Interaction Test on Online Workloads and ADD INDEX Operations
Test purpose
This document tests the interaction effects between online workloads and ADD INDEX operations in the OLTP scenario.
Test version, time, and place
TiDB version: v3.0.1
Time: July, 2019
Place: Beijing
Test environment
This test runs in a Kubernetes cluster deployed with 3 TiDB instances, 3 TiKV instances and 3 PD instances.
Version information
| Component | GitHash |
|---|---|
| TiDB | 9e4e8da3c58c65123db5f26409759fe1847529f8 |
| TiKV | 4151dc8878985df191b47851d67ca21365396133 |
| PD | 811ce0b9a1335d1b2a049fd97ef9e186f1c9efc1 |
Sysbench version: 1.0.17
TiDB parameter configuration
TiDB, TiKV and PD all use the default TiDB Operator configuration.
Cluster topology
| Machine IP | Deployment instance |
|---|---|
| 172.31.8.8 | Sysbench |
| 172.31.7.69, 172.31.5.152, 172.31.11.133 | PD |
| 172.31.4.172, 172.31.1.155, 172.31.9.210 | TiKV |
| 172.31.7.80, 172.31.5.163, 172.31.11.123 | TiDB |
Online workloads simulation using Sysbench
Use Sysbench to import a table with 2,000,000 rows of data into the Kubernetes cluster.
Execute the following command to import data:
sysbench oltp_common \
--threads=16 \
--rand-type=uniform \
--db-driver=mysql \
--mysql-db=sbtest \
--mysql-host=$tidb_host \
--mysql-port=$tidb_port \
--mysql-user=root \
prepare --tables=1 --table-size=2000000
