EXPLAIN
The EXPLAIN statement shows the execution plan for a query without executing it. It is complimented by EXPLAIN ANALYZE which will execute the query. If the output of EXPLAIN does not match the expected result, consider executing ANALYZE TABLE on each table in the query.
The statements DESC and DESCRIBE are aliases of this statement. The alternative usage of EXPLAIN <tableName> is documented under SHOW [FULL] COLUMNS FROM.
Synopsis
ExplainSym:
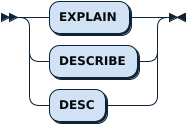
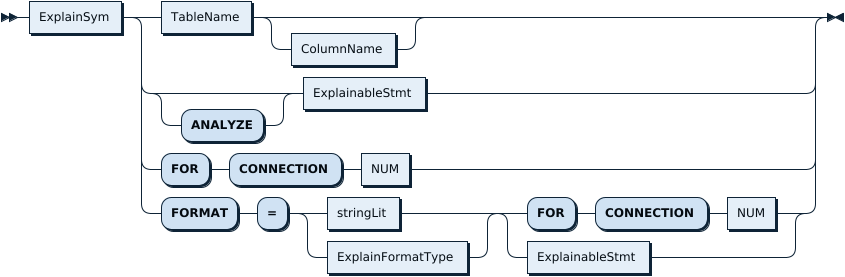
ExplainStmt:
ExplainableStmt:
Examples
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT 1;
+-------------------+-------+------+---------------+
| id | count | task | operator info |
+-------------------+-------+------+---------------+
| Projection_3 | 1.00 | root | 1 |
| └─TableDual_4 | 1.00 | root | rows:1 |
+-------------------+-------+------+---------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE TABLE t1 (id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, c1 INT NOT NULL);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO t1 (c1) VALUES (1), (2), (3);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE id = 1;
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
| Point_Get_1 | 1.00 | root | table:t1, handle:1 |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> DESC SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE id = 1;
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
| Point_Get_1 | 1.00 | root | table:t1, handle:1 |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> DESCRIBE SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE id = 1;
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
| Point_Get_1 | 1.00 | root | table:t1, handle:1 |
+-------------+-------+------+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> EXPLAIN INSERT INTO t1 (c1) VALUES (4);
ERROR 1105 (HY000): Unsupported type *core.Insert
mysql> EXPLAIN UPDATE t1 SET c1=5 WHERE c1=3;
+---------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info |
+---------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| TableReader_6 | 10.00 | root | data:Selection_5 |
| └─Selection_5 | 10.00 | cop | eq(test.t1.c1, 3) |
| └─TableScan_4 | 10000.00 | cop | table:t1, range:[-inf,+inf], keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
+---------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> EXPLAIN DELETE FROM t1 WHERE c1=3;
+---------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | count | task | operator info |
+---------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| TableReader_6 | 10.00 | root | data:Selection_5 |
| └─Selection_5 | 10.00 | cop | eq(test.t1.c1, 3) |
| └─TableScan_4 | 10000.00 | cop | table:t1, range:[-inf,+inf], keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
+---------------------+----------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
If you do not specify the FORMAT, or specify FORMAT = "row", EXPLAIN statement will output the results in a tabular format. See Understand the Query Execution Plan for more information.
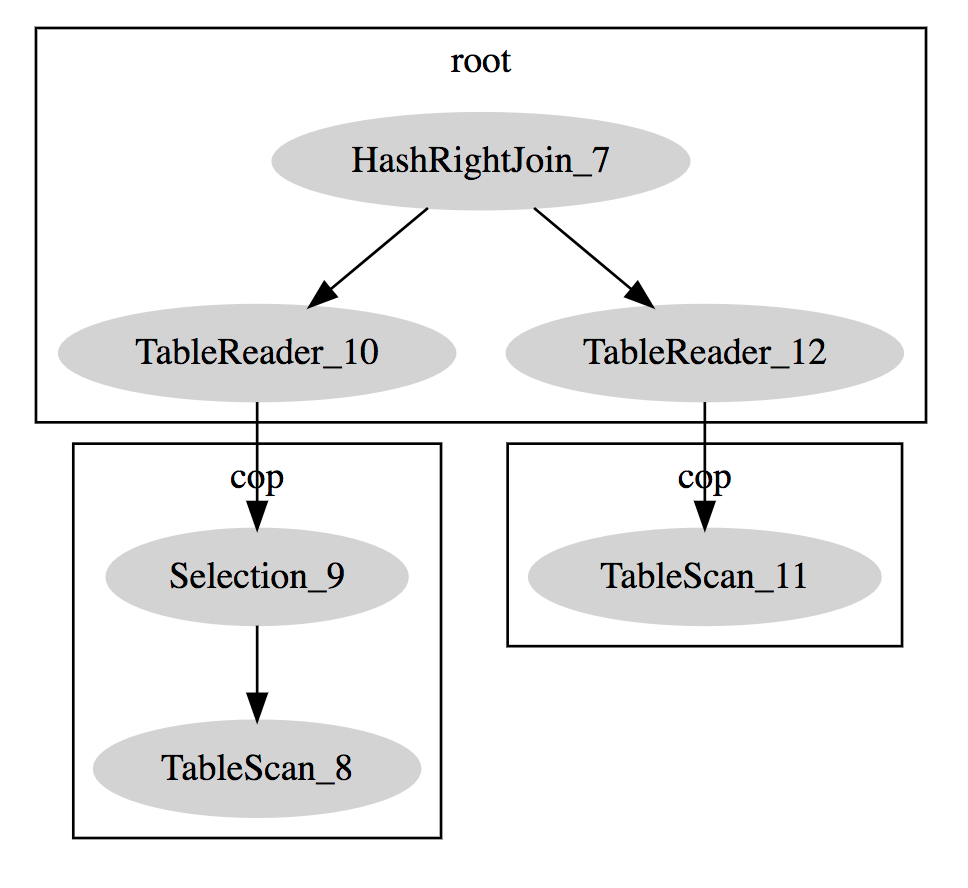
In addition to the MySQL standard result format, TiDB also supports DotGraph and you need to specify FORMAT = "dot" as in the following example:
create table t(a bigint, b bigint);
desc format = "dot" select A.a, B.b from t A join t B on A.a > B.b where A.a < 10;
TiDB > desc format = "dot" select A.a, B.b from t A join t B on A.a > B.b where A.a < 10;desc format = "dot" select A.a, B.b from t A join t B on A.a > B.b where A.a < 10;
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| dot contents |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
digraph HashRightJoin_7 {
subgraph cluster7{
node [style=filled, color=lightgrey]
color=black
label = "root"
"HashRightJoin_7" -> "TableReader_10"
"HashRightJoin_7" -> "TableReader_12"
}
subgraph cluster9{
node [style=filled, color=lightgrey]
color=black
label = "cop"
"Selection_9" -> "TableScan_8"
}
subgraph cluster11{
node [style=filled, color=lightgrey]
color=black
label = "cop"
"TableScan_11"
}
"TableReader_10" -> "Selection_9"
"TableReader_12" -> "TableScan_11"
}
|
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
If the dot program (in the graphviz package) is installed on your computer, you can generate a PNG file using the following method:
dot xx.dot -T png -O
The xx.dot is the result returned by the above statement.
If the dot program is not installed on your computer, copy the result to this website to get a tree diagram:
MySQL compatibility
- Both the format of
EXPLAINand the potential execution plans in TiDB differ substaintially from MySQL. - TiDB does not support the
EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSONas in MySQL. - TiDB does not currently support
EXPLAINfor insert statements.