Performance of EBS Snapshot Backup and Restore
This document describes the performance of EBS snapshot backup and restore, the factors that affect performance, and the performance test results. The performance metrics are based on the AWS region us-west-2.
Backup performance
This section introduces the performance of EBS snapshot backup using volumes, the factors that affect performance, and the performance test results.
Backup time consumption
EBS snapshot backup using volumes consists of the following processes: creates a backup task, stops scheduling, disables GC, and obtains the backupts and volume snapshots. For more detailed information about these processes, see Architecture of EBS snapshot volume backup and restore. Among these processes, creating a volume snapshot consumes most of the time. Volume snapshots are created in parallel, and the time taken to complete the entire backup task depends on when the most time-consuming volume is created.
Time consumption ratio of backup
| Backup stage | Time taken | Total ratio | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create volume snapshots | 16 minutes (50 GB) | 99% | Including the time for creating AWS EBS snapshots |
| Others | 1 second | 1% | Including the time for stopping scheduling, disabling GC, and obtaining the backupts |
Backup performance data
Time taken by snapshot backup using volumes depends on when the last volume snapshot is backed up, which is done by AWS EBS. For now, AWS does not provide quantitative metrics for volume snapshot backup. The time taken by the entire backup process is as follows under the recommended machine type and GP3 storage volume, with the configuration of 400 MiB/s and 7000 IOPS:
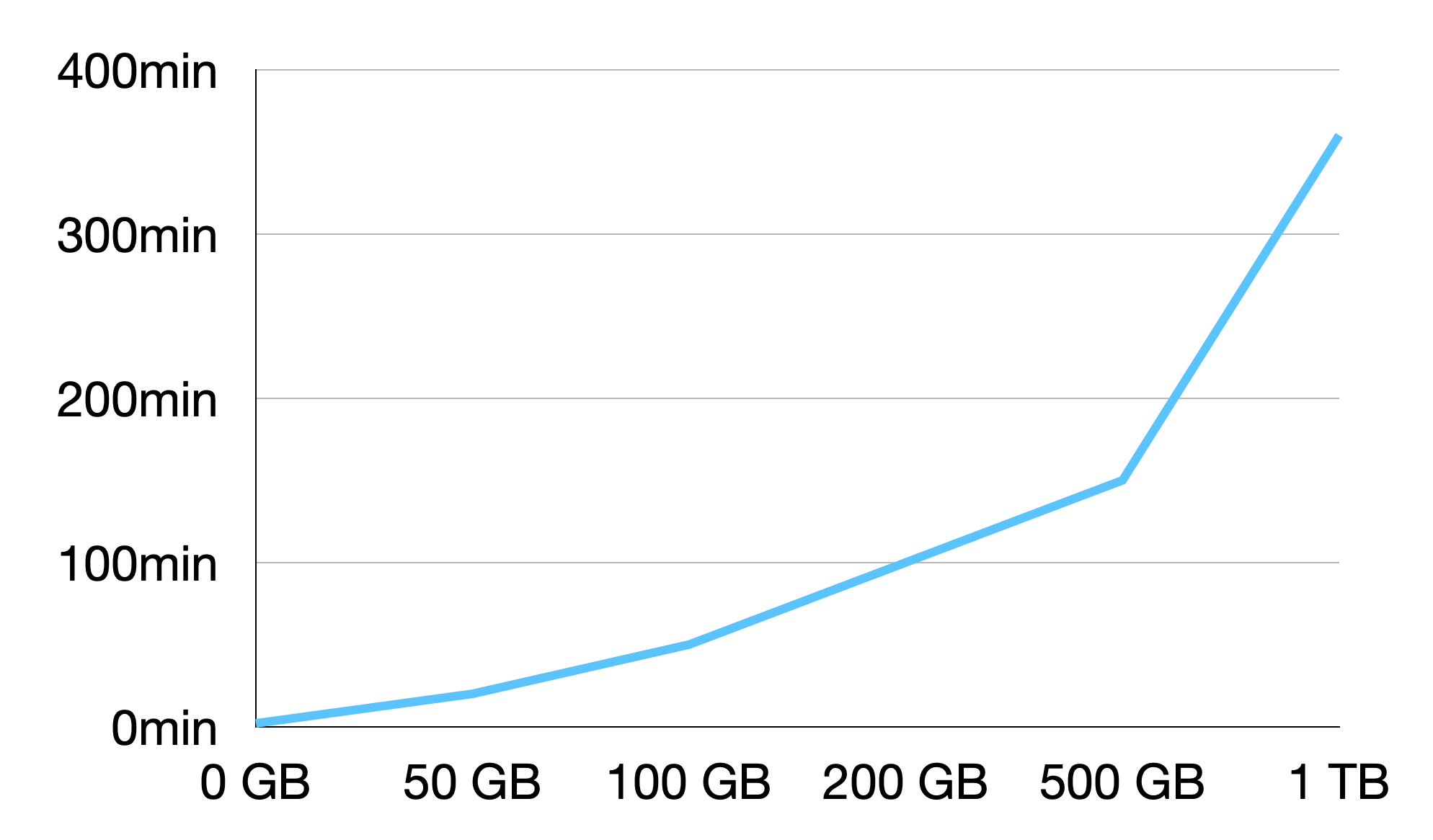
| Volume data | Total volume size | Volume configuration | Appropriate backup duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 GB | 500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 20 minutes |
| 100 GB | 500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 50 minutes |
| 200 GB | 500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 100 minutes |
| 500 GB | 1024 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 150 minutes |
| 1024 GB | 3500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 350 minutes |
Backup impact
It is tested that the backup impact on clusters in less than 3% when GP3 volumes are used. In the following figure, the backup is initiated after 10:25.
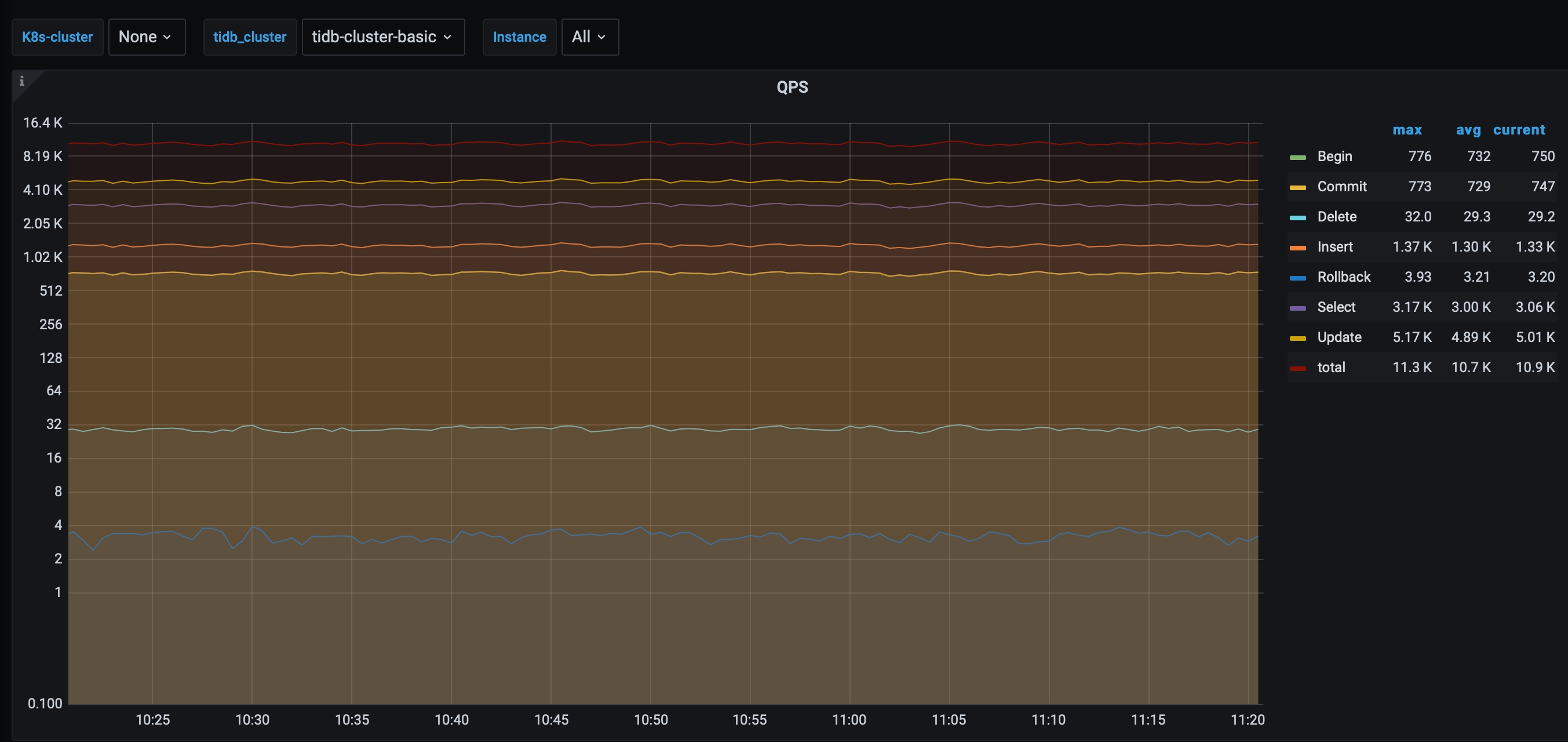
Restore performance
This document describes the performance of EBS snapshot restore using volumes, the factors that affect performance, and the performance test results.
Restore time consumption
EBS snapshot restore using volumes consists of the following processes. For detailed information, see Architecture of EBS snapshot volume backup and restore.
Create a cluster.
TiDB Operator creates a cluster in recoveryMode and starts all PD nodes.
Restore volumes.
