Key Monitoring Metrics of PD
If you use TiDB Ansible to deploy the TiDB cluster, the monitoring system is deployed at the same time. For more information, see Overview of the Monitoring Framework.
The Grafana dashboard is divided into a series of sub dashboards which include Overview, PD, TiDB, TiKV, Node_exporter, Disk Performance, and so on. A lot of metrics are there to help you diagnose.
You can get an overview of the component PD status from the PD dashboard, where the key metrics are displayed. This document provides a detailed description of these key metrics.
Key metrics description
To understand the key metrics displayed on the Overview dashboard, check the following table:
| Service | Panel name | Description | Normal range |
|---|---|---|---|
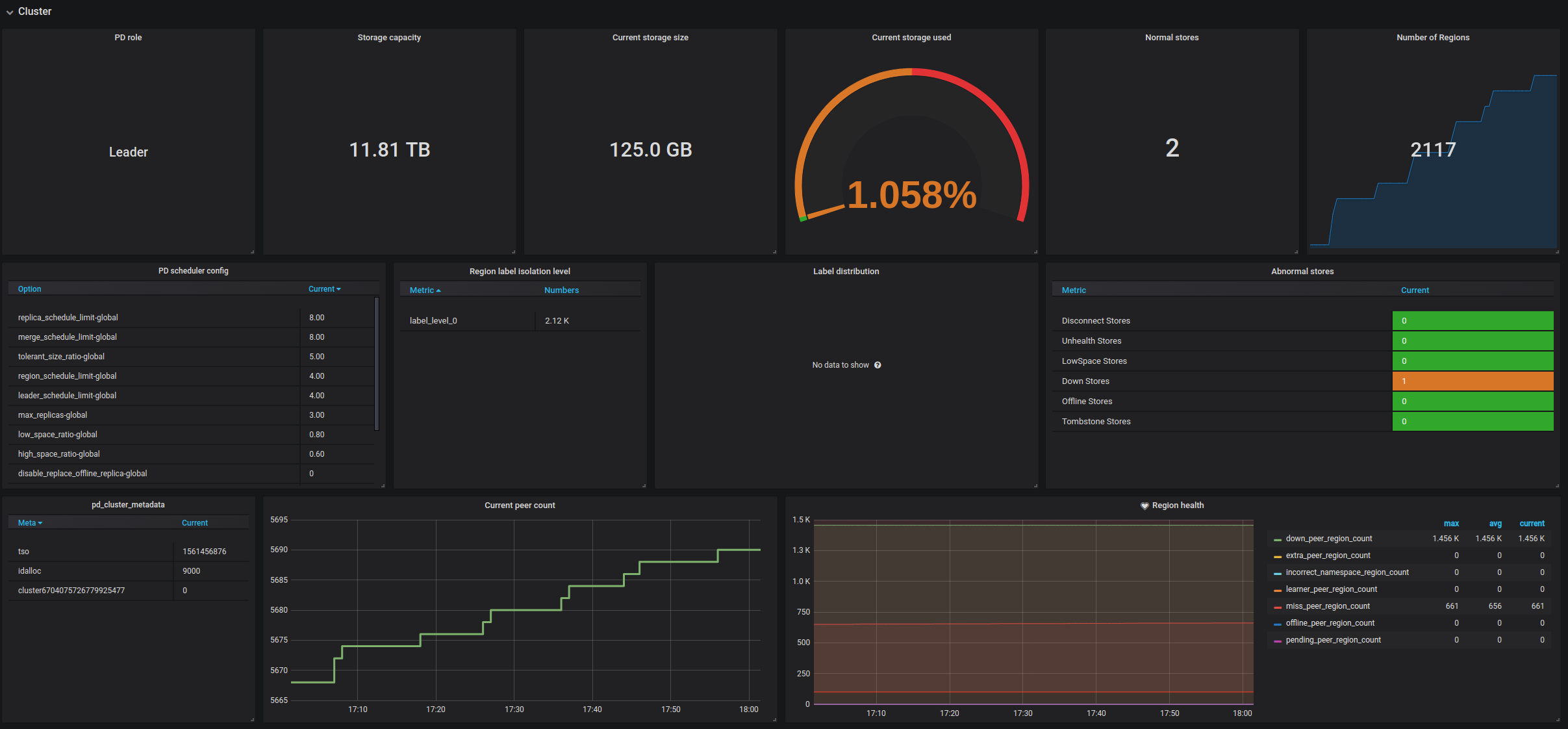
| Cluster | PD role | The role of the current PD | |
| Cluster | Storage capacity | The total capacity size of the cluster | |
| Cluster | Current storage size | The current storage size of the cluster | |
| Cluster | Current storage usage | The total number of Regions without replicas | |