Execute the following command to run the test:
sysbench $testname \
--threads=$threads \
--time=300000 \
--report-interval=15 \
--rand-type=uniform \
--rand-seed=$RANDOM \
--db-driver=mysql \
--mysql-db=sbtest \
--mysql-host=$tidb_host \
--mysql-port=$tidb_port \
--mysql-user=root \
run --tables=1 --table-size=2000000
Test plan 1: Frequently perform write operations to the target column of the ADD INDEX statement
- Start the
oltp_read_writetest. - Perform at the same time with step 1: use
alter table sbtest1 add index c_idx(c)to add an index. - Perform at the end of step 2: when the index is added successfully, stop the
oltp_read_writetest. - Get the duration of
alter table ... add indexand the average TPS and QPS of Sysbench in this period. - Gradually increase the value of two parameters
tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntandtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size, and then repeat step 1-4.
Test results
Test result of oltp_read_write without ADD INDEX operations
| sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|
| 350.31 | 6806 |
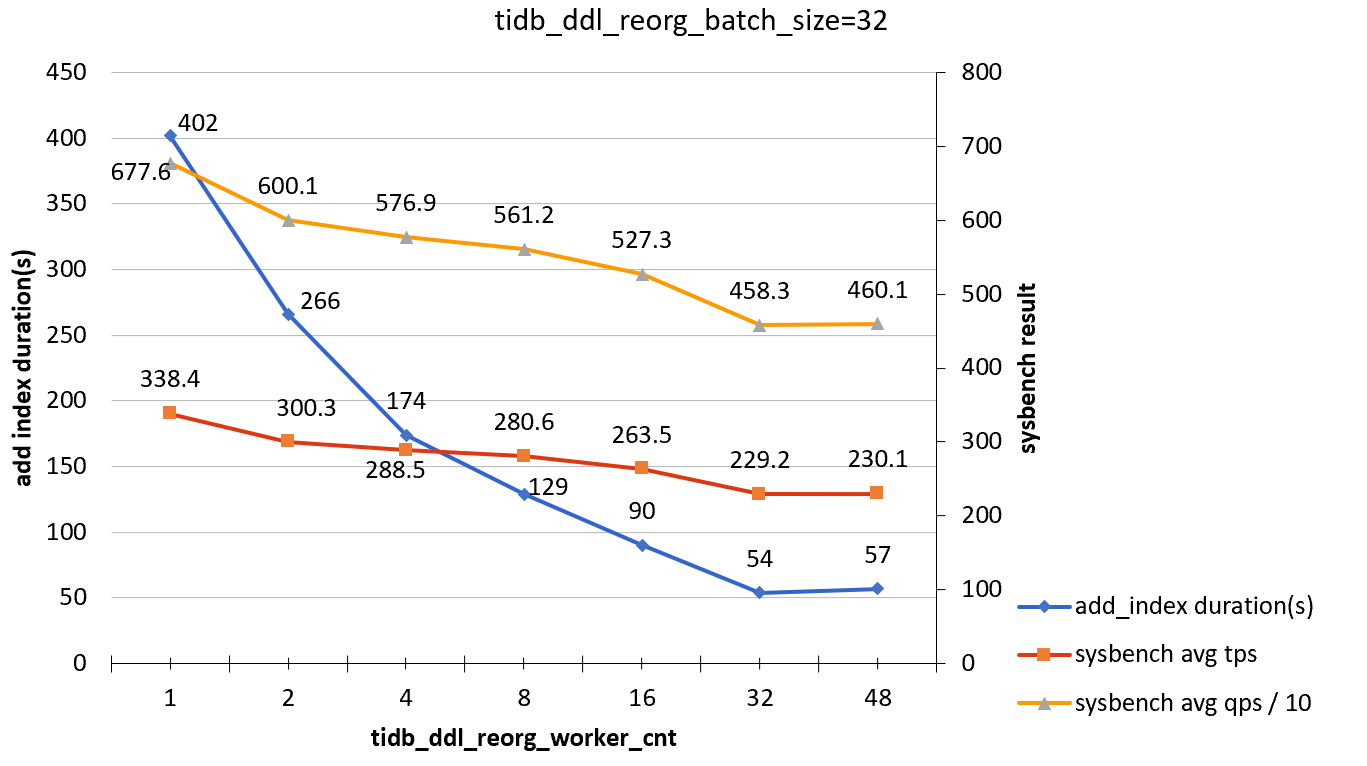
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 32
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 402 | 338.4 | 6776 |
| 2 | 266 | 330.3 | 6001 |
| 4 | 174 | 288.5 | 5769 |
| 8 | 129 | 280.6 | 5612 |
| 16 | 90 | 263.5 | 5273 |
| 32 | 54 | 229.2 | 4583 |