TiDB Operator creates volume restore subtasks using BR. BR restores the data volumes from the snapshots to start TiKV.
Start TiKV.
TiDB Operator mounts the TiKV volumes and starts TiKV.
Restore data.
TiDB Operator creates volume data restore subtasks. BR restores the data volumes to a consistent state.
Start TiDB.
TiDB is started and the restore is completed.
Time consumption ratio of restore
| Restore stage | Appropriate time taken | Restore ratio | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creates clusters | 30 seconds | 2% | Including the time for downloading docker image and starting PD |
| Restores volumes | 20 seconds | 1% | Including the time for starting the BR Pod and restoring volumes |
| Starts TiKV | 10 to 16 minutes | 42% | Including the time for starting RocksDB and reading the meta data of all Regions |
| Restores data | 2 to 20 minutes | 52% | Including the time for restoring data in the Raft consensus layer and deleting MVCC data |
| Starts TiDB | 1 minute | 3% | Including the time for downloading the tidb docker image and starting TiDB |
Restore performance data
Time taken by snapshot restore using volumes mainly depends on the time taken by starting TiKV and restoring data. TiKV startup and data restore need to read volume data that is restored from snapshots. Such volume data is loaded with certain latency. Specifically, the data does not reach optimal performance immediately after restore. This is because the data is available only after it is downloaded from Amazon S3 and written to the volumes.