| Cluster | Normal stores | The count of healthy stores | |
| Cluster | Abnormal stores | The count of unhealthy stores | The normal value is 0. If the number is bigger than 0, it means at least one instance is abnormal. |
| Cluster | Current peer count | The current peer count of the cluster | |
| Cluster | Number of Regions | The total number of Regions of the cluster | |
| Cluster | PD scheduler config | The list of PD scheduler configurations | |
| Cluster | Region label isolation level | The number of Regions in different label levels | |
| Cluster | Label distribution | The distribution status of the labels in the cluster | |
| Cluster | pd_cluster_metadata | The metadata of the PD cluster including cluster ID, the timestamp, and the generated ID. | |
| Cluster | Region health | The health status of Regions indicated via count of unusual Regions including pending peers, down peers, extra peers, offline peers, missing peers, learner peers and incorrect namespaces | The number of pending peers should be less than 100. The missing peers should not be persistently greater than 0. |
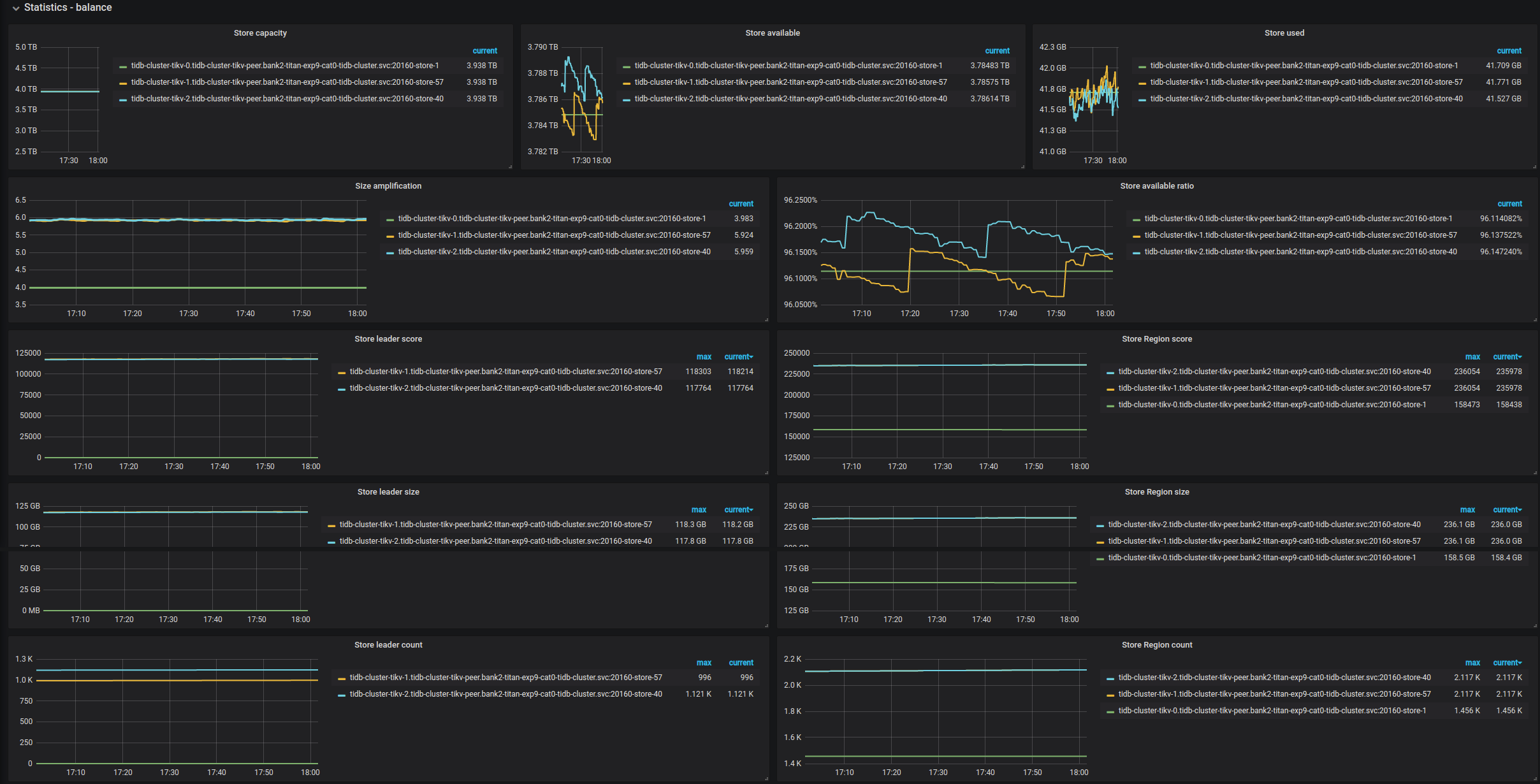
| Statistics - Balance | Store capacity | The capacity size per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store available | The available capacity size per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store used | The used capacity size per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Size amplification | The size amplification ratio per TiKV instance, which is equal to (Store Region size)/(Store used capacity size) | |
| Statistics - Balance | Size available ratio | The size availability ratio per TiKV instance, which is equal to (Store available capacity size)/(Store capacity size) | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store leader score | The leader score per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store Region score | The Region score per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store leader size | The total leader size per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store Region size | The total Region size per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store