| 48 | 57 | 230.1 | 4601 |
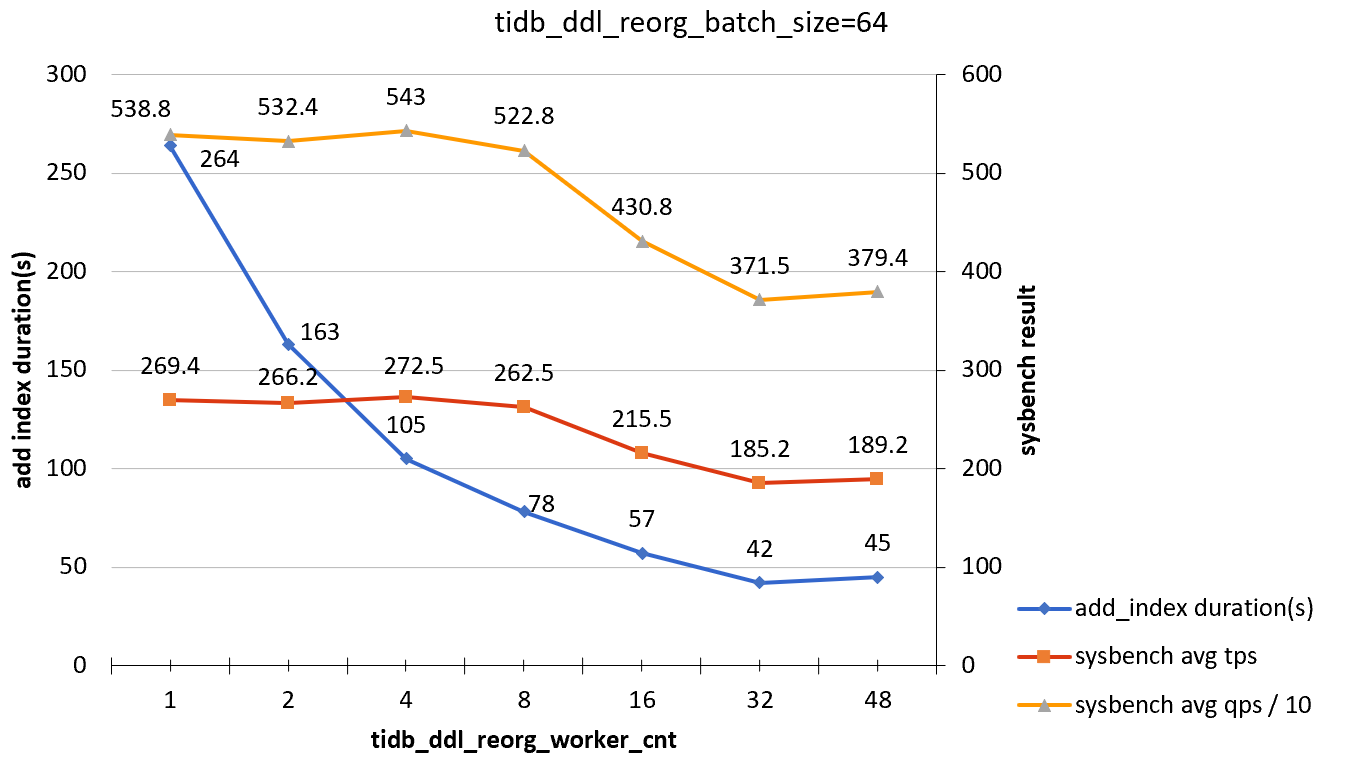
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 64
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 264 | 269.4 | 5388 |
| 2 | 163 | 266.2 | 5324 |
| 4 | 105 | 272.5 | 5430 |
| 8 | 78 | 262.5 | 5228 |
| 16 | 57 | 215.5 | 4308 |
| 32 | 42 | 185.2 | 3715 |
| 48 | 45 | 189.2 | 3794 |
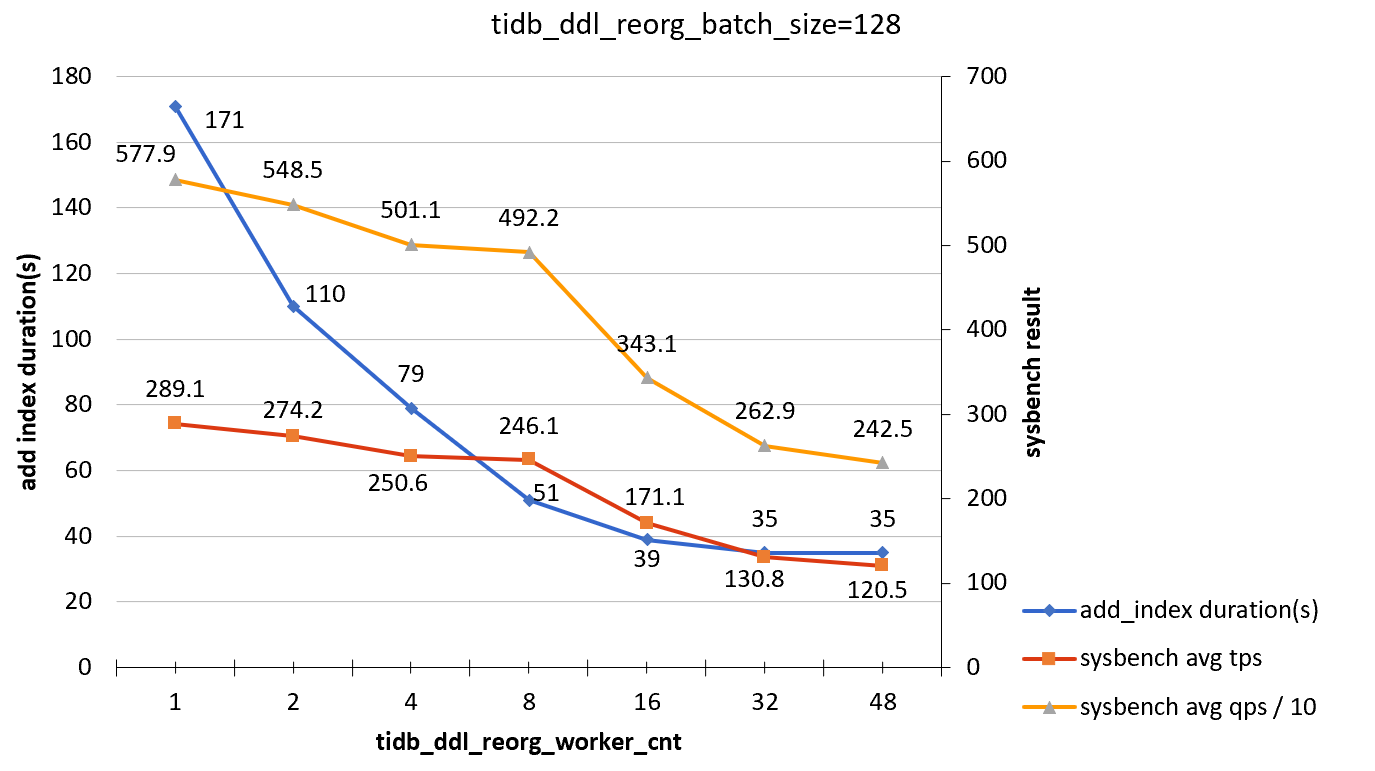
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 128
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 171 | 289.1 | 5779 |
| 2 | 110 | 274.2 | 5485 |
| 4 | 79 | 250.6 | 5011 |
| 8 | 51 | 246.1 | 4922 |
| 16 | 39 | 171.1 | 3431 |
| 32 | 35 | 130.8 | 2629 |
| 48 | 35 | 120.5 | 2425 |
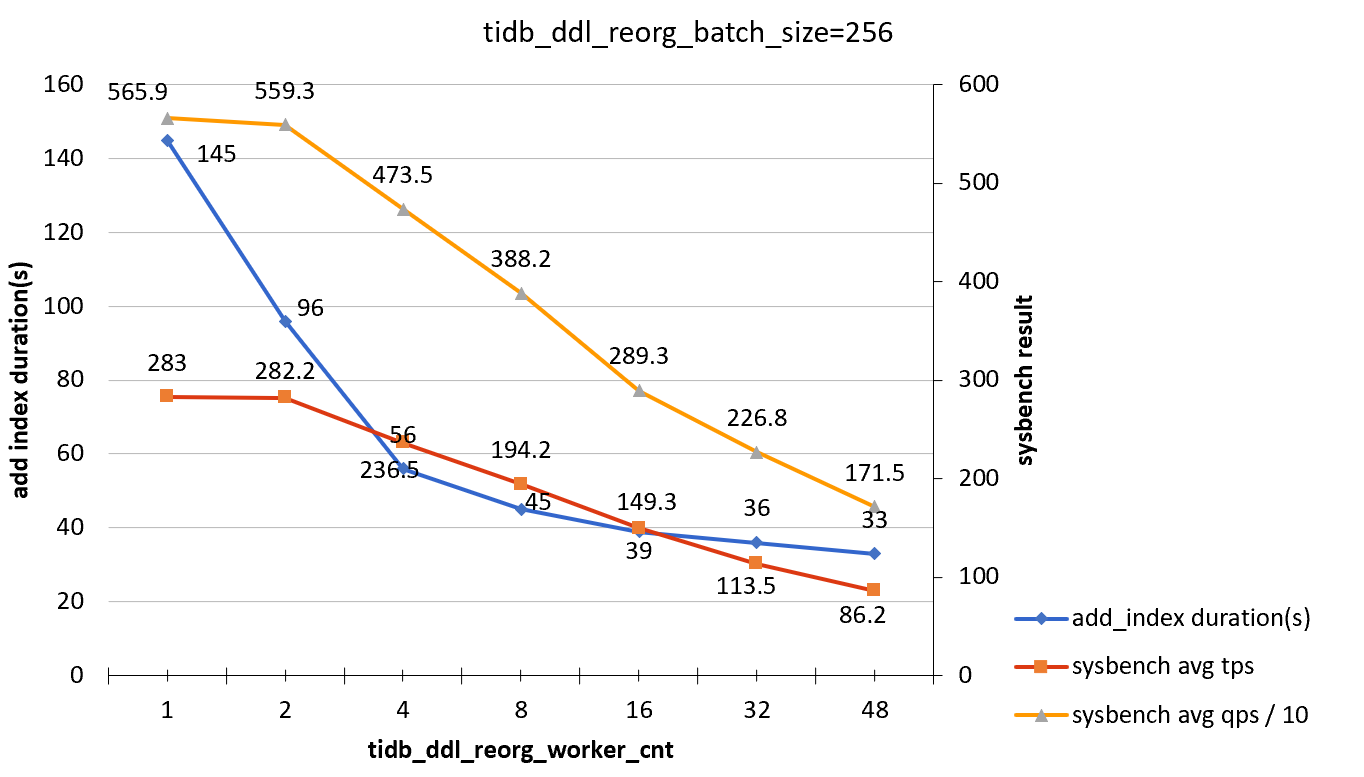
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 256
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 145 | 283.0 | 5659 |
| 2 | 96 | 282.2 | 5593 |
| 4 | 56 | 236.5 | 4735 |
| 8 | 45 | 194.2 | 3882 |
| 16 | 39 | 149.3 | 2893 |
| 32 | 36 | 113.5 | 2268 |
| 48 | 33 | 86.2 | 1715 |
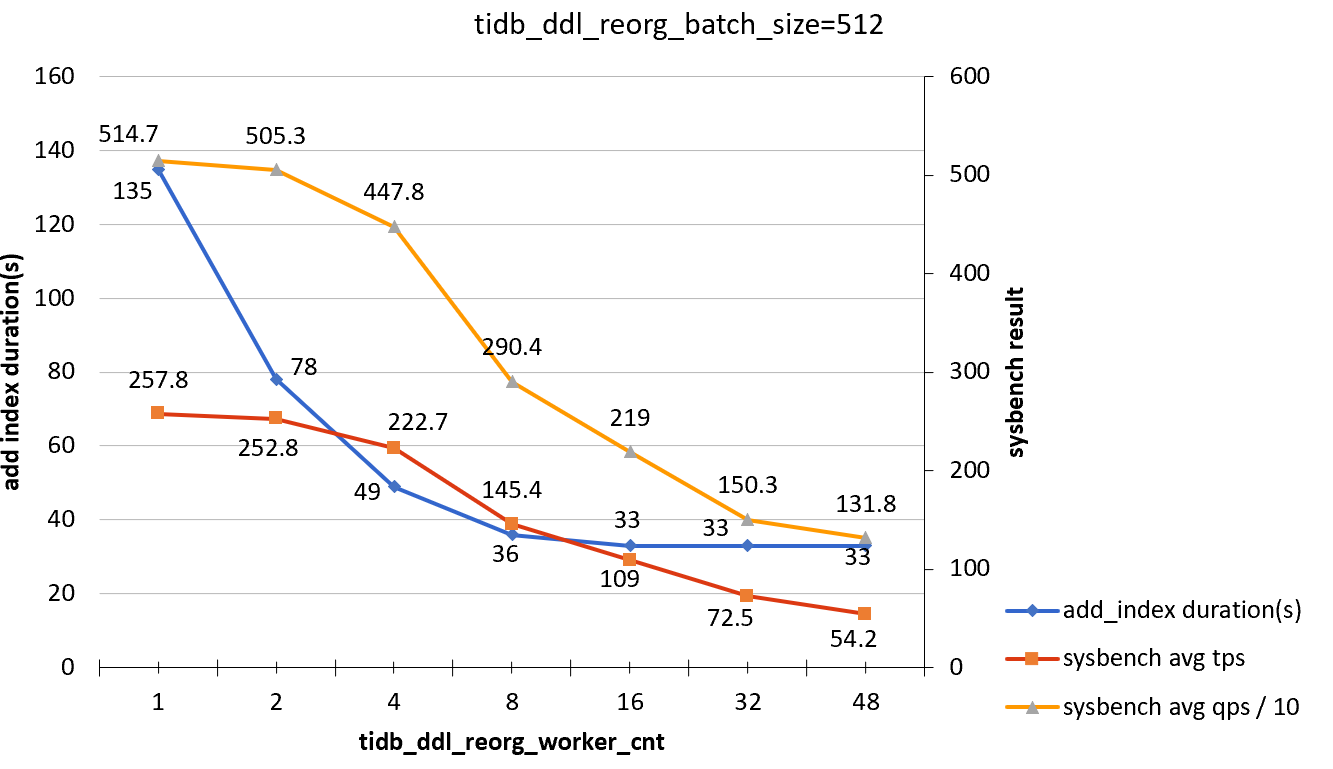
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 512
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 135 | 257.8 | 5147 |
| 2 | 78 | 252.8 | 5053 |
| 4 | 49 | 222.7 | 4478 |
| 8 | 36 | 145.4 | 2904 |
| 16 | 33 | 109 | 2190 |
| 32 | 33 | 72.5 | 1503 |
| 48 | 33 | 54.2 | 1318 |
