Use TiFlash MPP Mode
This document introduces the Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) mode of TiFlash and how to use it.
TiFlash supports using the MPP mode to execute queries, which introduces cross-node data exchange (data shuffle process) into the computation. TiDB automatically determines whether to select the MPP mode using the optimizer's cost estimation. You can change the selection strategy by modifying the values of tidb_allow_mpp and tidb_enforce_mpp.
The following diagram shows how the MPP mode works.
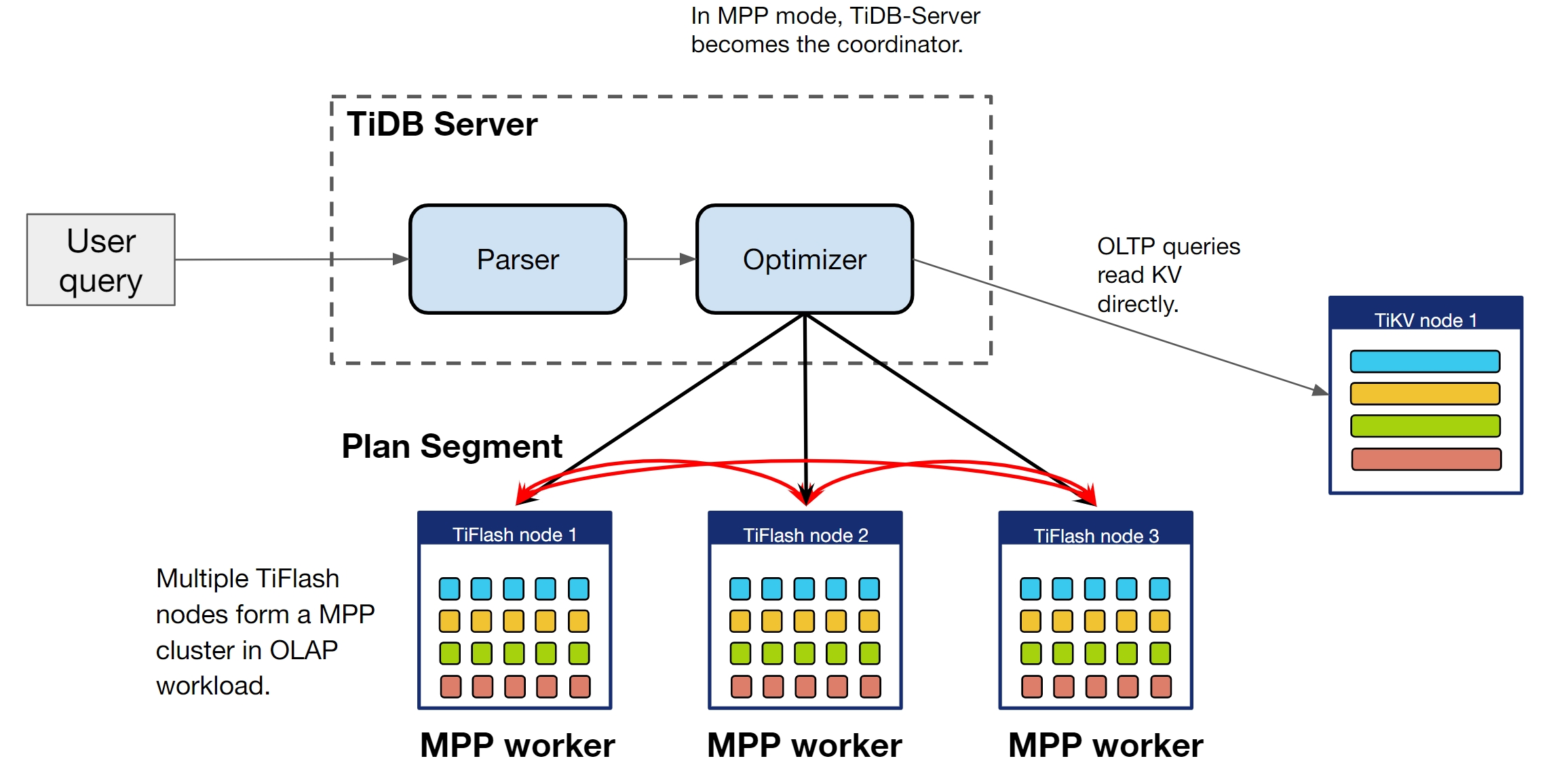
Control whether to select the MPP mode
The tidb_allow_mpp variable controls whether TiDB can select the MPP mode to execute queries. The tidb_enforce_mpp variable controls whether the optimizer's cost estimation is ignored and the MPP mode of TiFlash is forcibly used to execute queries.
The results corresponding to all values of these two variables are as follows:
| tidb_allow_mpp=off | tidb_allow_mpp=on (by default) | |
|---|---|---|
| tidb_enforce_mpp=off (by default) | The MPP mode is not used. | The optimizer selects the MPP mode based on cost estimation. (by default) |
| tidb_enforce_mpp=on | The MPP mode is not used. | TiDB ignores the cost estimation and selects the MPP mode. |
For example, if you do not want to use the MPP mode, you can execute the following statements:
set @@session.tidb_allow_mpp=0;
If you want TiDB's cost-based optimizer to automatically decide whether to use the MPP mode (by default), you can execute the following statements:
set @@session.tidb_allow_mpp=1;
set @@session.tidb_enforce_mpp=0;
If you want TiDB to ignore the optimizer's cost estimation and to forcibly select the MPP mode, you can execute the following statements:
set @@session.tidb_allow_mpp=1;
set @@session.tidb_enforce_mpp=1;
The initial value of the tidb_enforce_mpp session variable is equal to the enforce-mpp configuration value of this tidb-server instance (which is false by default). If multiple tidb-server instances in a TiDB cluster only perform analytical queries and you want to make sure that the MPP mode is used on these instances, you can change their enforce-mpp configuration values to true.