leader count | The leader count per TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Balance | Store Region count | The Region count per TiKV instance | |
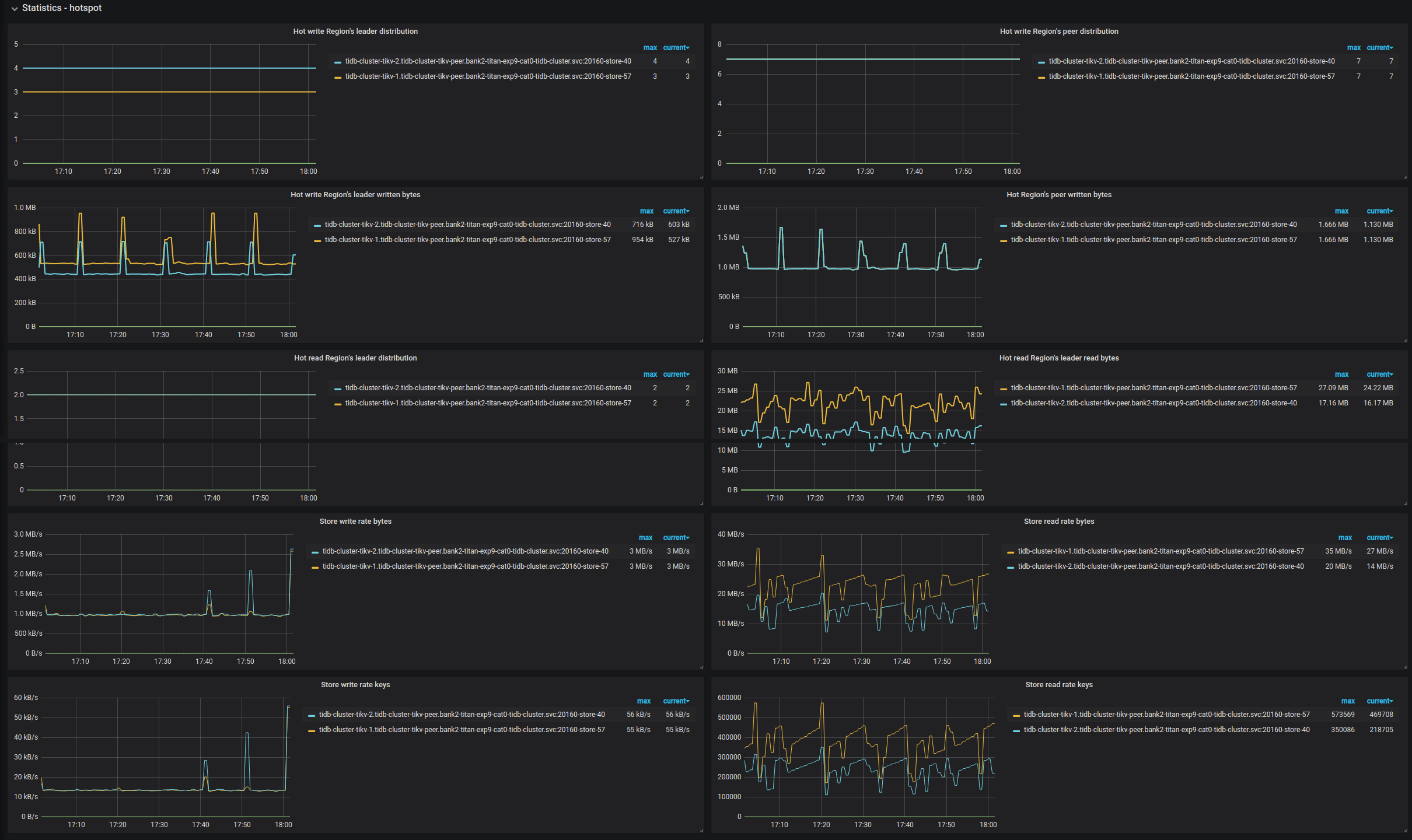
| Statistics - Hotspot | Leader distribution in hot write Regions | The total number of leader Regions in hot write on each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Peer distribution in hot write Regions | The total number of peer Regions under in hot write on each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Leader written bytes in hot write Regions | The total written bytes by Leader regions in hot write on leader Regions for each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Peer written bytes in hot write Regions | The total bytes of hot write on peer Regions per each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Leader distribution in hot read Regions | The total number of leader Regions in hot read per each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Peer distribution in hot read Regions | The total number of