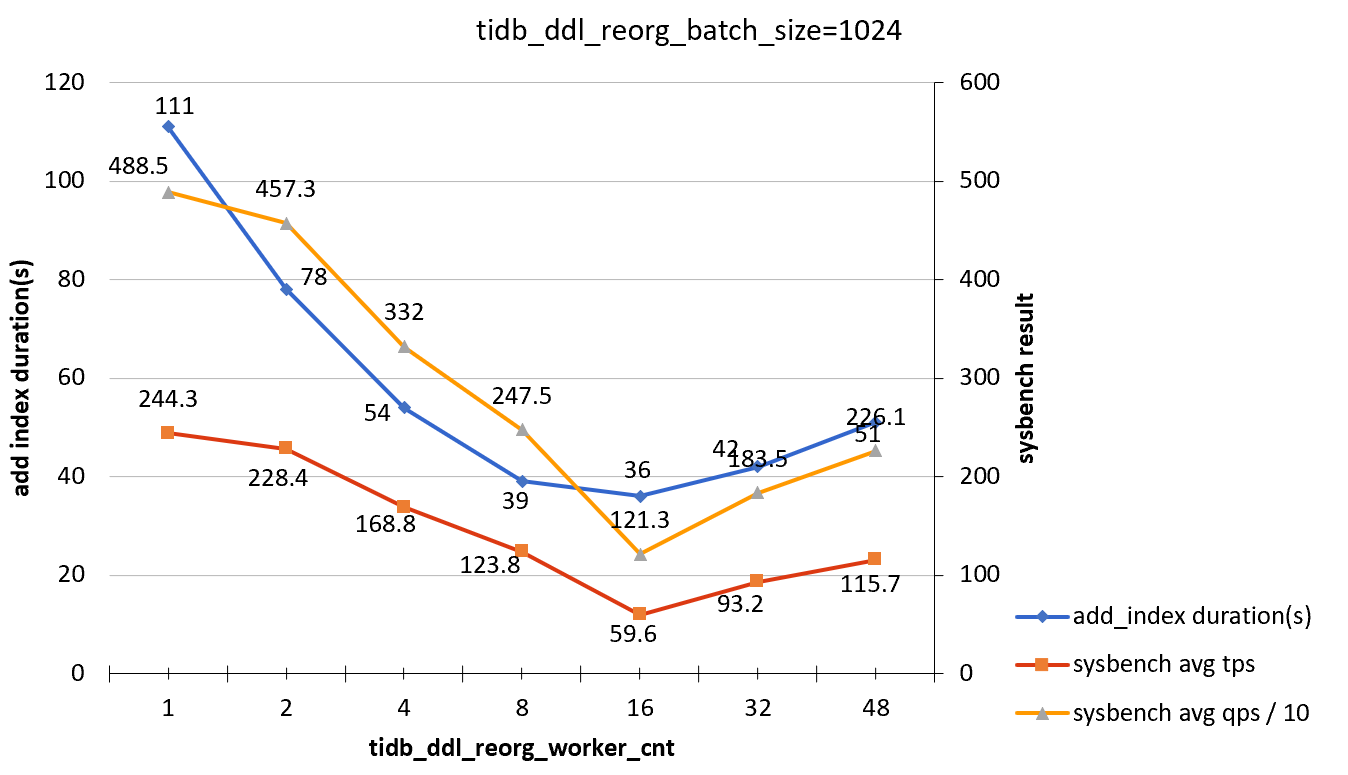
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 1024
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 111 | 244.3 | 4885 |
| 2 | 78 | 228.4 | 4573 |
| 4 | 54 | 168.8 | 3320 |
| 8 | 39 | 123.8 | 2475 |
| 16 | 36 | 59.6 | 1213 |
| 32 | 42 | 93.2 | 1835 |
| 48 | 51 | 115.7 | 2261 |
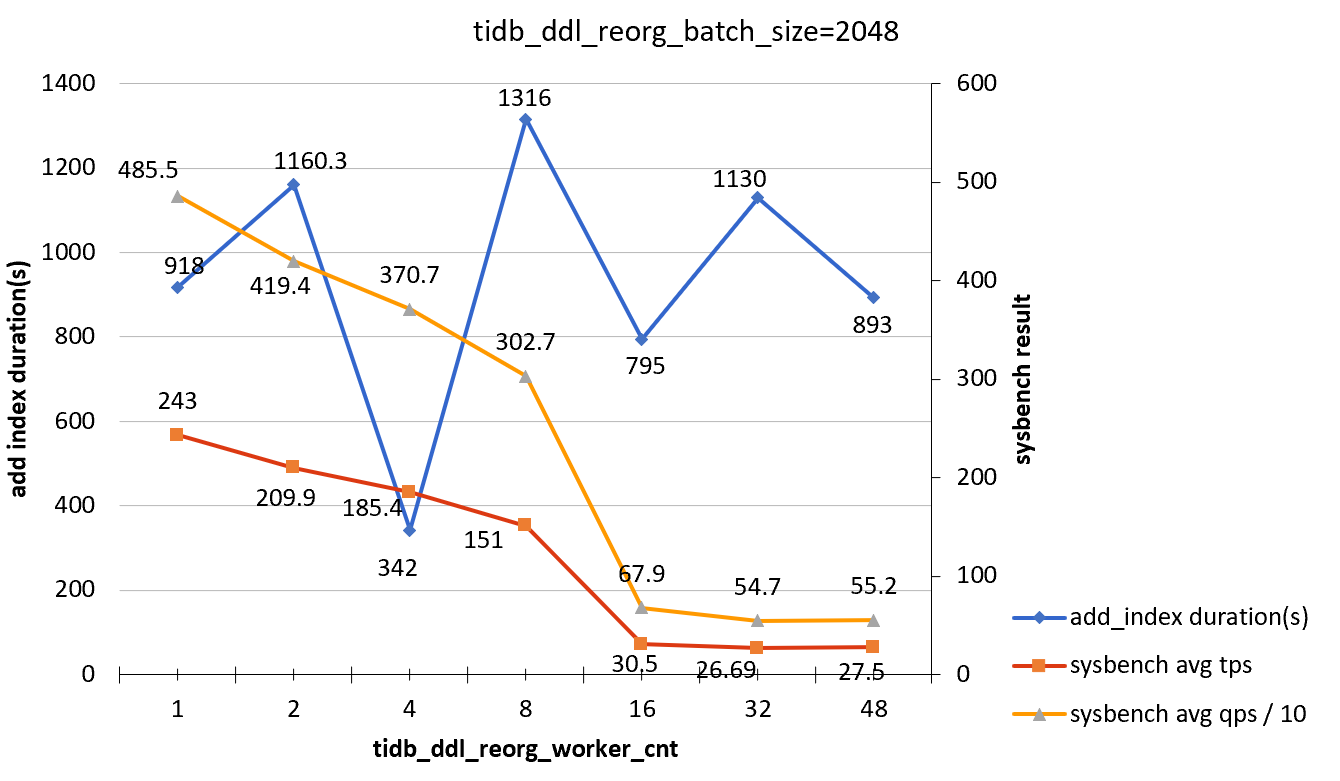
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 2048
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 918 | 243.3 | 4855 |
| 2 | 1160 | 209.9 | 4194 |
| 4 | 342 | 185.4 | 3707 |
| 8 | 1316 | 151.0 | 3027 |
| 16 | 795 | 30.5 | 679 |
| 32 | 1130 | 26.69 | 547 |
| 48 | 893 | 27.5 | 552 |
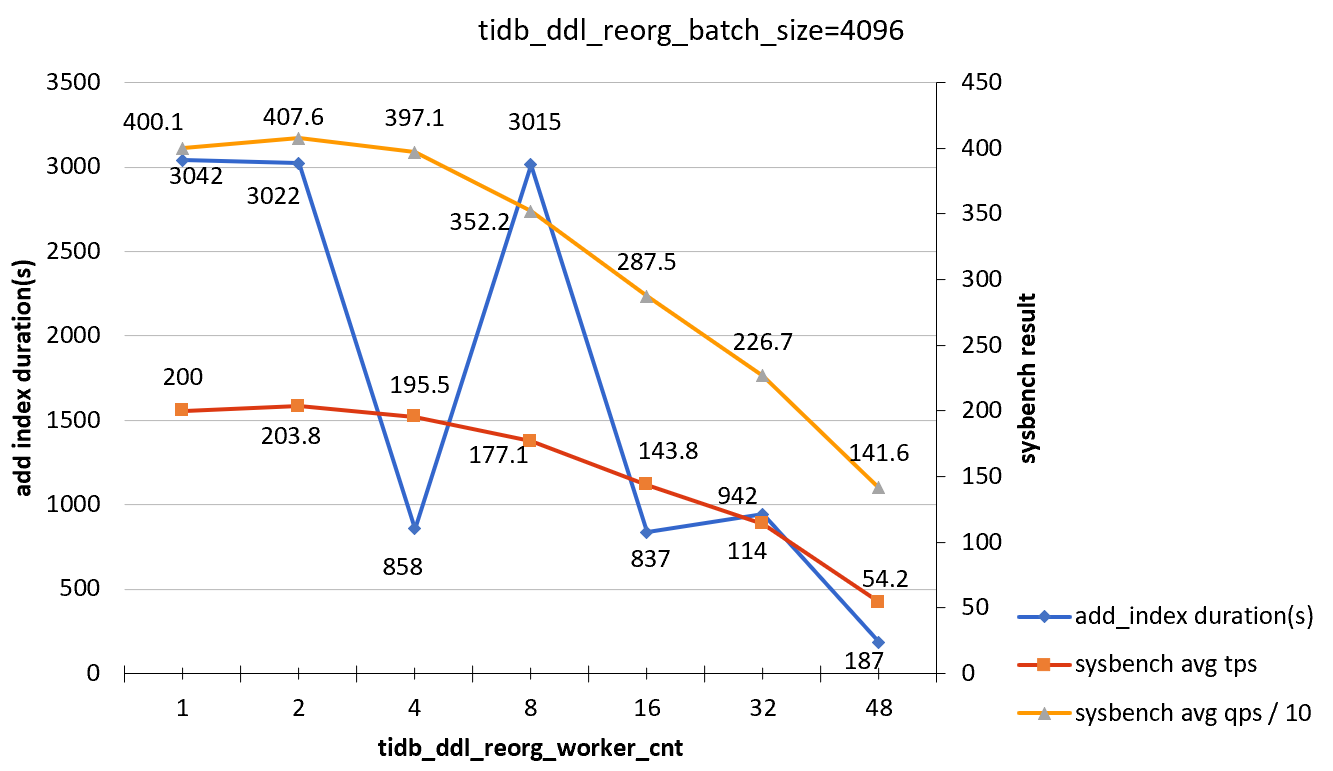
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 4096
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3042 | 200.0 | 4001 |
| 2 | 3022 | 203.8 | 4076 |
| 4 | 858 | 195.5 | 3971 |
| 8 | 3015 | 177.1 | 3522 |
| 16 | 837 | 143.8 | 2875 |
| 32 | 942 | 114 | 2267 |
| 48 | 187 | 54.2 | 1416 |
Test conclusion
When you perform frequent write operations (this test involves UPDATE, INSERT and DELETE operations) to the target column of the ADD INDEX statement, the default ADD INDEX configuration has a significant impact on the online workload of the system. It is mainly because of the write conflicts caused by the concurrent ADD INDEX operation and column update. The performance of the system is as follows:
- As the value of
tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntandtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_sizeparameters increase, the value ofTiKV_prewrite_latch_wait_durationincreases significantly, slowing down the write speed. - When the value of
tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntandtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_sizeare very large, you can execute theadmin show ddlcommand to see multiple retry attempts of the DDL job, such asWrite conflict, txnStartTS 410327455965380624 is stale [try again later], ErrCount:38, SnapshotVersion: 410327228136030220. In this situation, theADD INDEXoperation takes a very long time to complete.
Test plan 2: Do not perform write operations to the target column of the ADD INDEX statement (query-only)
- Start the
oltp_read_onlytest. - Perform at the same time with step 1: use
alter table sbtest1 add index c_idx(c)to add an index. - Perform at the end of step 2: when the index is added successfully, stop the
oltp_read_onlytest. - Get the duration of
alter table ... add indexand the average TPS and QPS of Sysbench in this period. - Gradually increase the value of two parameters
tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntandtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size, and then repeat step 1-4.
