TiSpark User Guide
TiSpark is a thin layer built for running Apache Spark on top of TiDB/TiKV to answer the complex OLAP queries. It takes advantages of both the Spark platform and the distributed TiKV cluster and seamlessly glues to TiDB, the distributed OLTP database, to provide a Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing (HTAP) solution to serve as a one-stop solution for both online transactions and analysis.
TiSpark depends on the TiKV cluster and the PD cluster. You also need to set up a Spark cluster. This document provides a brief introduction to how to setup and use TiSpark. It requires some basic knowledge of Apache Spark. For more information, see Spark website.
Overview
TiSpark is an OLAP solution that runs Spark SQL directly on TiKV, the distributed storage engine.
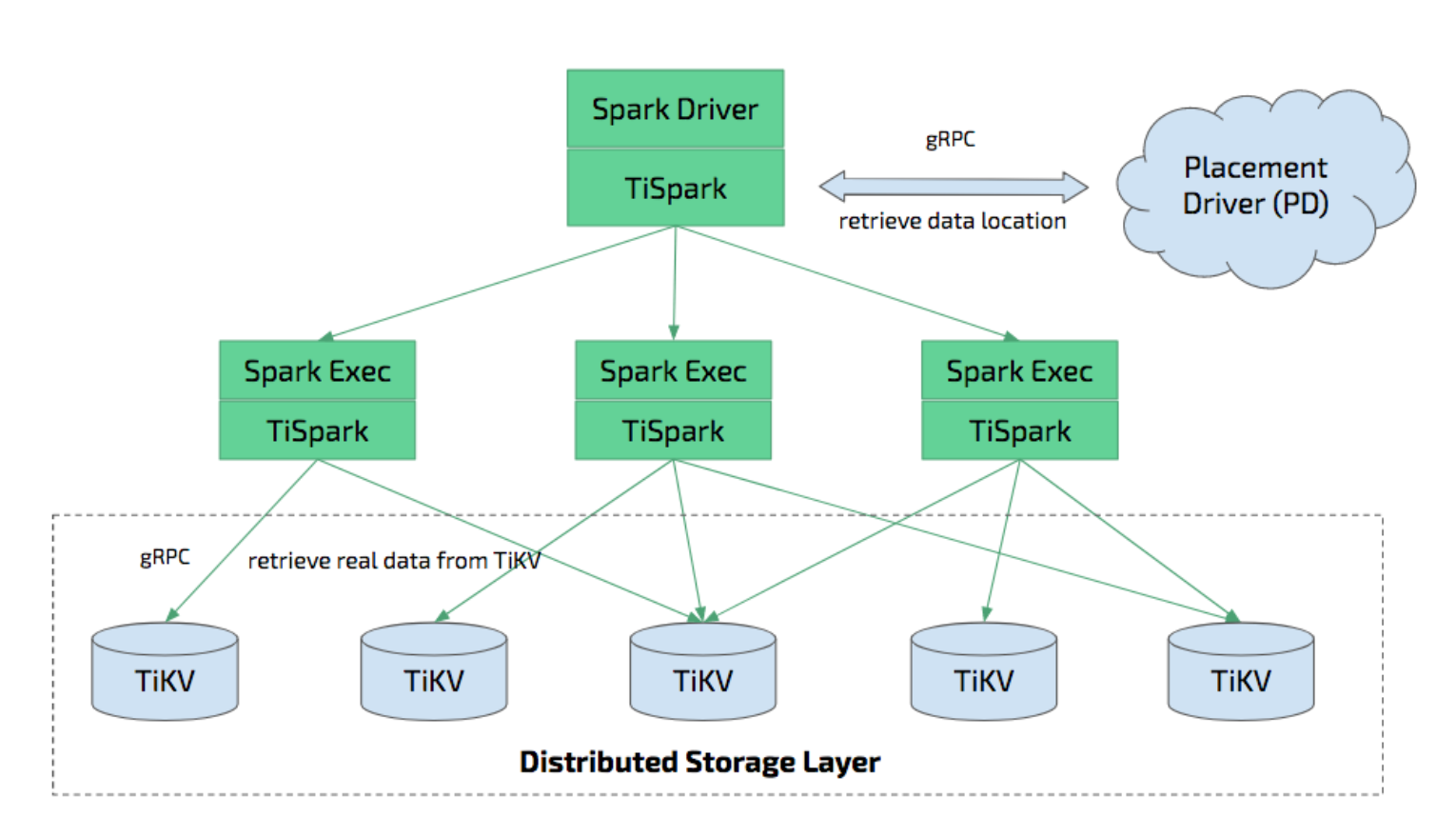
- TiSpark integrates with Spark Catalyst Engine deeply. It provides precise control of the computing, which allows Spark read data from TiKV efficiently. It also supports index seek, which improves the performance of the point query execution significantly.