Regions which are not leader under hot read per each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Leader read bytes in hot read Regions | The total bytes of hot read on leader Regions per each TiKV instance | |
| Statistics - Hotspot | Peer read bytes in hot read Regions | The total bytes of hot read on peer Regions per TiKV instance | |
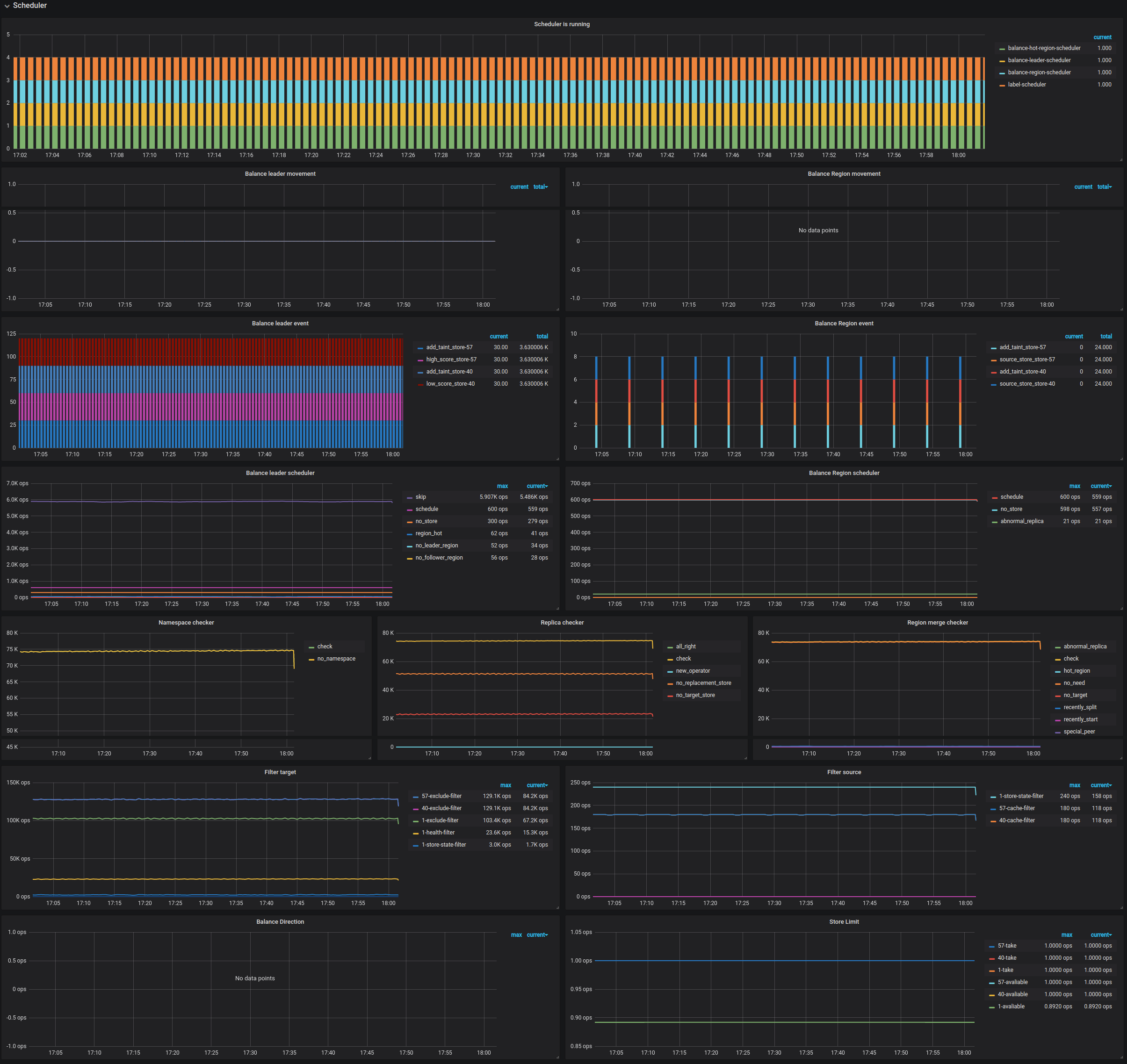
| Scheduler | Running schedulers | The current running schedulers | |
| Scheduler | Balance leader movement | The leader movement details among TiKV instances | |
| Scheduler | Balance Region movement | The Region movement details among TiKV instances | |
| Scheduler | Balance leader event | The count of balance leader events | |
| Scheduler | Balance Region event | The count of balance Region events | |
| Scheduler | Balance leader scheduler | The inner status of balance leader scheduler | |
| Scheduler | Balance Region scheduler | The inner status of balance Region scheduler | |
| Scheduler | Namespace checker | The namespace checker's status | |
| Scheduler | Replica checker | The replica checker's status | |
