MODIFY COLUMN
The ALTER TABLE.. MODIFY COLUMN statement modifies a column on an existing table. The modification can include changing the data type and attributes. To rename at the same time, use the CHANGE COLUMN statement instead.
Synopsis
AlterTableStmt:
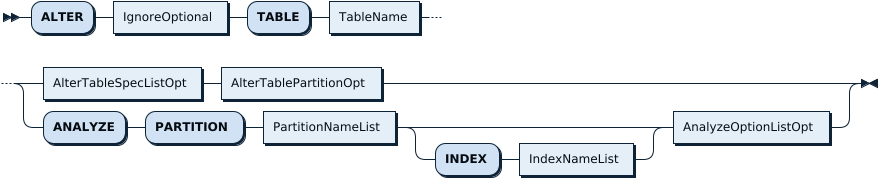
AlterTableSpec:

ColumnKeywordOpt:

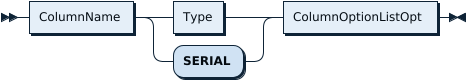
ColumnDef:
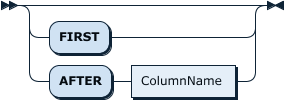
ColumnPosition:
Examples
mysql> CREATE TABLE t1 (id int not null primary key AUTO_INCREMENT, col1 INT);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO t1 (col1) VALUES (1),(2),(3),(4),(5);
Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 5 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> ALTER TABLE t1 MODIFY col1 BIGINT;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)
mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE t1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`col1` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_bin AUTO_INCREMENT=30001
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> ALTER TABLE t1 MODIFY col1 INT;
ERROR 1105 (HY000): unsupported modify column length 11 is less than origin 20
mysql> ALTER TABLE t1 MODIFY col1 BLOB;
ERROR 1105 (HY000): unsupported modify column type 252 not match origin 8
mysql> ALTER TABLE t1 MODIFY col1 BIGINT, MODIFY id BIGINT NOT NULL;
ERROR 1105 (HY000): can't run multi schema change
MySQL compatibility
- Making multiple changes in a single
ALTER TABLEstatement is not currently supported. - Only certain types of data type changes are supported. For example, an
INTEGERtoBIGINTis supported, but the reverse is not possible. Changing from an integer to a string format or blob is not supported. - Modifying precision of the
DECIMALdata type is not supported.