Test results
Test result of oltp_read_only without ADD INDEX operations
| sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|
| 550.9 | 8812.8 |
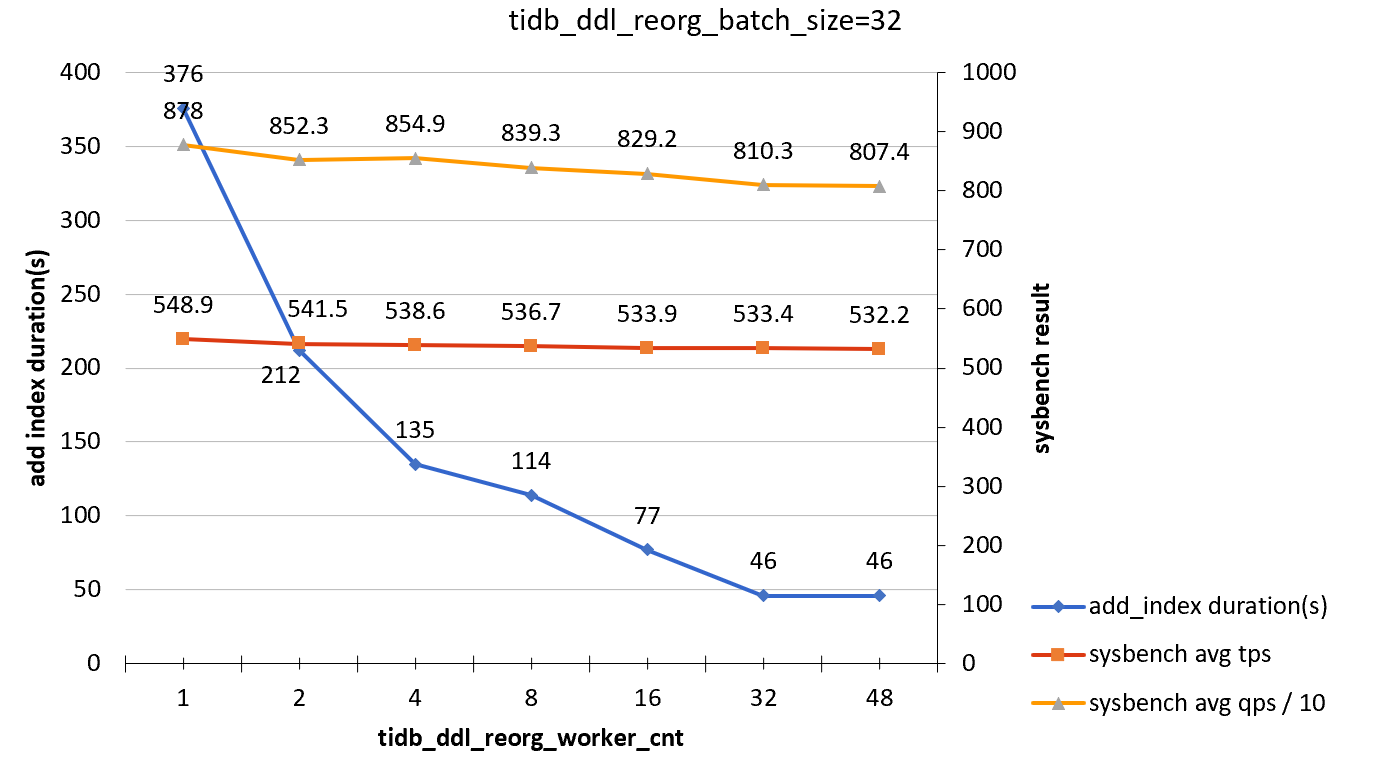
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 32
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 376 | 548.9 | 8780 |
| 2 | 212 | 541.5 | 8523 |
| 4 | 135 | 538.6 | 8549 |
| 8 | 114 | 536.7 | 8393 |
| 16 | 77 | 533.9 | 8292 |
| 32 | 46 | 533.4 | 8103 |
| 48 | 46 | 532.2 | 8074 |
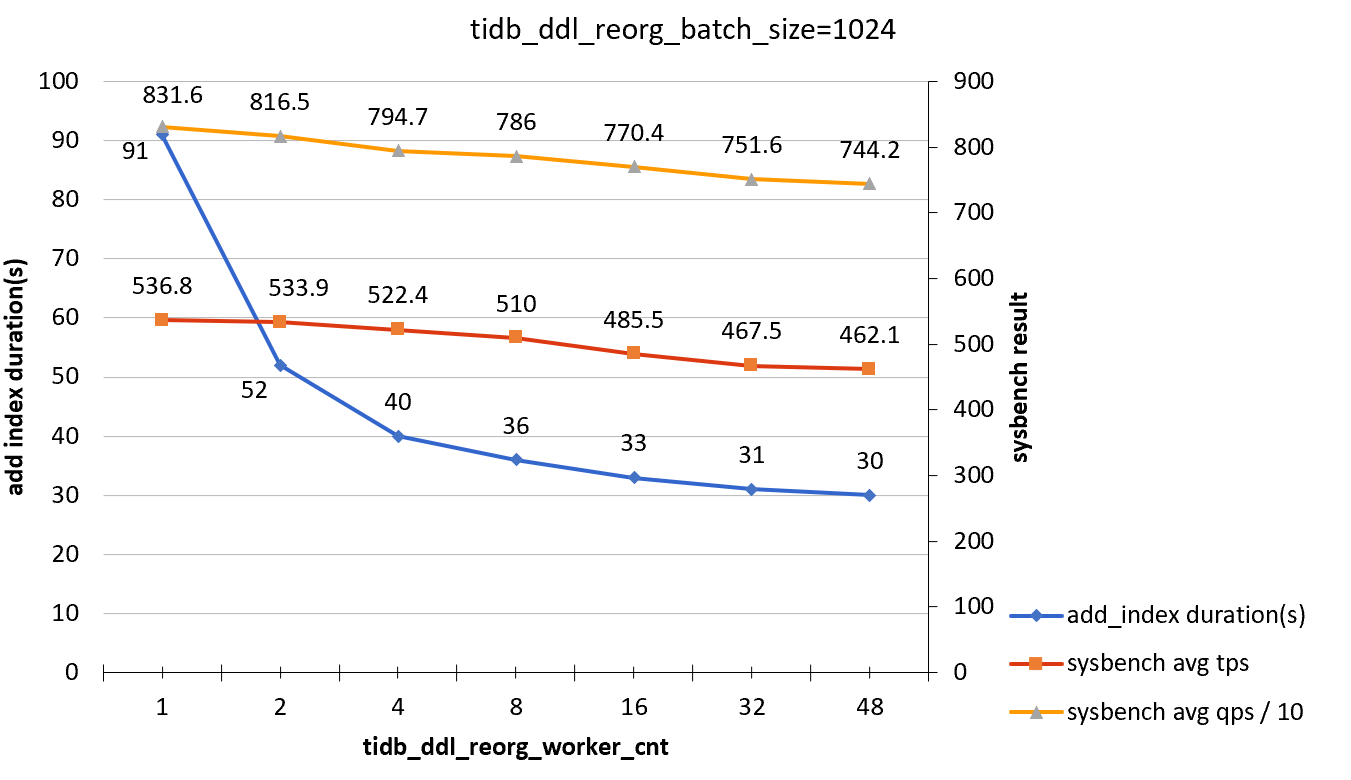
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 1024
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91 | 536.8 | 8316 |
| 2 | 52 | 533.9 | 8165 |
| 4 | 40 | 522.4 | 7947 |
| 8 | 36 | 510 | 7860 |
| 16 | 33 | 485.5 | 7704 |
| 32 | 31 | 467.5 | 7516 |
| 48 | 30 | 562.1 | 7442 |
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 4096
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 103 | 502.2 | 7823 |
| 2 | 63 | 486.5 | 7672 |