- It utilizes several strategies to push down the computing to reduce the size of dataset handling by Spark SQL, which accelerates the query execution. It also uses the TiDB built-in statistical information for the query plan optimization.
- From the data integration point of view, TiSpark and TiDB serve as a solution for running both transaction and analysis directly on the same platform without building and maintaining any ETLs. It simplifies the system architecture and reduces the cost of maintenance.
- You can deploy and utilize tools from the Spark ecosystem for further data processing and manipulation on TiDB. For example, using TiSpark for data analysis and ETL; retrieving data from TiKV as a machine learning data source; generating reports from the scheduling system and so on.
- Also, TiSpark supports distributed writes to TiKV. Compared to using Spark combined with JDBC to write to TiDB, distributed writes to TiKV can implement transactions (either all data are written successfully or all writes fail), and the writes are faster.
Environment setup
- The TiSpark 2.x supports Spark 2.3.x and Spark 2.4.x. If you want to use Spark 2.1.x, use TiSpark 1.x instead.
- TiSpark requires JDK 1.8+ and Scala 2.11 (Spark2.0 + default Scala version).
- TiSpark runs in any Spark mode such as YARN, Mesos, and Standalone.
Recommended configuration
This section describes the configuration of independent deployment of TiKV and TiSpark, independent deployment of Spark and TiSpark, and hybrid deployment of TiKV and TiSpark.
Configuration of independent deployment of TiKV and TiSpark
For independent deployment of TiKV and TiSpark, it is recommended to refer to the following recommendations:
- Hardware configuration
- For general purposes, refer to the TiDB and TiKV hardware configuration recommendations.
- If the usage is more focused on the analysis scenarios, you can increase the memory of the TiKV nodes to at least 64G.
Configuration of independent deployment of Spark and TiSpark
See the Spark official website for the detail hardware recommendations.
The following is a short overview of TiSpark configuration.
It is recommended to allocate 32G memory for Spark, and reserve at least 25% of the memory for the operating system and buffer cache.
It is recommended to provision at least 8 to 16 cores on per machine for Spark. Initially, you can assign all the CPU cores to Spark.
See the official configuration on the Spark website. The following is an example based on the spark-env.sh configuration:
SPARK_EXECUTOR_CORES: 5
SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY: 10g
SPARK_WORKER_CORES: 5
SPARK_WORKER_MEMORY: 10g
In the spark-defaults.conf file, add the following lines:
spark.tispark.pd.addresses $your_pd_servers
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.spark.sql.TiExtensions
Add the following configuration in the CDH spark version:
spark.tispark.pd.addresses=$your_pd_servers
spark.sql.extensions=org.apache.spark.sql.TiExtensions
your_pd_servers are comma-separated PD addresses, with each in the format of $your_pd_address:$port.
For example, when you have multiple PD servers on 10.16.20.1,10.16.20.2,10.16.20.3 with the port 2379, put it as 10.16.20.1:2379,10.16.20.2:2379,10.16.20.3:2379.
Configuration of hybrid deployment of TiKV and TiSpark
For the hybrid deployment of TiKV and TiSpark, add TiSpark required resources to the TiKV reserved resources, and allocate 25% of the memory for the system.