| Scheduler | Region merge checker | The merge checker's status | |
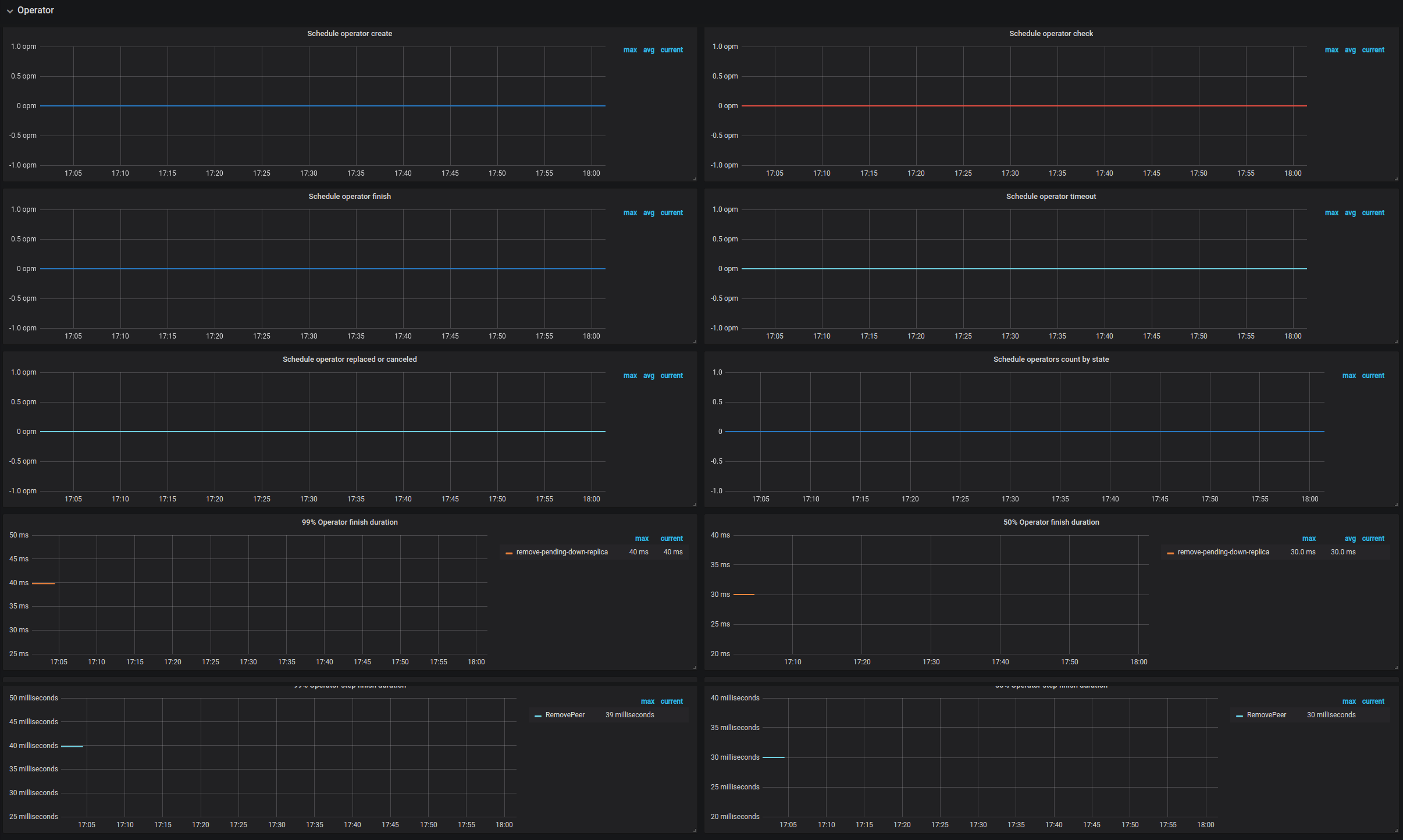
| Operator | Schedule operator create | The number of newly created operators per type | |
| Operator | Schedule operator check | The number of checked operator per type. It mainly checks if the current step is finished; if yes, it returns the next step to be executed. | |
| Operator | Schedule operator finish | The number of finished operators per type | |
| Operator | Schedule operator timeout | The number of timeout operators per type | |
| Operator | Schedule operator replaced or canceled | The number of replaced or canceled operators per type | |
| Operator | Schedule operators count by state | The number of operators per state | |
| Operator | 99% Operator finish duration | The operator step duration (P99) | |
| Operator | 50% Operator finish duration | The operator duration (P50) | |
| Operator | 99% Operator step duration | The operator step duration (P99) | |
| Operator | 50% Operator step duration | The operator step duration (P50) | |