| 4 | 52 | 467.4 | 7516 |
| 8 | 39 | 452.5 | 7302 |
| 16 | 35 | 447.2 | 7206 |
| 32 | 30 | 441.9 | 7057 |
| 48 | 30 | 440.1 | 7004 |
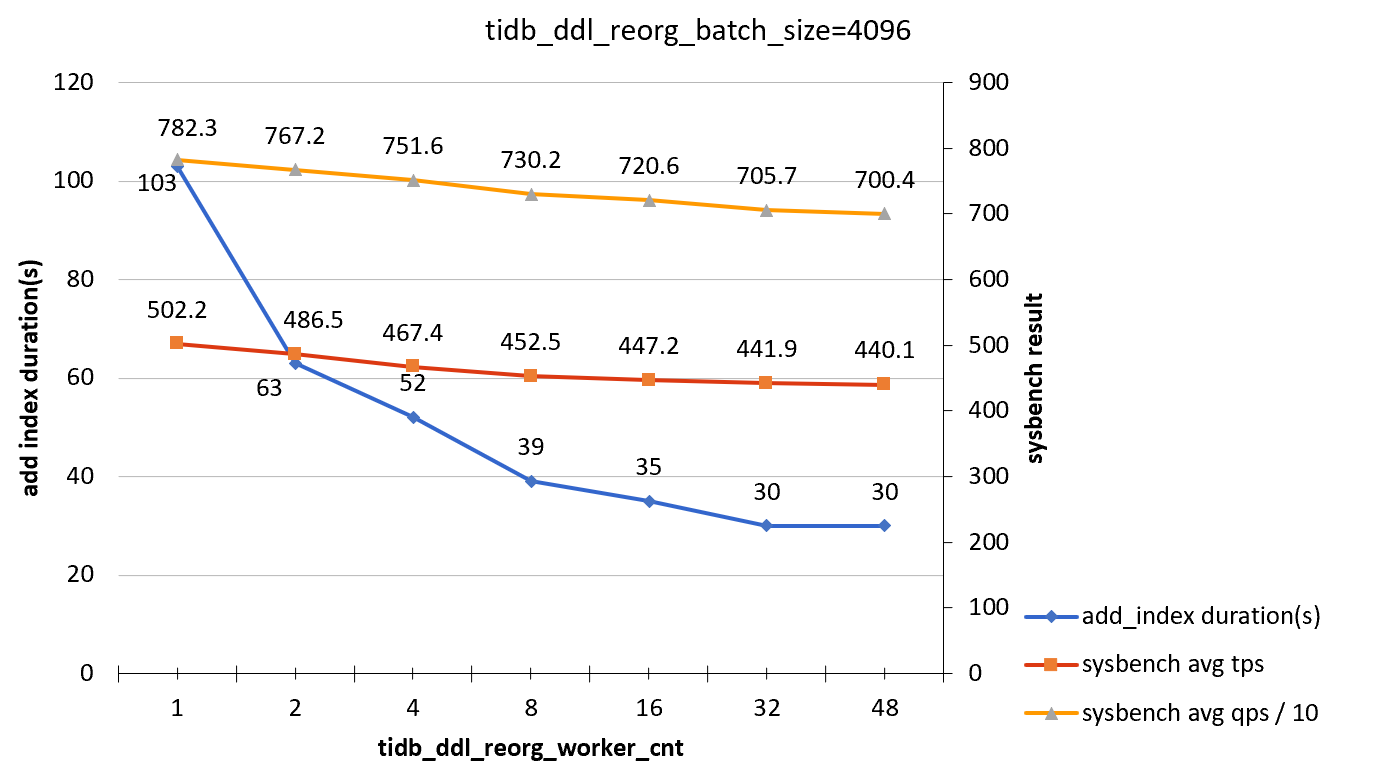
Test conclusion
When you only perform query operations to the target column of the ADD INDEX statement, the effect of ADD INDEX operations on online workloads is not obvious.
Test plan 3: The target column of the ADD INDEX statement is irrelevant to online workloads
- Start the
oltp_read_writetest. - Perform at the same time with step 1: use
alter table test add index pad_idx(pad)to add an index. - Perform at the end of step 2: when the index is added successfully, stop the
oltp_read_onlytest. - Get the duration of
alter table ... add indexand the average TPS and QPS of Sysbench in this period. - Gradually increase the value of two parameters
tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntandtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size, and then repeat step 1-4.
