TiDB Operator Architecture
This document describes the architecture of TiDB Operator and how it works.
Architecture
The following diagram is an overview of the architecture of TiDB Operator.
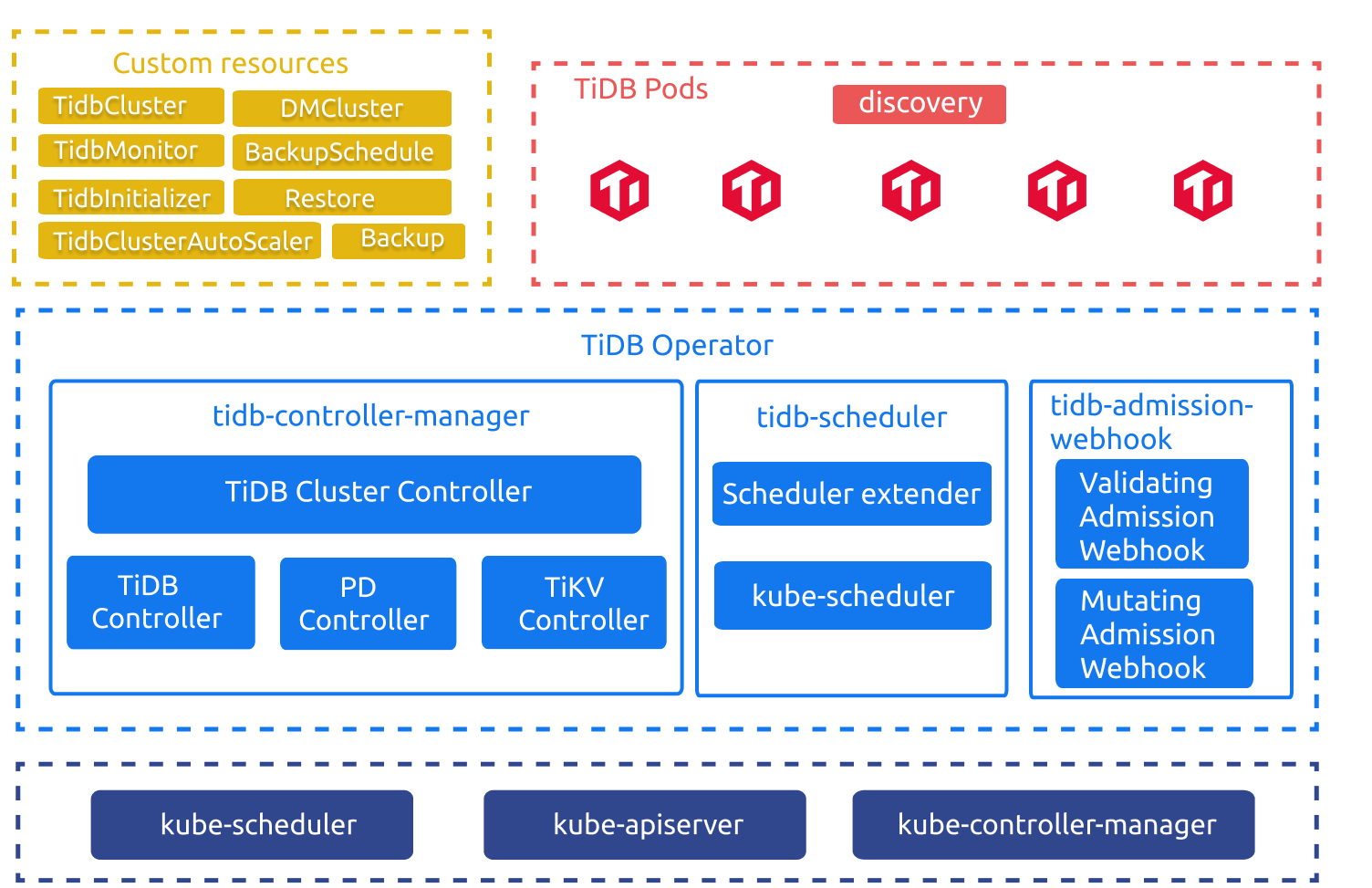
TidbCluster, TidbMonitor, TidbInitializer, Backup, Restore, BackupSchedule, and TidbClusterAutoScaler are custom resources defined by CRD (CustomResourceDefinition).
TidbClusterdescribes the desired state of the TiDB cluster.TidbMonitordescribes the monitoring components of the TiDB cluster.TidbInitializerdescribes the desired initialization Job of the TiDB cluster.Backupdescribes the desired backup of the TiDB cluster.Restoredescribes the desired restoration of the TiDB cluster.BackupScheduledescribes the scheduled backup of the TiDB cluster.TidbClusterAutoScalerdescribes the automatic scaling of the TiDB cluster.
The following components are responsible for the orchestration and scheduling logic in a TiDB cluster:
tidb-controller-manageris a set of custom controllers in Kubernetes. These controllers constantly compare the desired state recorded in theTidbClusterobject with the actual state of the TiDB cluster. They adjust the resources in Kubernetes to drive the TiDB cluster to meet the desired state and complete the corresponding control logic according to other CRs;tidb-scheduleris a Kubernetes scheduler extension that injects the TiDB specific scheduling policies to the Kubernetes scheduler;tidb-admission-webhookis a dynamic admission controller in Kubernetes, which completes the modification, verification, operation, and maintenance of Pod, StatefulSet, and other related resources.discoveryis a service for inter-components discovery. Each TiDB cluster contains a discovery Pod which is used for the componets to discover other existing components in the same cluster.