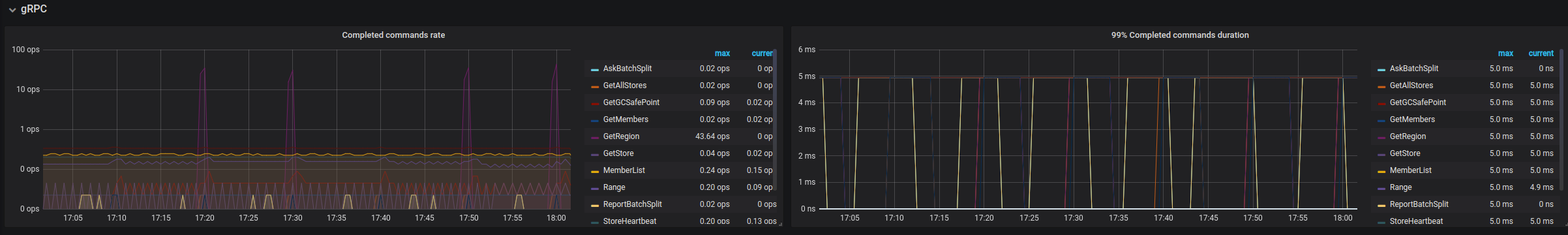
| gRPC | Completed commands rate | The rate per command type type at which gRPC commands are completed | |
| gRPC | 99% Completed commands duration | The rate per command type type at which gRPC commands are completed (P99) | |
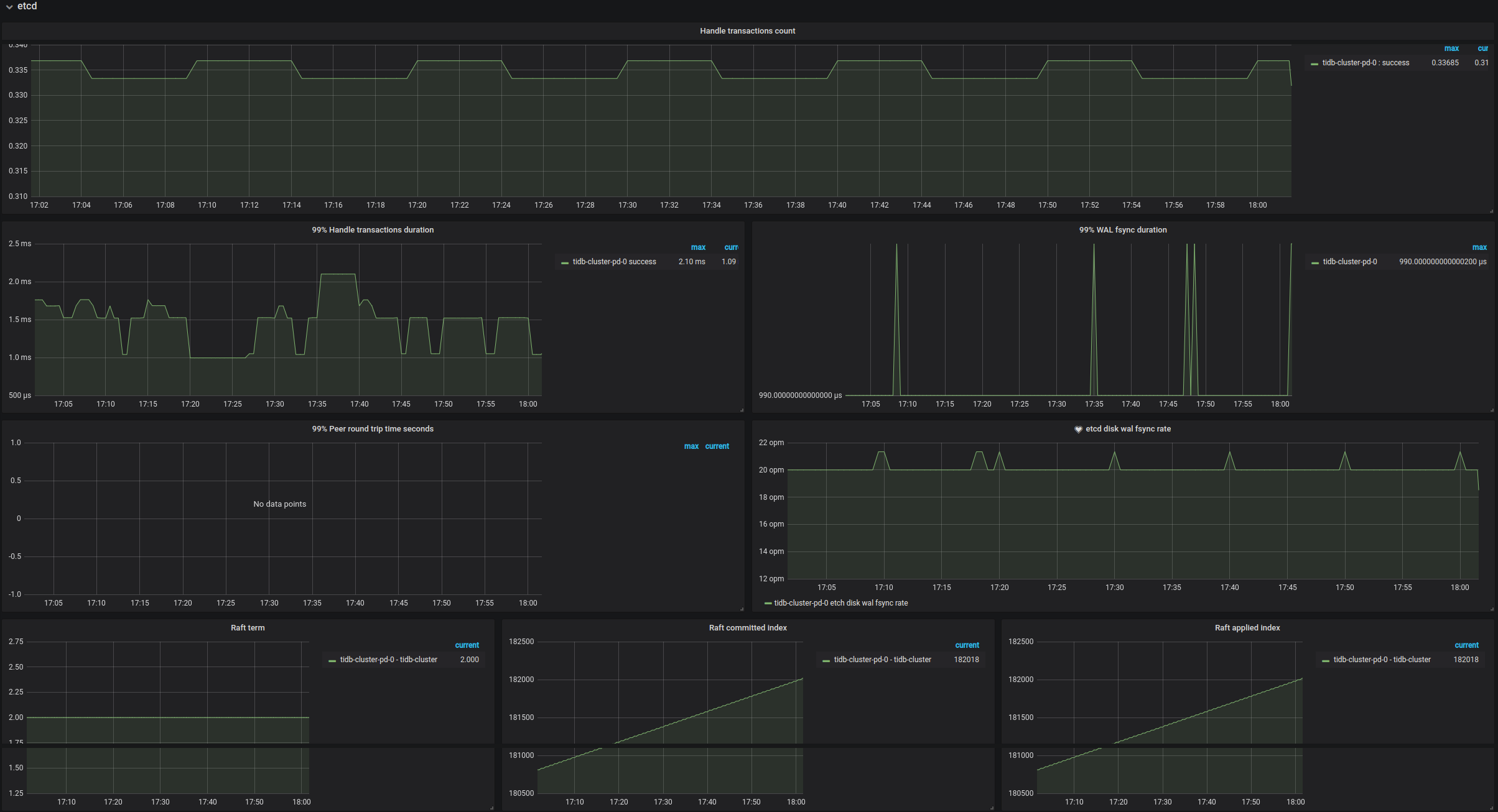
| etcd | Transaction handling rate | The rate at which etcd handles transactions | |
| etcd | 99% transactions duration | The transaction handling rate (P99) | |
| etcd | 99% WAL fsync duration | The time consumed for writing WAL into the persistent storage (P99) | The value is less than 1s. |
| etcd | 99% Peer round trip time seconds | The network latency for etcd (P99) | The value is less than 1s. |
| etcd | etcd disk wal fsync rate | The rate of writing WAL into the persistent storage | |
| etcd | Raft term | The current term of Raft | |
| etcd | Raft committed index | The last committed index of Raft | |
| etcd | Raft applied index | The last applied index of Raft | |
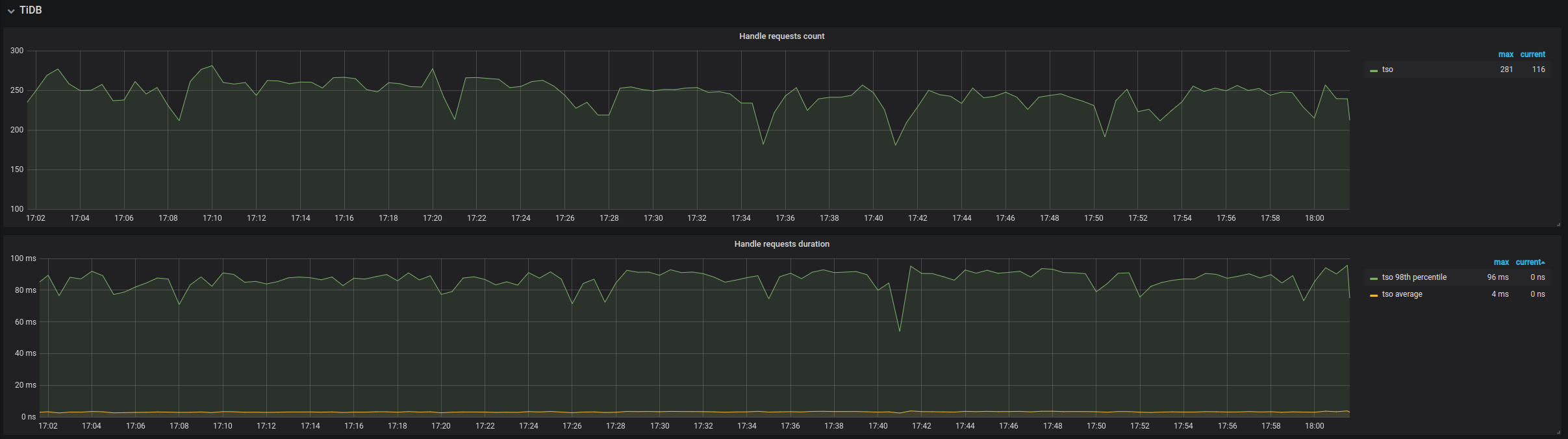
| TiDB | Handled requests count | The count of TiDB requests | |