Deploy the TiSpark cluster
Download TiSpark's jar package in the TiSpark releases page. Download your desired version of jar package and copy the content to the appropriate folder.
Deploy TiSpark on the existing Spark cluster
Running TiSpark on an existing Spark cluster does not require a reboot of the cluster. You can use Spark's --jars parameter to introduce TiSpark as a dependency:
spark-shell --jars $TISPARK_FOLDER/tispark-${name_with_version}.jar
Deploy TiSpark without the Spark cluster
If you do not have a Spark cluster, we recommend using the standalone mode. To use the Spark Standalone model, you can simply place a compiled version of Spark on each node of the cluster. If you encounter problems, see its official website. And you are welcome to file an issue on our GitHub.
If you are using TiDB Ansible to deploy a TiDB cluster, you can also use TiDB Ansible to deploy a Spark standalone cluster, and TiSpark is also deployed at the same time.
Download and install
You can download Apache Spark
For the Standalone mode without Hadoop support, use Spark 2.3.x and any version of Pre-build with Apache Hadoop 2.x with Hadoop dependencies. If you need to use the Hadoop cluster, choose the corresponding Hadoop version. You can also choose to build from the source code to match the previous version of the official Hadoop 2.x.
Suppose you already have a Spark binaries, and the current PATH is SPARKPATH, you can copy the TiSpark jar package to the ${SPARKPATH}/jars directory.
Start a Master node
Execute the following command on the selected Spark Master node:
cd $SPARKPATH
./sbin/start-master.sh
After the above step is completed, a log file will be printed on the screen. Check the log file to confirm whether the Spark-Master is started successfully. You can open the http://spark-master-hostname:8080 to view the cluster information (if you does not change the Spark-Master default port number). When you start Spark-Worker, you can also use this panel to confirm whether the Worker is joined to the cluster.
Start a Worker node
Similarly, you can start a Spark-Worker node with the following command:
./sbin/start-slave.sh spark://spark-master-hostname:7077
After the command returns, you can see if the Worker node is joined to the Spark cluster correctly from the panel as well. Repeat the above command at all Worker nodes. After all Workers are connected to the master, you have a Standalone mode Spark cluster.
Spark SQL shell and JDBC server
TiSpark supports Spark 2.3, so you can use Spark's ThriftServer and SparkSQL directly.
Demo
Assuming that you have successfully started the TiSpark cluster as described above, here's a quick introduction to how to use Spark SQL for OLAP analysis. Here we use a table named lineitem in the tpch database as an example.
Assuming that your PD node is located at 192.168.1.100, port 2379, add the following command to $SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-defaults.conf:
spark.tispark.pd.addresses 192.168.1.100:2379
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.spark.sql.TiExtensions
And then enter the following command in the Spark-Shell as in native Apache Spark:
spark.sql("use tpch")
spark.sql("select count(*)from lineitem").show
The result is:
+-------------+
| Count (1) |
+-------------+
| 600000000 |
+-------------+
Spark SQL Interactive shell remains the same:
spark-sql> use tpch;
Time taken: 0.015 seconds
spark-sql> select count(*) from lineitem;
2000
Time taken: 0.673 seconds, Fetched 1 row(s)
For JDBC connection with Thrift Server, you can try it with various JDBC supported tools including SQuirreLSQL and hive-beeline. For example, to use it with beeline:
./beeline
Beeline version 1.2.2 by Apache Hive
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
1: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000> use testdb;
+---------+--+
| Result |
+---------+--+
+---------+--+
No rows selected (0.013 seconds)
select count(*) from account;
+-----------+--+
| count(1) |
+-----------+--+
| 1000000 |
+-----------+--+
1 row selected (1.97 seconds)
Use TiSpark together with Hive
You can use TiSpark together with Hive.