Control flow
The following diagram is the analysis of the control flow of TiDB Operator. Starting from TiDB Operator v1.1, the TiDB cluster, monitoring, initialization, backup, and other components are deployed and managed using CR.
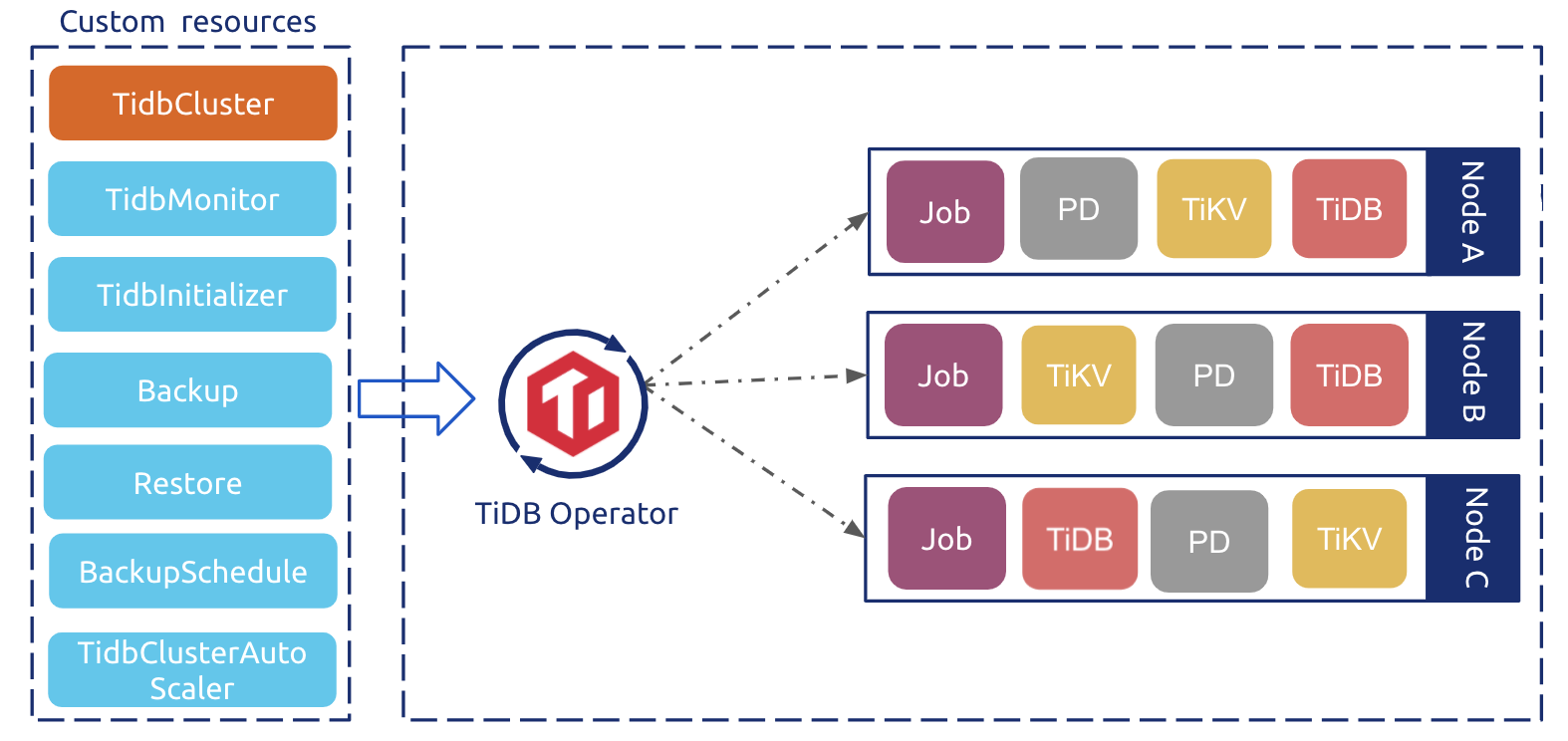
The overall control flow is described as follows:
- The user creates a
TidbClusterobject and other CR objects through kubectl, such asTidbMonitor; - TiDB Operator watches
TidbClusterand other related objects, and constantly adjust theStatefulSet,Deployment,Service, and other objects of PD, TiKV, TiDB, Monitor or other components based on the actual state of the cluster; - Kubernetes' native controllers create, update, or delete the corresponding
Podbased on objects such asStatefulSet,Deployment, andJob; - If you configure the components to use
tidb-schedulerin theTidbClusterCR, thePoddeclaration of PD, TiKV, and TiDB specifiestidb-scheduleras the scheduler.tidb-schedulerapplies the specific scheduling logic of TiDB when scheduling the correspondingPod.
Based on the above declarative control flow, TiDB Operator automatically performs health check and fault recovery for the cluster nodes. You can easily modify the TidbCluster object declaration to perform operations such as deployment, upgrade, and scaling.