter all TRUNCATE TABLE statements in the schema test.
Schema and table routing
The schema and table routing feature means that DM can migrate a certain table of the source database to the specified table in the downstream. For example, you can migrate the table structure and data from the table test.sbtest1 in the source database to the table test.sbtest2 in TiDB. This is also a core feature for merging and migrating sharded databases and tables.
Advanced features
Shard merge and migration
DM supports merging and migrating the original sharded instances and tables from the source databases into TiDB, but with some restrictions. For details, see Sharding DDL usage restrictions in the pessimistic mode and Sharding DDL usage restrictions in the optimistic mode.
Optimization for third-party online-schema-change tools in the migration process
In the MySQL ecosystem, tools such as gh-ost and pt-osc are widely used. DM provides support for these tools to avoid migrating unnecessary intermediate data. For details, see Online DDL Tools
Filter certain row changes using SQL expressions
In the phase of incremental replication, DM supports the configuration of SQL expressions to filter out certain row changes, which lets you replicate the data with a greater granularity. For more information, refer to Filter Certain Row Changes Using SQL Expressions.
Usage restrictions
Before using the DM tool, note the following restrictions:
Database version requirements
MySQL version > 5.5
MariaDB version >= 10.1.2
DDL syntax compatibility
Currently, TiDB is not compatible with all the DDL statements that MySQL supports. Because DM uses the TiDB parser to process DDL statements, it only supports the DDL syntax supported by the TiDB parser. For details, see MySQL Compatibility.
DM reports an error when it encounters an incompatible DDL statement. To solve this error, you need to manually handle it using dmctl, either skipping this DDL statement or replacing it with a specified DDL statement(s). For details, see Skip or replace abnormal SQL statements.
Sharding merge with conflicts
If conflict exists between sharded tables, solve the conflict by referring to handling conflicts of auto-increment primary key. Otherwise, data migration is not supported. Conflicting data can cover each other and cause data loss.
For other sharding DDL migration restrictions, see Sharding DDL usage restrictions in the pessimistic mode and Sharding DDL usage restrictions in the optimistic mode.
Switch of MySQL instances for data sources
When DM-worker connects the upstream MySQL instance via a virtual IP (VIP), if you switch the VIP connection to another MySQL instance, DM might connect to the new and old MySQL instances at the same time in different connections. In this situation, the binlog migrated to DM is not consistent with other upstream status that DM receives, causing unpredictable anomalies and even data damage. To make necessary changes to DM manually, see Switch DM-worker connection via virtual IP.