Before starting Spark, you need to set the HADOOP_CONF_DIR environment variable to your Hadoop configuration folder and copy hive-site.xml to the spark/conf folder.
val tisparkDF = spark.sql("select * from tispark_table").toDF
tisparkDF.write.saveAsTable("hive_table") // save table to hive
spark.sql("select * from hive_table a, tispark_table b where a.col1 = b.col1").show // join table across Hive and Tispark
Load Spark Dataframe into TiDB using JDBC
TiSpark does not provide a direct way of loading data into your TiDB cluster, but you can load data using JDBC like this:
import org.apache.spark.sql.execution.datasources.jdbc.JDBCOptions
val customer = spark.sql("select * from customer limit 100000")
// You might repartition the source to make it balance across nodes
// and increase the concurrency.
val df = customer.repartition(32)
df.write
.mode(saveMode = "append")
.format("jdbc")
.option("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
// Replace the host and port with that of your own and be sure to use the rewrite batch
.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:4000/test?rewriteBatchedStatements=true")
.option("useSSL", "false")
// As tested, 150 is good practice
.option(JDBCOptions.JDBC_BATCH_INSERT_SIZE, 150)
.option("dbtable", s"cust_test_select") // database name and table name here
.option("isolationLevel", "NONE") // recommended to set isolationLevel to NONE if you have a large DF to load.
.option("user", "root") // TiDB user here
.save()
It is recommended to set isolationLevel to NONE to avoid large single transactions which might potentially lead to TiDB OOM.
Statistics information
TiSpark uses TiDB statistic information for the following items:
- Determining which index to ues in your query plan with the estimated lowest cost.
- Small table broadcasting, which enables efficient broadcast join.
If you would like TiSpark to use statistic information, first you need to make sure that concerning tables have already been analyzed. Read more about how to analyze tables.
Starting from TiSpark 2.0, statistics information is default to auto load.
Note that table statistics are cached in the memory of your Spark driver node, so you need to make sure that your memory size is large enough for your statistics information.
Currently, you can adjust these configurations in your spark-defaults.conf file.
| Property name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| spark.tispark.statistics.auto_load | true | Whether to load statistics information automatically during database mapping. |
FAQ
Q: What are the pros/cons of independent deployment as opposed to a shared resource with an existing Spark / Hadoop cluster?
A: You can use the existing Spark cluster without a separate deployment, but if the existing cluster is busy, TiSpark will not be able to achieve the desired speed.
Q: Can I mix Spark with TiKV?
A: If TiDB and TiKV are overloaded and run critical online tasks, consider deploying TiSpark separately. You also need to consider using different NICs to ensure that OLTP's network resources are not compromised and affect online business. If the online business requirements are not high or the loading is not large enough, you can consider mixing TiSpark with TiKV deployment.
Q: What can I do if warning:WARN ObjectStore:568 - Failed to get database is returned when executing SQL statements using TiSpark?
A: You can ignore this warning. It occurs because Spark tries to load two nonexistent databases (default and global_temp) in its catalog. If you want to mute this warning, modify log4j by adding log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.ObjectStore=ERROR to the log4j file in tispark/conf. You can add the parameter to the log4j file of the config under Spark. If the suffix is template, you can use the mv command to change it to properties.
Q: What can I do if java.sql.BatchUpdateException: Data Truncated is returned when executing SQL statements using TiSpark?
A: This error occurs because the length of the data written exceeds the length of the data type defined by the database. You can check the field length and adjust it accordingly.
Q: Does TiSpark read Hive metadata by default?
A: By default, TiSpark searches for the Hive database by reading the Hive metadata in hive-site. If the search task fails, it searches for the TiDB database instead, by reading the TiDB metadata.
If you do not need this default behavior, do not configure the Hive metadata in hive-site.
Q: What can I do if Error:java.io.InvalidClassException: com.pingcap.tikv.region.TiRegion; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID ... is returned when TiSpark is executing a Spark task?
A: The error message shows a serialVersionUID conflict, which occurs because you have used class and TiRegion of different versions. Because TiRegion only exists in TiSpark, multiple versions of TiSpark packages might be used. To fix this error, you need to make sure the version of TiSpark dependency is consistent among all nodes in the cluster.