| TiDB | Request handling duration | The time consumed for handling TiDB requests | It should be less than 100ms (P99). |
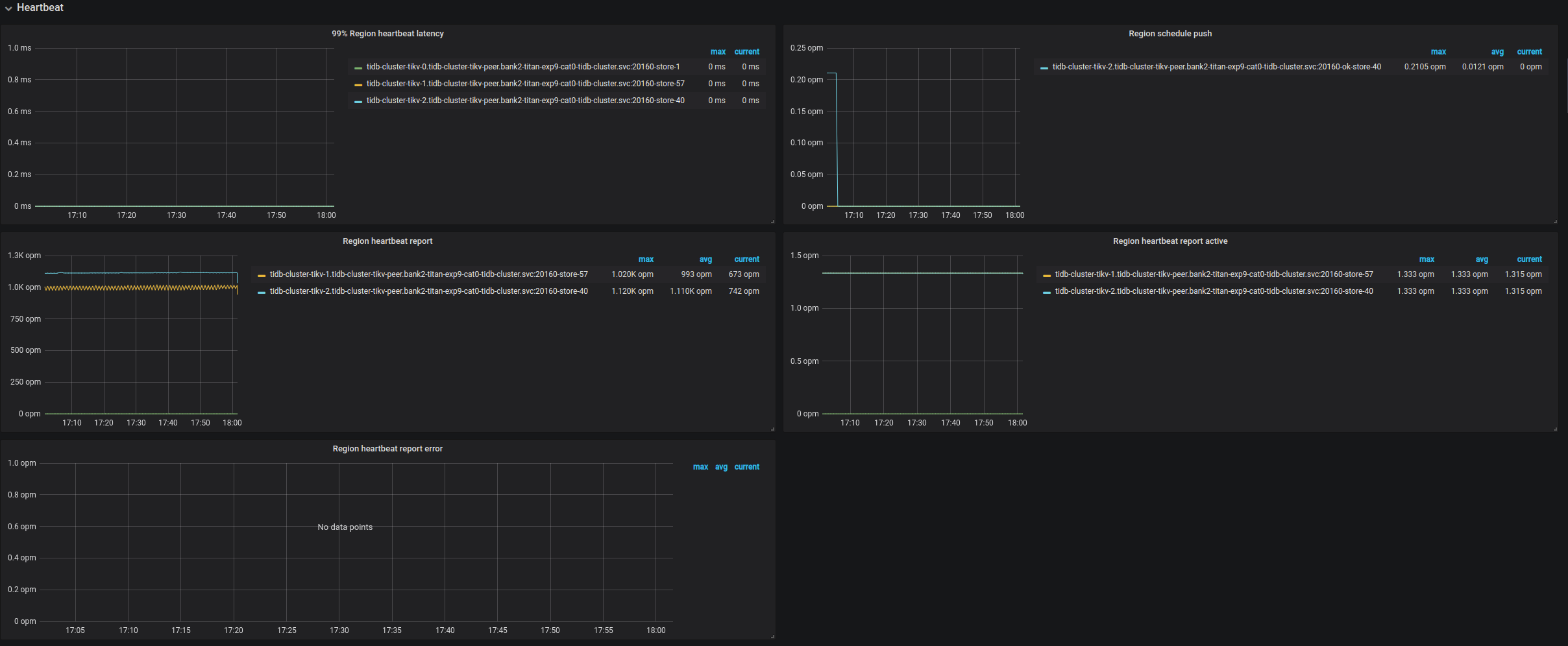
| Heartbeat | Region heartbeat report | The count of heartbeats reported reported to PD per instance | |
| Heartbeat | Region heartbeat report error | The count of heartbeats with the error status | |
| Heartbeat | Region heartbeat report active | The count of heartbeats with the ok status | |
| Heartbeat | Region schedule push | The count of corresponding schedule commands sent from PD per TiKV instance | |
| Heartbeat | 99% Region heartbeat latency | The heartbeat latency per TiKV instance (P99) | |
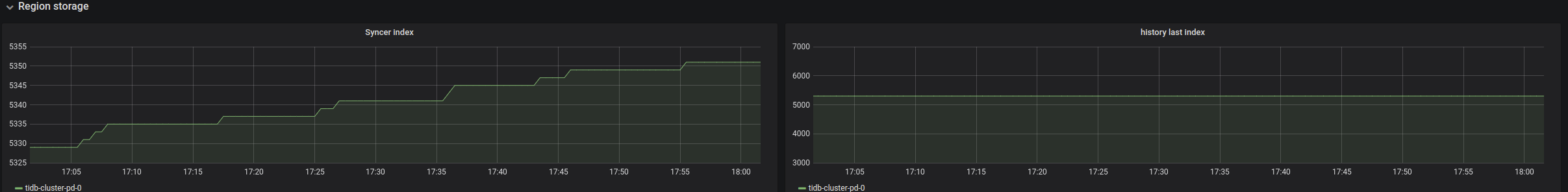
| Region storage | Syncer index | The maximum index in the Region change history recorded by the leader | |
| Region storage | History last index | The last index where the Region change history is synchronized | successfully with the follower |
PD dashboard interface
Cluster
Statistics - Balance
Statistics - Hotspot
Scheduler
Operator
gRPC
etcd
TiDB
Heartbeat
Region storage