Algorithm support for the MPP mode
The MPP mode supports these physical algorithms: Broadcast Hash Join, Shuffled Hash Join, Shuffled Hash Aggregation, Union All, TopN, and Limit. The optimizer automatically determines which algorithm to be used in a query. To check the specific query execution plan, you can execute the EXPLAIN statement. If the result of the EXPLAIN statement shows ExchangeSender and ExchangeReceiver operators, it indicates that the MPP mode has taken effect.
The following statement takes the table structure in the TPC-H test set as an example:
explain select count(*) from customer c join nation n on c.c_nationkey=n.n_nationkey;
+------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| HashAgg_23 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#16)->Column#15 |
| └─TableReader_25 | 1.00 | root | | data:ExchangeSender_24 |
| └─ExchangeSender_24 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | ExchangeType: PassThrough |
| └─HashAgg_12 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#16 |
| └─HashJoin_17 | 3000000.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | inner join, equal:[eq(tpch.nation.n_nationkey, tpch.customer.c_nationkey)] |
| ├─ExchangeReceiver_21(Build) | 25.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | |
| │ └─ExchangeSender_20 | 25.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | ExchangeType: Broadcast |
| │ └─TableFullScan_18 | 25.00 | mpp[tiflash] | table:n | keep order:false |
| └─TableFullScan_22(Probe) | 3000000.00 | mpp[tiflash] | table:c | keep order:false |
+------------------------------------------+------------+--------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
In the example execution plan, the ExchangeReceiver and ExchangeSender operators are included. The execution plan indicates that after the nation table is read, the ExchangeSender operator broadcasts the table to each node, the HashJoin and HashAgg operations are performed on the nation table and the customer table, and then the results are returned to TiDB.
TiFlash provides the following 3 global/session variables to control whether to use Broadcast Hash Join:
tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_size: The unit of the value is bytes. If the table size (in the unit of bytes) is less than the value of the variable, the Broadcast Hash Join algorithm is used. Otherwise, the Shuffled Hash Join algorithm is used.tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_count: The unit of the value is rows. If the objects of the join operation belong to a subquery, the optimizer cannot estimate the size of the subquery result set, so the size is determined by the number of rows in the result set. If the estimated number of rows in the subquery is less than the value of this variable, the Broadcast Hash Join algorithm is used. Otherwise, the Shuffled Hash Join algorithm is used.tidb_prefer_broadcast_join_by_exchange_data_size: controls whether to use the algorithm with the minimum overhead of network transmission. If this variable is enabled, TiDB estimates the size of the data to be exchanged in the network usingBroadcast Hash JoinandShuffled Hash Joinrespectively, and then chooses the one with the smaller size.tidb_broadcast_join_threshold_countandtidb_broadcast_join_threshold_sizewill not take effect after this variable is enabled.
Access partitioned tables in the MPP mode
To access partitioned tables in the MPP mode, you need to enable dynamic pruning mode first.
Example:
mysql> DROP TABLE if exists test.employees;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE TABLE test.employees
(id int NOT NULL,
fname varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
lname varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
hired date NOT NULL DEFAULT '1970-01-01',
separated date DEFAULT '9999-12-31',
job_code int DEFAULT NULL,
store_id int NOT NULL) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_bin
PARTITION BY RANGE (store_id)
(PARTITION p0 VALUES LESS THAN (6),
PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (11),
PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN (16),
PARTITION p3 VALUES LESS THAN (MAXVALUE));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> ALTER table test.employees SET tiflash replica 1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)
mysql> SET tidb_partition_prune_mode=static;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT count(*) FROM test.employees;
+----------------------------------+----------+-------------------+-------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+----------------------------------+----------+-------------------+-------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
| HashAgg_18 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#10)->Column#9 |
| └─PartitionUnion_20 | 4.00 | root | | |
| ├─StreamAgg_35 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#12)->Column#10 |
| │ └─TableReader_36 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_26 |
| │ └─StreamAgg_26 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#12 |
| │ └─TableFullScan_34 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p0 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| ├─StreamAgg_52 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#14)->Column#10 |
| │ └─TableReader_53 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_43 |
| │ └─StreamAgg_43 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#14 |
| │ └─TableFullScan_51 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p1 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| ├─StreamAgg_69 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#16)->Column#10 |
| │ └─TableReader_70 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_60 |
| │ └─StreamAgg_60 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#16 |
| │ └─TableFullScan_68 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p2 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| └─StreamAgg_86 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#18)->Column#10 |
| └─TableReader_87 | 1.00 | root | | data:StreamAgg_77 |
| └─StreamAgg_77 | 1.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#18 |
| └─TableFullScan_85 | 10000.00 | batchCop[tiflash] | table:employees, partition:p3 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
+----------------------------------+----------+-------------------+-------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
18 rows in set (0,00 sec)
mysql> SET tidb_partition_prune_mode=dynamic;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT count(*) FROM test.employees;
+------------------------------+----------+--------------+-----------------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+------------------------------+----------+--------------+-----------------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| HashAgg_17 | 1.00 | root | | funcs:count(Column#11)->Column#9 |
| └─TableReader_19 | 1.00 | root | partition:all | data:ExchangeSender_18 |
| └─ExchangeSender_18 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | ExchangeType: PassThrough |
| └─HashAgg_8 | 1.00 | mpp[tiflash] | | funcs:count(1)->Column#11 |
| └─TableFullScan_16 | 10000.00 | mpp[tiflash] | table:employees | keep order:false, stats:pseudo, PartitionTableScan:true |
+------------------------------+----------+--------------+-----------------+---------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows in set (0,00 sec)