The data load latency results in high I/O operation latency when each block is accessed for the first time. Due to the impact of data load latency, TiKV startup and data restore consume most of the time in the whole process of snapshot restore using volumes. Test data is as follows under the recommended machine type and GP3 storage volume:
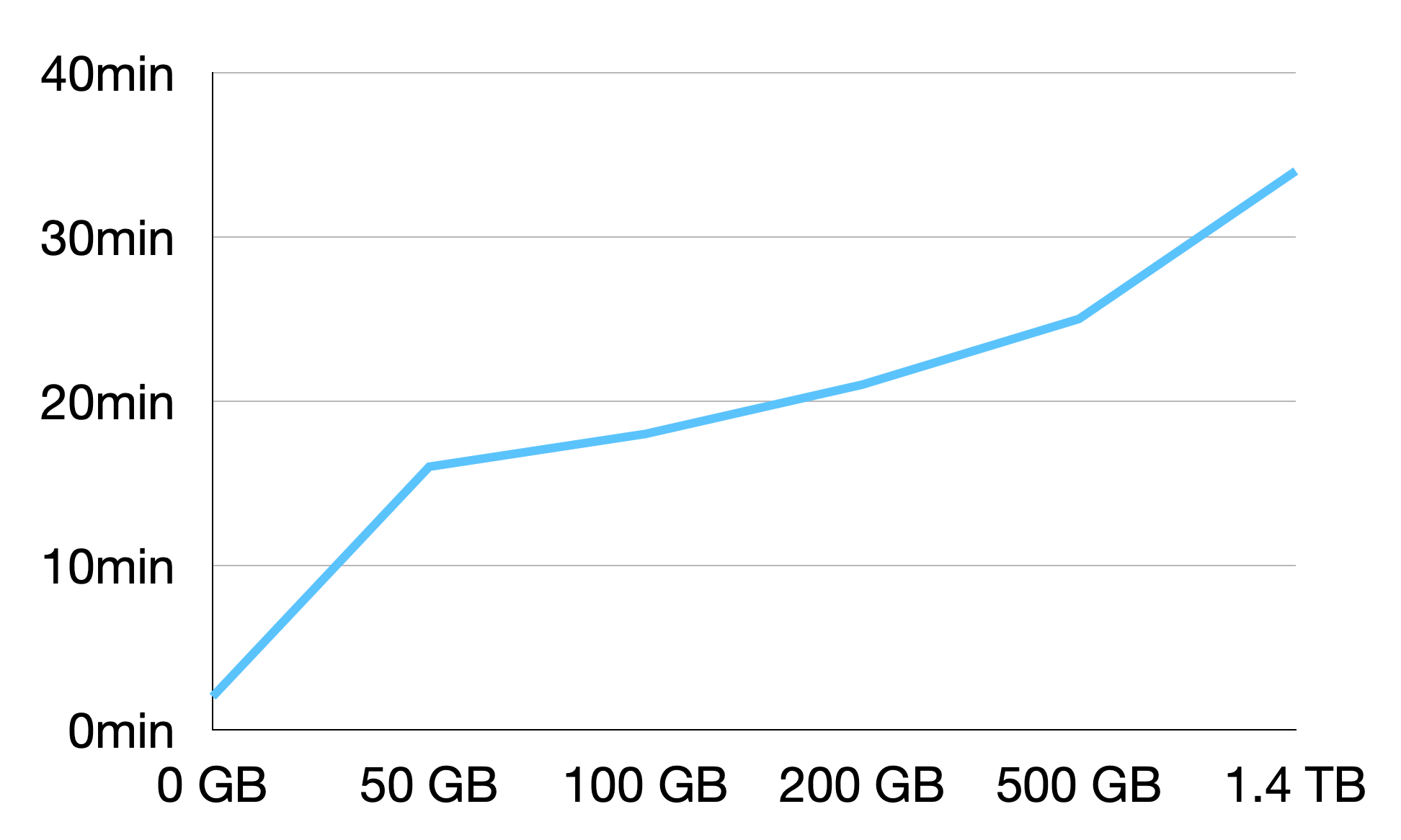
| Volume data | Total volume size | Volume configuration | Appropriate restore duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 GB | 500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 16 minutes |
| 100 GB | 500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 18 minutes |
| 200 GB | 500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 21 minutes |
| 500 GB | 1024 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 25 minutes |
| 1024 GB | 3500 GB | 7000IOPS/400MiB/s | 34 minutes |