Test results
Test result of oltp_read_write without ADD INDEX operations
| sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|
| 350.31 | 6806 |
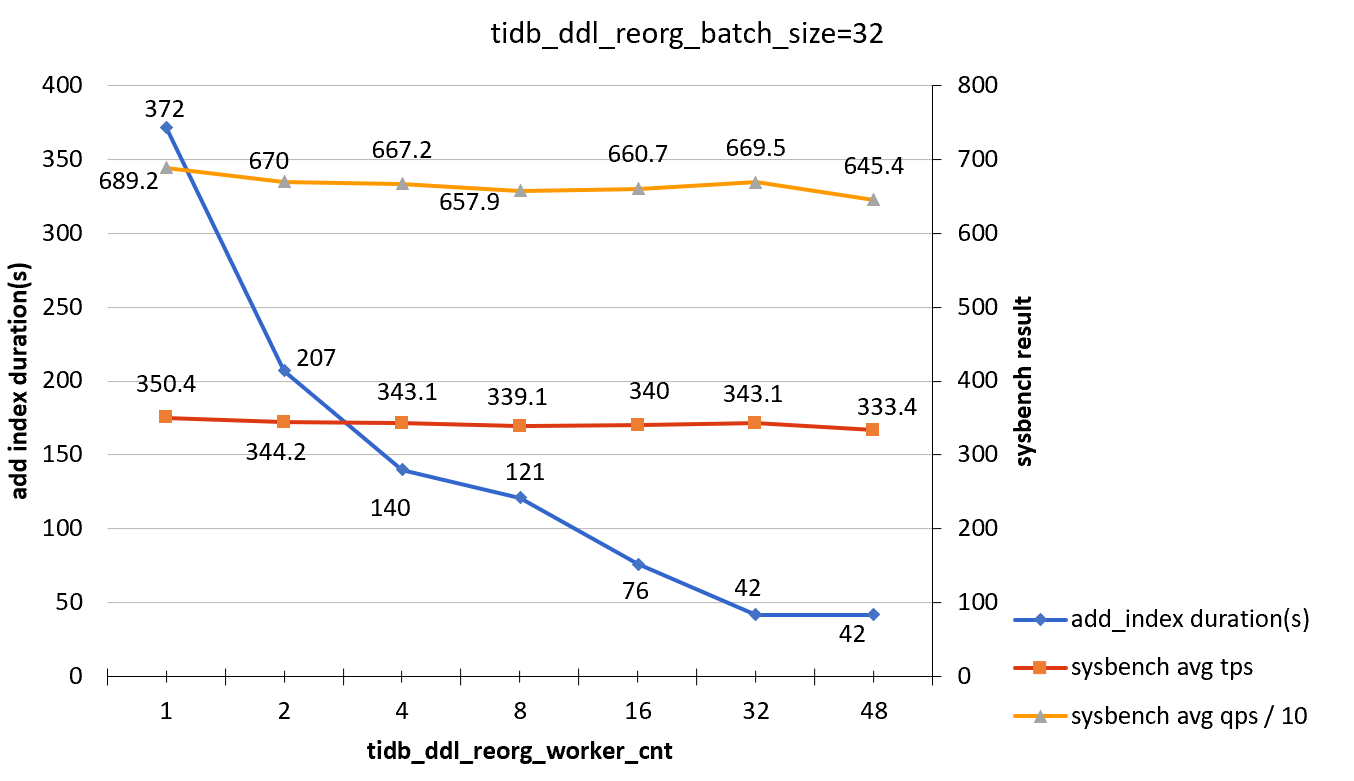
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 32
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 372 | 350.4 | 6892 |
| 2 | 207 | 344.2 | 6700 |
| 4 | 140 | 343.1 | 6672 |
| 8 | 121 | 339.1 | 6579 |
| 16 | 76 | 340 | 6607 |
| 32 | 42 | 343.1 | 6695 |
| 48 | 42 | 333.4 | 6454 |
tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 1024
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94 | 352.4 | 6794 |
| 2 | 50 | 332 | 6493 |
| 4 | 45 | 330 | 6456 |
| 8 | 36 | 325.5 | 6324 |
| 16 | 32 | 312.5 | 6294 |
| 32 | 32 | 300.6 | 6017 |
| 48 | 31 | 279.5 | 5612 |

tidb_ddl_reorg_batch_size = 4096
| tidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cnt | add_index_durations(s) | sysbench TPS | sysbench QPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 116 | 325.5 | 6324 |
| 2 | 65 | 312.5 | 6290 |
| 4 | 50 | 300.6 | 6017 |
| 8 | 37 | 279.5 | 5612 |
| 16 | 34 | 250.4 | 5365 |
| 32 | 32 | 220.2 | 4924 |
| 48 | 33 | 214.8 | 4544 |
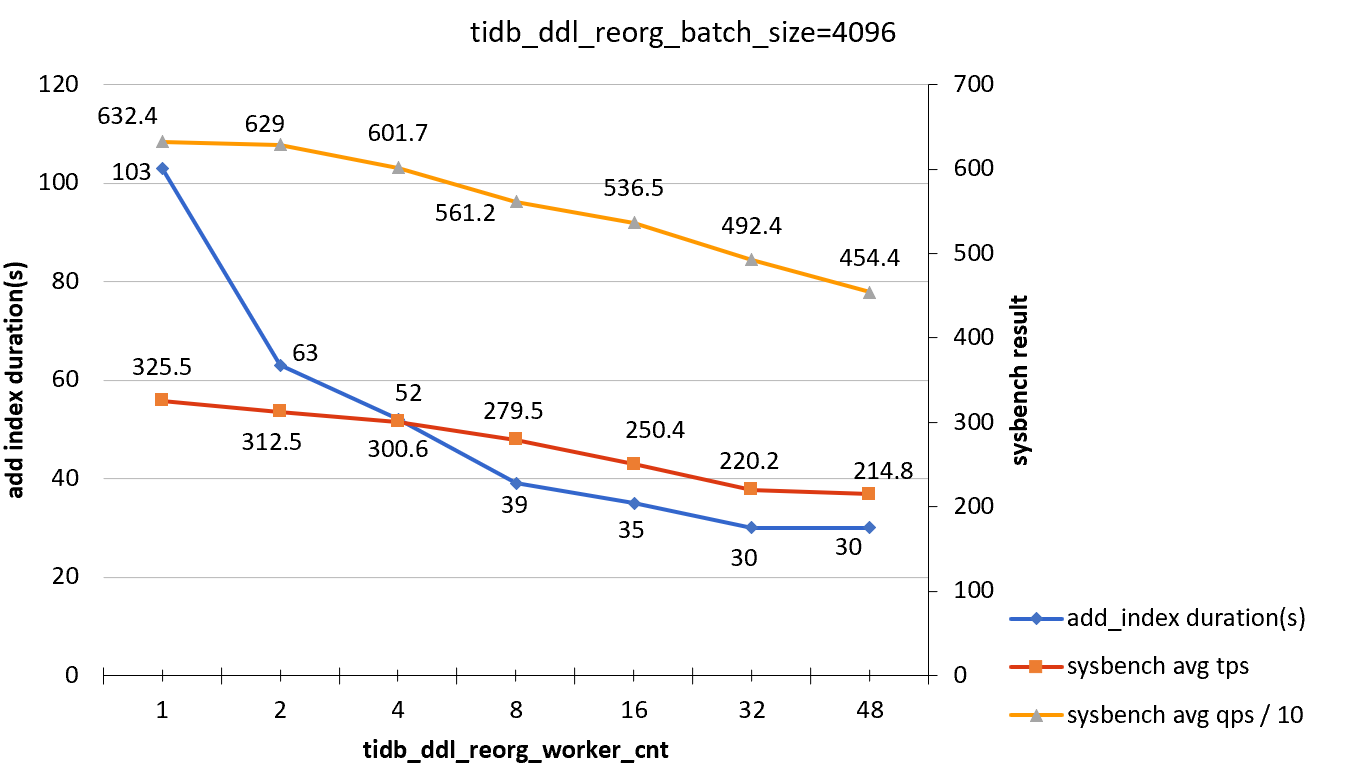
Test conclusion
When the target column of the ADD INDEX statement is irrelevant to online workloads, the effect of ADD INDEX operations on the workload is not obvious.
Summary
- When you perform frequent write operations (including
INSERT,DELETEandUPDATEoperations) to the target column of theADD INDEXstatement, the defaultADD INDEXconfiguration causes relatively frequent write conflicts, which has a great impact on online workloads. At the same time, theADD INDEXoperation takes a long time to complete due to continuous retry attempts. In this test, you can modify the product oftidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntandtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_sizeto 1/32 of the default value. For example, you can settidb_ddl_reorg_worker_cntto4andtidb_ddl_reorg_batch_sizeto256for better performance. - When only performing query operations to the target column of the
ADD INDEXstatement or the target column is not directly related to online workloads, you can use the defaultADD INDEXconfiguration.